Appendix D – CE Certificate--Introduction to Device Power Dissipation
13 - 1
Appendix E -- Heat in Interface 1000 MultEchem Systems
Introduction to Device Power Dissipation
All electronic devices require power to operate. In most cases, this power generates heat within the device.
The simplest model for device power assumes the device can be modeled as a simple resistor across the power
supply inputs. This simple, but often useful, model ignores the details of internal power supplies within the
device, active circuitry, and power in I/O circuitry.
The power dissipated in a resistor is given by:
V
RIIVP
2
2
==⋅=
P is power in Watts, V is voltage in Volts, I is current in Amperes, and R is the resistance in Ohms.
In this simple model, a device powered from +48 volts with a power supply current of 0.1 Ampere will
dissipate the same power as a 480 Ω resistor – 4.8 W.
Normally the power supply voltage is assumed to be constant, so a device’s power depends on the current
requirements which vary with the device's operating conditions.
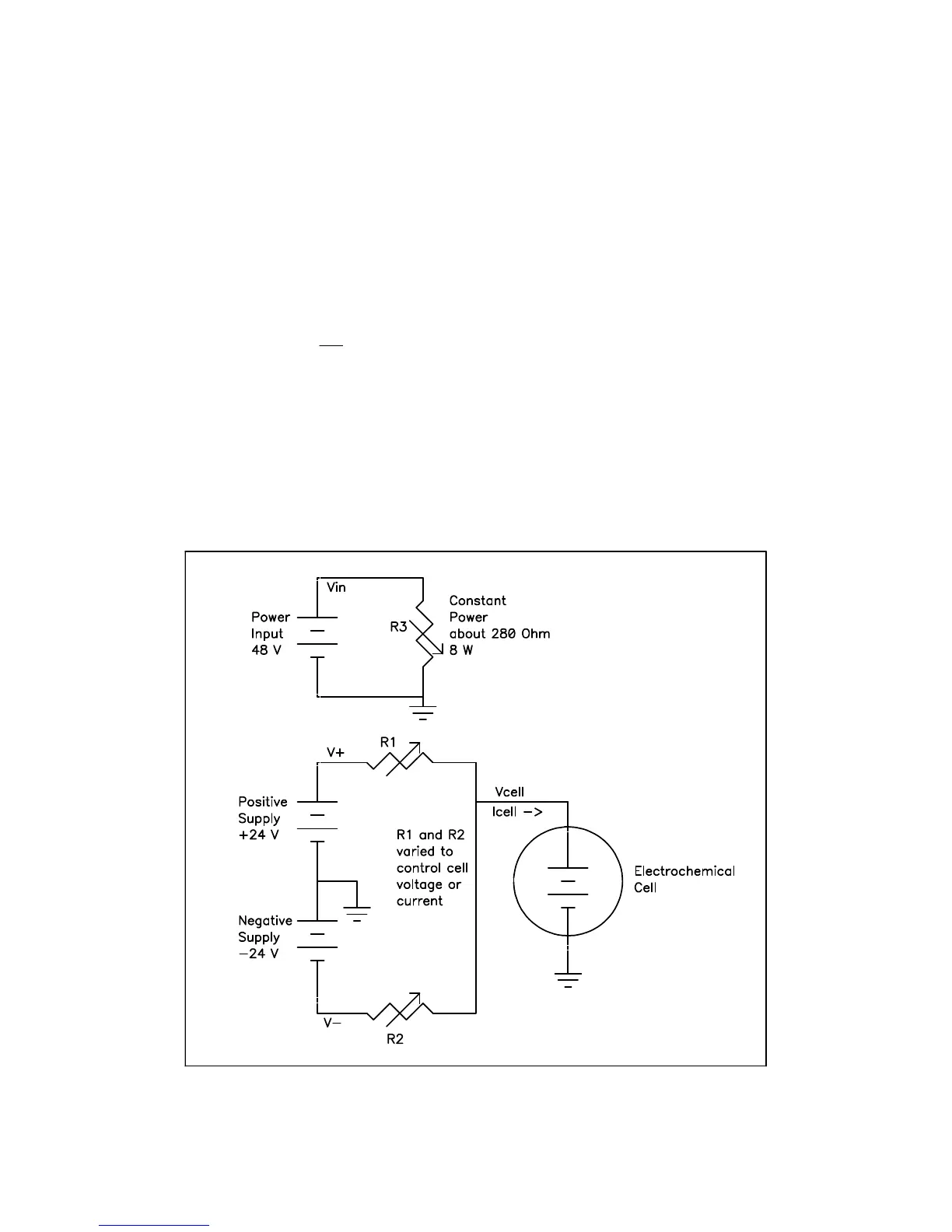
Figure E-1
Interface 1000 Simplified Power Model

 Loading...
Loading...