FC6A S
ERIES
MICROS
MART
L
ADDER
P
ROGRAMMING
M
ANUAL
FC9Y-B1726 18-17
18: P
ULSE
O
UTPUT
I
NSTRUCTIONS
3. S1 (source 1): Control register
S1 specifies the first data register of the data registers to use with RAMP1, RAMP2, RAMP3 or RAMP4 instructions.
Starting from the specified data register, 12 consecutive data registers are used.
Specify the first data register so that the device range is not exceeded.
*1 The upper and lower data registers change according to the 32-bit data storage method specified.
For details, see "32-bit Data Storage" on page 3-9.
*2 Stores the number of pulses that were output, regardless of whether specify absolute position mode is enabled or disabled. For details on
specify absolute position mode, see "ABS (Set Absolute Position)" on page 18-68.
4. S2 (source 2): Initialization Input
S2 specifies the initialization input.
When the initialization input S2 is turned on, the initial values configured in the WindLDR RAMP (Ramp Pulse Output) dialog
box, on the Settings tab, are stored in the control registers.
An external input or an internal relay can be specified.
When the initialization input is on, the initial values are written to the data registers with each scan. To only initialize the values
one time, use the initialization input in combination with the SOTU (single output up) instruction or the SOTD (single output
down) instruction.
5. D1 (destination 1): Operation Status
D1 specifies the first internal relay of the internal relays to use with the RAMP instructions. Starting from the specified internal
relay, 4 sequential internal relays are used. Specify the first internal relay so that the device range is not exceeded.
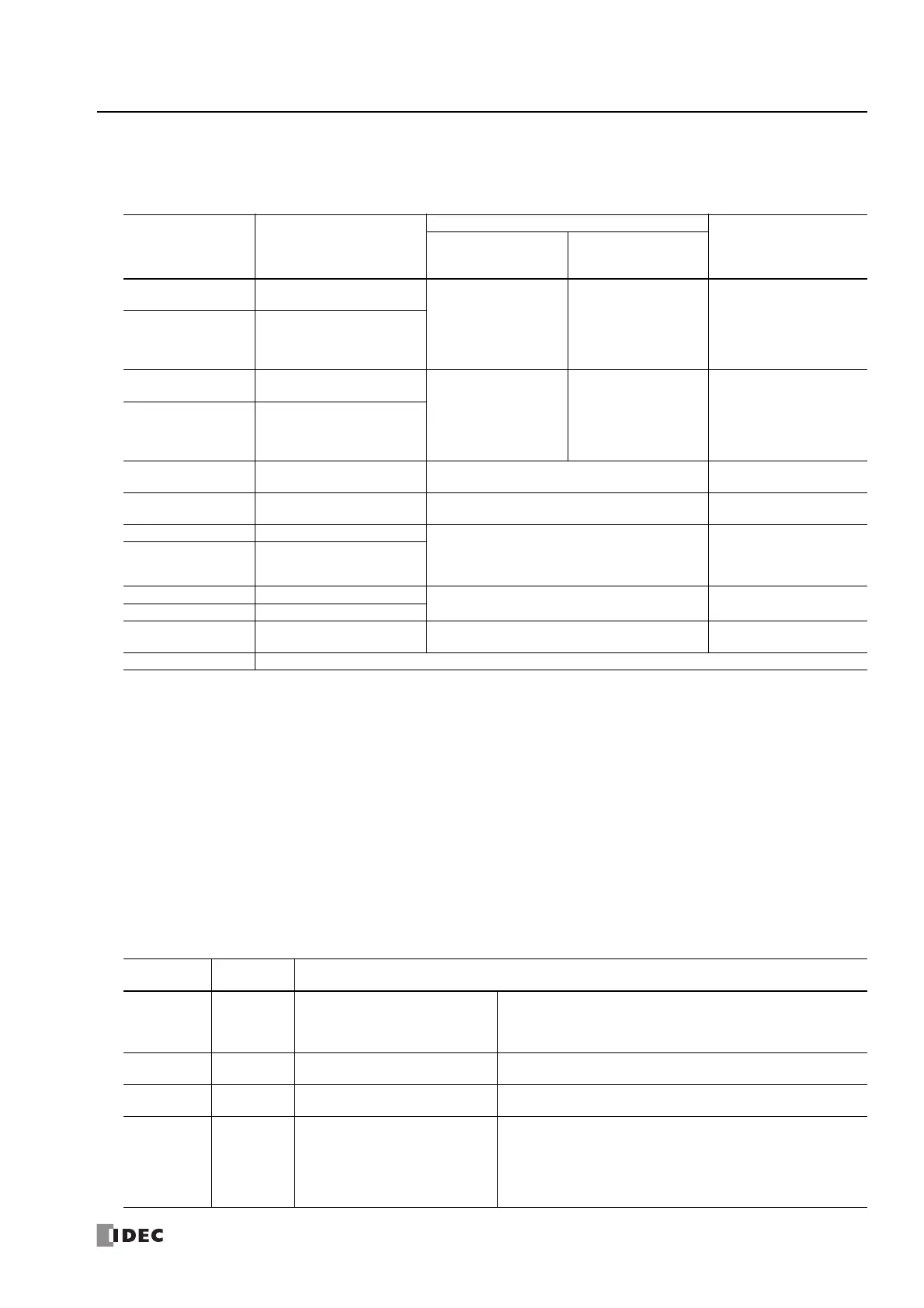
Storage
Destination
Function
Setting
Reference
All-in-One CPU
Module
CAN J1939 All-in-
One CPU Module/
Plus CPU Module
Starting number+0
Steady pulse frequency
(high word)
*1
RAMP1, RAMP2:
15 to 100,000
(increments of 1 Hz)
RAMP3, RAMP4:
15 to 5,000
(increments of 1 Hz)
RAMP1 to RAMP4:
15 to 100,000
(increments of 1 Hz)
"6. Steady pulse
frequency" on page 18-18
Starting number+1
Steady pulse frequency
(low word)
*1
