Page 17-1
Chapter 17
Numbers in Different Bases
Besides our decimal (base 10, digits = 0-9) number system, you can work
with a binary system (base 2, digits = 0,1), an octal system (base 8, digits =
0-7), or a hexadecimal system (base 16, digits=0-9,A-F), among others. The
same way that the decimal integer 321 means 3x10
2
+2x10
1
+1x10
0
, the
number 100110, in binary notation, means
1x2
5
+ 0x2
4
+ 0x2
3
+ 1x2
2
+ 1x2
1
+ 0x2
0
= 32+0+0+4+2+0 = 38.
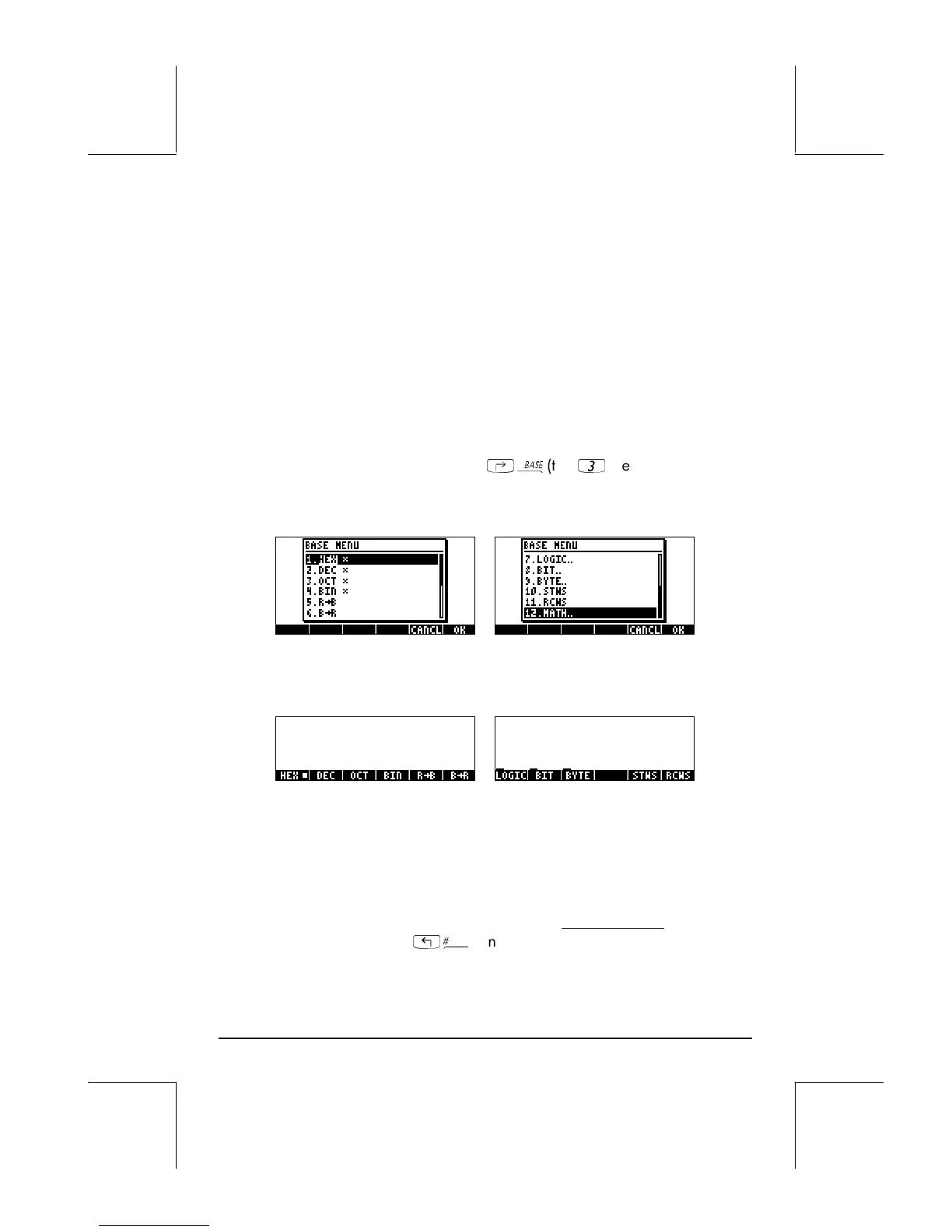
The BASE menu
The BASE menu is accessible through
‚ã
(the
3
key). With system
flag 117 set to CHOOSE boxes (see Chapter 1 in this guide), the following
entries are available:
With system flag 117 set to SOFT menus, the BASE menu shows the
following:
This figure shows that the LOGIC, BIT, and BYTE entries within the BASE menu
are themselves sub-menus. These menus are discussed in detail in Chapter 19
of the calculator’s User’s Guide.
Writing non-decimal numbers
Numbers in non-decimal systems, referred to as binary integers, are written
preceded by the # symbol (
„â
) in the calculator. To select the current

 Loading...
Loading...