Appendix C: Power over Ethernet
The IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet (PoE) and the IEEE 802.3at Power over Ethernet (PoE+) standards enable
Ethernet switches to provide power, as well as network signals, for compliant devices over existing CAT-5 cable.
PoE/PoE+ has several benefits:
•Lower-costinstallationsbecauseasinglecableprovidespoweralongwithdataconnectivity
•Noneedtomodifyexistingnetworkcabling
•Providesatrulyinternationalstandardforpowerdistribution
•Enablesremoteresetandpower-offcapability
PoE/PoE+ device types
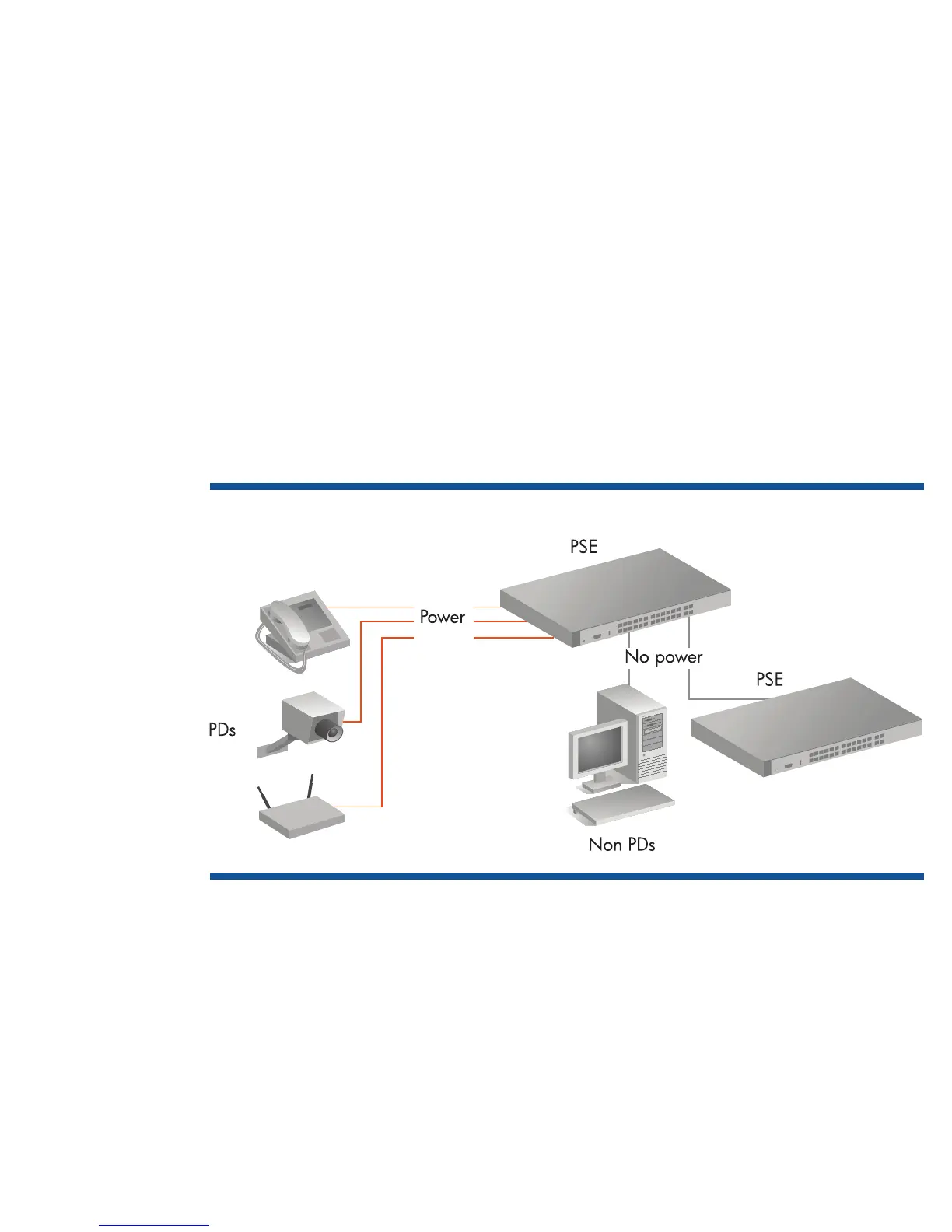
There are two types of devices that are defined for PoE/PoE+ implementations. The first type, called the
powered device (PD), receives power from the second type, called the power sourcing equipment (PSE).
Powered devices include any Ethernet device capable of receiving power through a data port such as IP
telephones, IP cameras, PDAs, and tablet PCs.
Power sourcing equipment, such as HP ProCurve switches with PoE support, must meet IEEE 802.3af
specifications for voltage (47 to 57 volts DC) and wattage (up to 15.4 watts), with further limitations on the
devices that receive power.
HP ProCurve switches that are PoE-enabled support both IEEE 802.3af-compliant devices as well as some pre-
802.3af standard devices.
Figure A3.
Power delivery options
The IEEE 802.3af standard provides two options for providing power over CAT 5 Ethernet cable. They are:
•Unused pairs—This option takes advantage of the fact that 10Base-T and 100Base-TX signals use only two of
the four twisted pairs in the cable. In this option, the pins on pairs 1/2 and 3/6 are used for data, and the
pins on pairs 4/5 and 7/8 are used for power. The 4/5 pair is twisted together to form the positive supply,
and the 7/8 pair is twisted together to form the negative supply.
•Data pairs—This option provides power over pairs that also provide data and is necessary because
1000Base-T signals use all four pairs. In this option, either the 1/2 pair or the 3/6 pair can form the positive
supply.
61
 Loading...
Loading...