Starting number+2
Initial pulse frequency
(high word)
*1
RAMP1, RAMP2:
15 to 100,000
(increments of 1 Hz)
RAMP3, RAMP4:
15 to 5,000
(increments of 1 Hz)
RAMP1 to RAMP4:
15 to 100,000
(increments of 1 Hz)
"7. Initial pulse frequency"
on page 18-18
Starting number+3
Initial pulse frequency
(low word)
*1
Starting number+4 Frequency change time 10 to 10,000 ms
"8. Frequency change
time" on page 18-18
Starting number+5 Control direction
0: Forward
1: Reverse
"11. Control direction" on
page 18-19
Starting number+6 Preset value (high word)
*1
When specify absolute position mode is disabled:
1 to 100,000,000 pulses
When specify absolute position mode is enabled:
-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 pulses
"13. Preset value" on page
18-20
Starting number+7 Preset value (low word)
*1
Starting number+8 Current value (high word)
*1
1 to 100,000,000 pulses
*2
"14. Current value" on
page 18-20
Starting number+9 Current value (low word)
*1
Starting number+10 Error status 0 to 4
"15. Error status" on page
18-20
Starting number+11 Reserved
Storage
Destination
Function Setting
Starting
number+0
Pulse output
ON
0: Pulse output OFF
1: Pulse output ON
This relay turns on during pulse output.
This relay turns off when pulse output stops.
This relay turns off when the specified number of pulses are output
and output ends.
Starting
number+1
Pulse output
complete
0: Pulse output not complete
1: Pulse output complete
This relay turns on when pulse output is complete.
This relay turns off when pulse output starts.
Starting
number+2
Pulse output
status
0: Steady pulse output
1: Changing output pulse frequency
This relay turns off when the pulse output status is steady.
This relay turns on when the pulse output is changing.
Starting
number+3
Overflow
0: None
1: An overflow has occurred
When pulse counting is enabled, this relay turns on when a pulse is
output that exceeds the configured preset value. Pulse output
continues even if an the overflow occurs during steady output or
while the pulse frequency is changing.
However, pulse counting is suspended at the point when the
overflow occurred.

 Loading...
Loading...