Installation procedures—All deployments26
Striping methods
A storage array combines the capacity of several physical hard drives into one virtual unit called an
array. These arrays are then presented to the operating system as a single disk device. The physical
layout of an array can be one of two configurations:
• Vertical striping—Offers ultimate fault tolerance and performance, but at the price of storage
efficiency.
• Horizontal striping—Allows for the creation of large arrays and efficient use of storage capacity,
but at the price of I/O performance and less fault tolerance.
In a vertical configuration, an array uses hard drives from separate storage enclosures and different
SCSI buses. In a horizontal configuration, the array uses multiple drives contained within the same
storage enclosure.
RAID levels
In conjunction with the striping method, the assigned RAID level also determines the fault-tolerance,
I/O performance, and storage efficiency of the LUN.
See Table 4 below for a comparison list of the different RAID levels.
When selecting a RAID level for a LUN, consider the type of data that will be stored on the array.
For example:
• For transitional data: you may want to use RAID 0, which provides no fault tolerance, but
provides rapid storage and access of large amounts of data.
• For critical data: use a fault-tolerant RAID level such as RAID 1, RAID 1+0, RAID 5, or RAID 6.
Choose the RAID level that offers the desired combination of fault-tolerance, I/O performance,
and storage efficiency.
Depending on the assigned RAID level, one or more drives within a LUN can fail without bringing
the drive sub-system down.
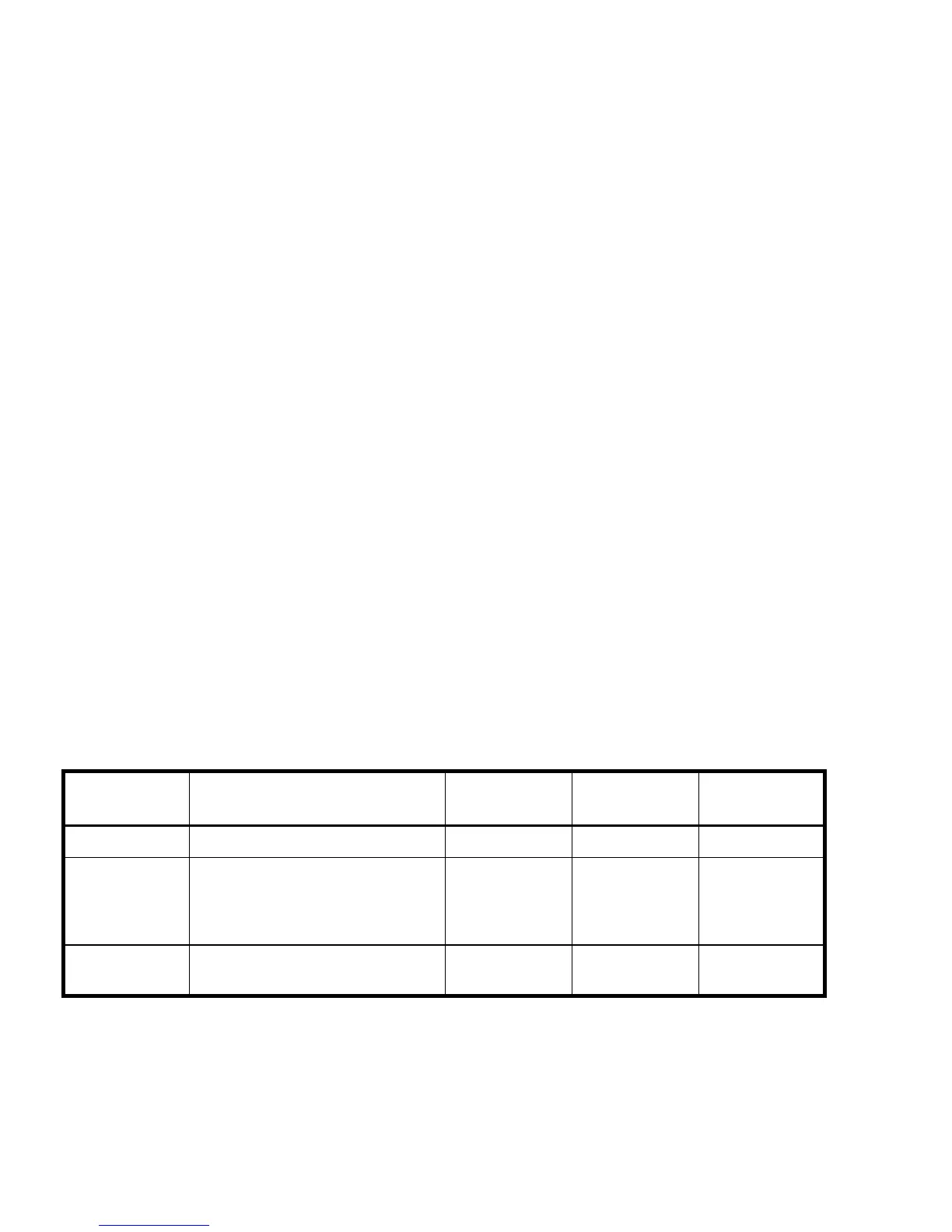
Table 4 RAID level comparison
RAID level Alternative name I/O
performance
Fault tolerance Storage
efficiency
RAID 0 Data striping Highest None Highest
RAID 1
RAID 1+0
Drive mirroring
Data striping plus drive mirroring
High * Highest * Low
RAID 5 Data striping, with one set of
distributed parity data
Medium Medium High

 Loading...
Loading...