ES749 Flow Computer
11
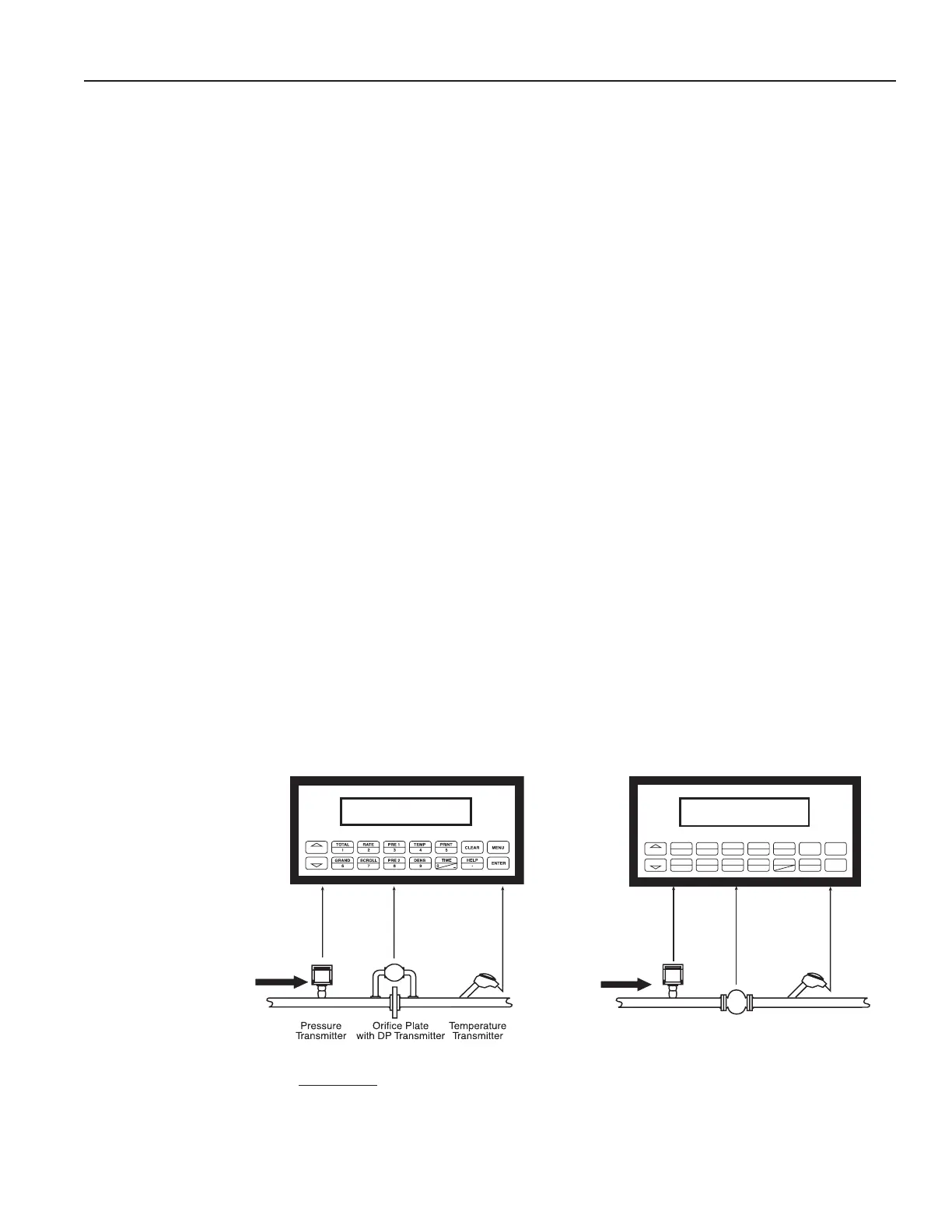
3.1 Steam Mass
Measurements:
A owmeter measures the actual volume ow in a steam line. A temperature and/or
pressure sensor is installed to measure temperature and/or pressure.
Calculations:
• Density and mass ow are calculated using the steam tables stored in the ow
computer.
• With square law device measurement the actual volume is calculated from the
differential pressure, taking into account temperature and pressure compensation.
• Saturated steam requires either a pressure or temperature measurement with the other
variable calculated using the saturated steam curve.
• Optional steam trap monitoring using Compensation Input 1.
Input Variables:
Superheated Steam: Flow, temperature and pressure
Saturated Steam: Flow, temperature or pressure
Output Results:
• Display Results
Mass or Volume Flow Rate, Resettable Total, Non-Resettable Total, Temperature,
Pressure, Density (optional: peak demand, demand last hour, time/date stamp)
• Analog Output
Mass or Volume Flow Rate, Temperature, Pressure Density, Peak Demand,
Demand Last Hour
• Pulse Output
Mass or Volume Total
• Relay Outputs
Mass or Volume Flow Rate , Total, Pressure, Temperature, Alarms, Peak
Demand, Demand Last Hour
Applications:
Monitoring mass ow and total of steam. Flow alarms are provided via relays and
datalogging is available via analog (4-20mA) and serial outputs.
STEAM MASS
Steam Mass
Illustration
3. Applications
FlowmeterTemperature
Transmitter
PRINT
5
0
–
TIME
CLEAR
•
MENU
ENTER
HELP
TEMP
4
PRE 1
3
RATE
2
TOTAL
1
GRAND
6
SCROLL
7
PRE 2
8
DENS
9
Pressure
Transmitter
Mass Flow
Mass Flow = volume ow • density (T, p)
Calculations
*
* or Steam Trap Monitor
*
* or Steam Trap Monitor
 Loading...
Loading...