A. Technical specifications
Festo P.BE-CMMP-AS-3A-HW-EN 0708NH 105
The resolver offset angle, which is automatically determined during identification, can be
read and written for servicing purposes.
7 V
eff
, short-circuit protected
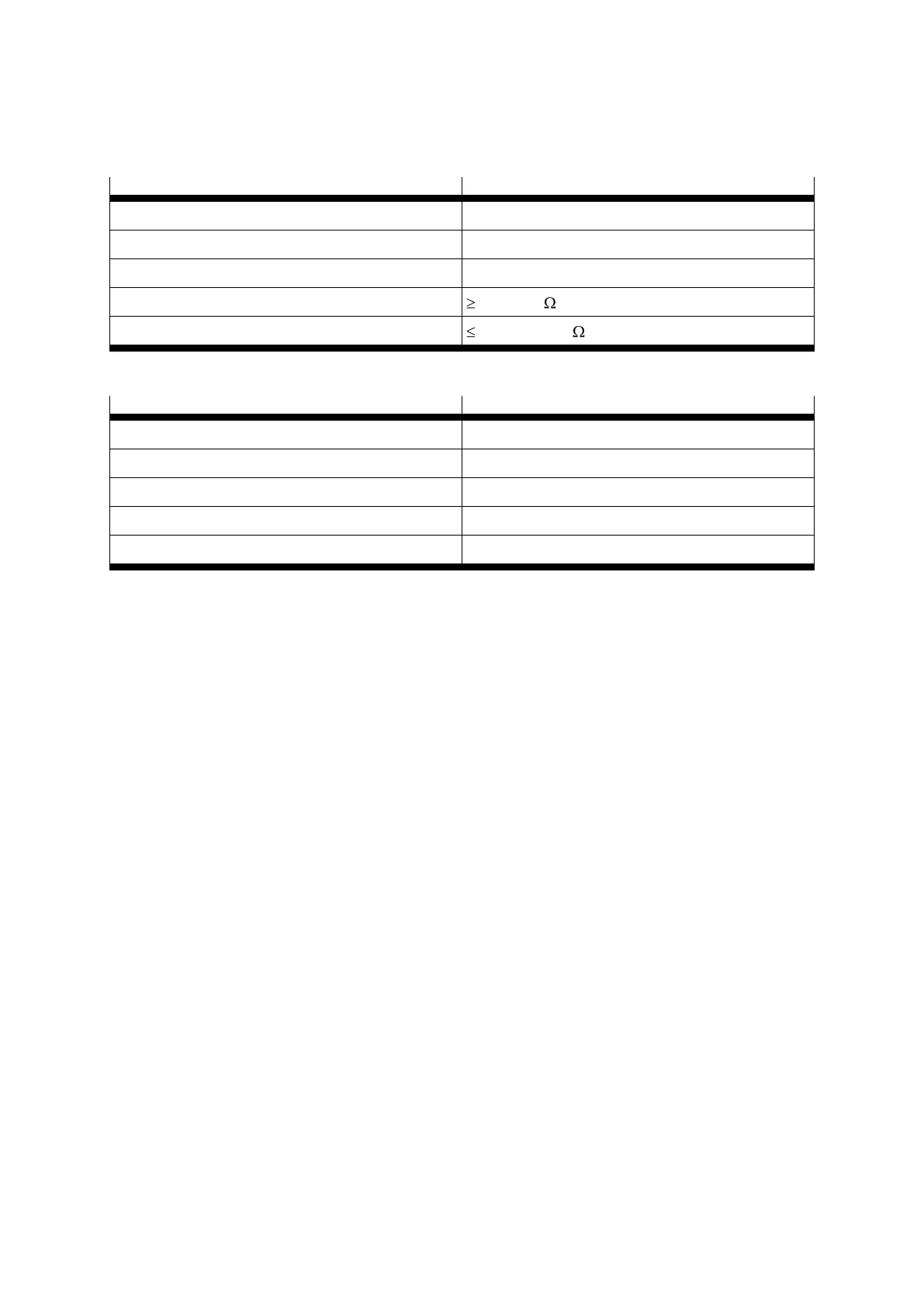
Exciter impedance (at 10 kHz)
Table A.13 Technical data: Resolver [X2A]
Signal acquisition time delay
Absolute accuracy of angle acquisition
Table A.14 Technical data: Resolver interface [X2A]
A.4.2 Encoder connection [X2B]
Motors with encoders can be fed back via the 15-pin D-SUB connection [X2B]. The possible
incremental encoders for the encoder connection are divided into several groups. If in doubt
when using other encoder types, contact your sales partner.
A.4.3 Encoder connection [X2B] for EMMS-AS
Standard incremental encoder without commutation signals:
These encoders are used in low-cost linear motors to reduce the cost of producing the
commutation signal (hall-effect encoder). With these encoders, an automatic pole position
determination is performed by the CMMP-AS servo positioning controller at power on.
Standard incremental encoder with commutation signals:
In this variant, standard incremental encoders with three additional hall-effect encoder
signals are used. The number of lines in the encoder can be freely parameterised
(1 - 16384 lines/rotation).
An additional offset angle applies to hall-effect encoder signals. This is determined during
motor identification or can be defined using the parameterising software. The hall-effect
encoder offset angle is usually zero.
Stegmann encoder:
Encoders with HIPERFACE from the Stegmann company are supported in single-turn and
multi-turn. The following encoder series (e.g.) can be connected:
- Single-turn SinCos encoders: SCS 60, SCS 70, SKS 36, SR 50, SR 60

 Loading...
Loading...











