14
2.11. SAFETY AND CONTROL SYSTEMS
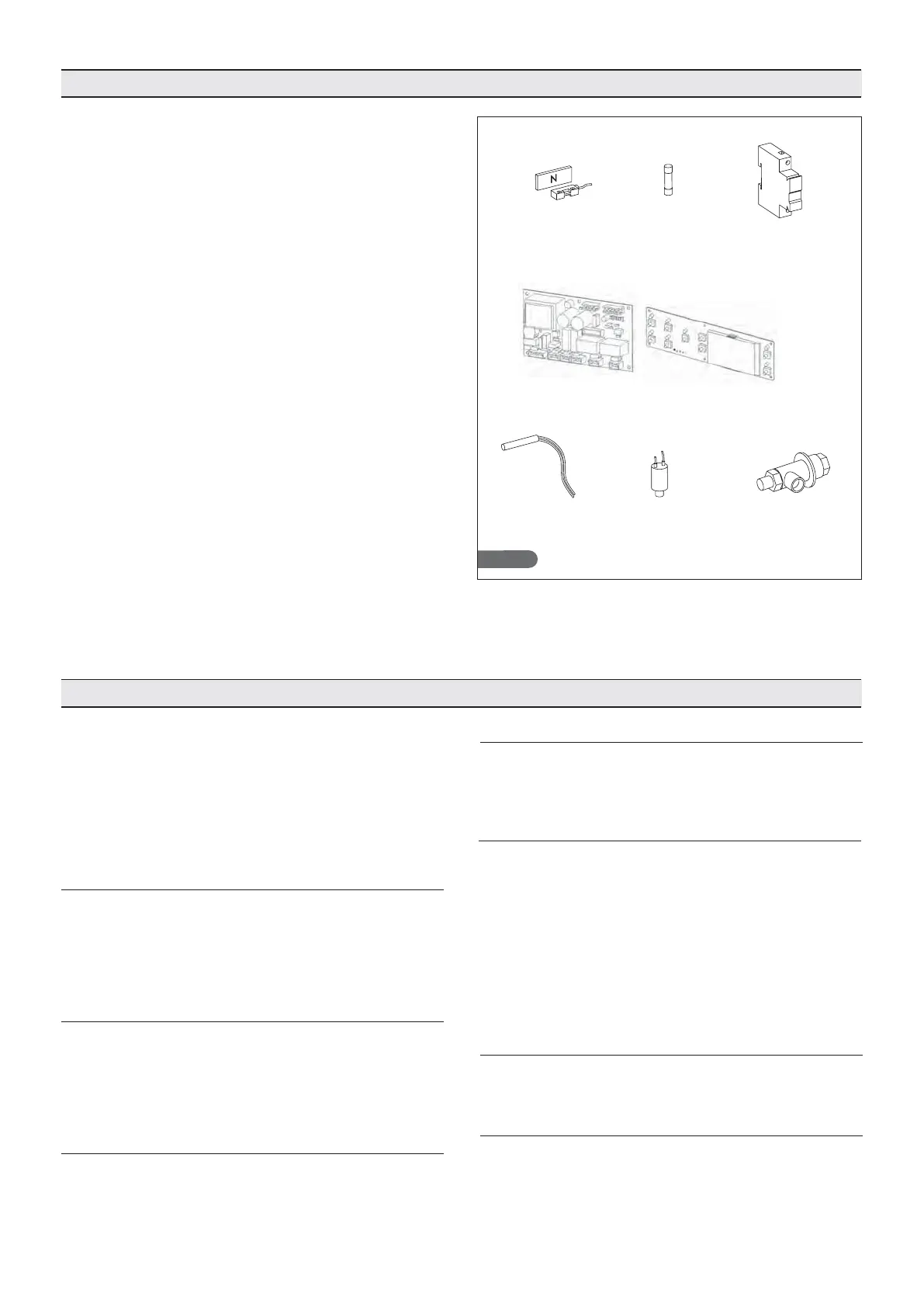
Fig. 14
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Door micro switch (A): blocks the fans when the door
is opened.
Protection fuses (B): protects circuits from short-t-
circuits and overloads.
Fuse holders (C): contain the fuses and allow circuit
opening and disconnection.
Circuit boards (D): depending on the parameters
acquired, they command and control the various
blast chiller devices connected to them.
Cell temperature control (E): managed by a circuit
board by means of a PT1000 probe.
Safety pressure switch (F): intervenes when there is
too much pressure in the refrigerating circuit.
Safety valve (G): intervenes when there is too much
pressure in the system and when the safety pressure
switchdoesnotintervene.Theinterventiondischarges
excess gas from the ambient.
Fig.A Fig.B Fig.C
Fig.D
Fig.GFig.FFig.E
2.12. R404A GAS SAFETY BOARD
• Identification of dangers
Elevated inhalation exposure can have anaesthetic
effects. Very high exposure can cause cardiac rhythm
anomalies and cause sudden death. The nebulised or
squirted product can cause frost burns to the eyes or
skin. Dangerous for the ozone layer.
• First aide measures
Inhalation
Move the injured person away from exposure and keep
him/her warm and at rest. Give oxygen if needed. Perform
artificial respiration if breathing has stopped or gives
signs of stopping. In case of cardiac arrest, perform an
external heart massage.
Seek immediate medical assistance.
Skin contact
Have the concerned areas thaw with water.
Remove contaminated clothing.
Attention: clothing can stick to the skin for frost burns.
For skin contact, wash immediately and abundantly
with lukewarm water. If symptoms occur (irritation or
formation of blisters) seek medical assistance.
Eye contact
Wash immediately with an eye-wash solution or with clean
water, keeping the eyelids aside, for at least 10 minutes.
Seek medical assistance.
Swallowing
Do not provoke vomiting.
If the injured person is conscious, have the mouth rinsed
with water and have him/her drink 200-300 ml of water.
Seek immediate medical assistance.
Further medical care
Symptom treatment and support therapy when indicated.
Do not administer adrenalin or similar sympathomimetic
drugs after exposure, due to the risk of cardiac arrhythmia
with possible cardiac arrest.
• Fire-prevention measures
Non flammable.
Thermal decomposition causes the emission of toxic
and corrosive vapours (hydrogen chloride, hydrogen
fluoride). In case of fire, use a self-contained breathing
apparatus and suitable protective clothing.
Fire extinguishers
Use extinguishing agents appropriate for the surround-
ing fire.
• Toxicological information
Inhalation
More elevated atmospheric concentrations can cause
anaesthetic effects with possible losing of conscience.
Very high exposure can cause cardiac rhythm anomalies
and cause sudden death.
More elevated concentrations can cause asphyxiation
due to the reduced content of oxygen in the air.
 Loading...
Loading...