ES749 Flow Computer
19
3.9 Liquid Mass
Measurements:
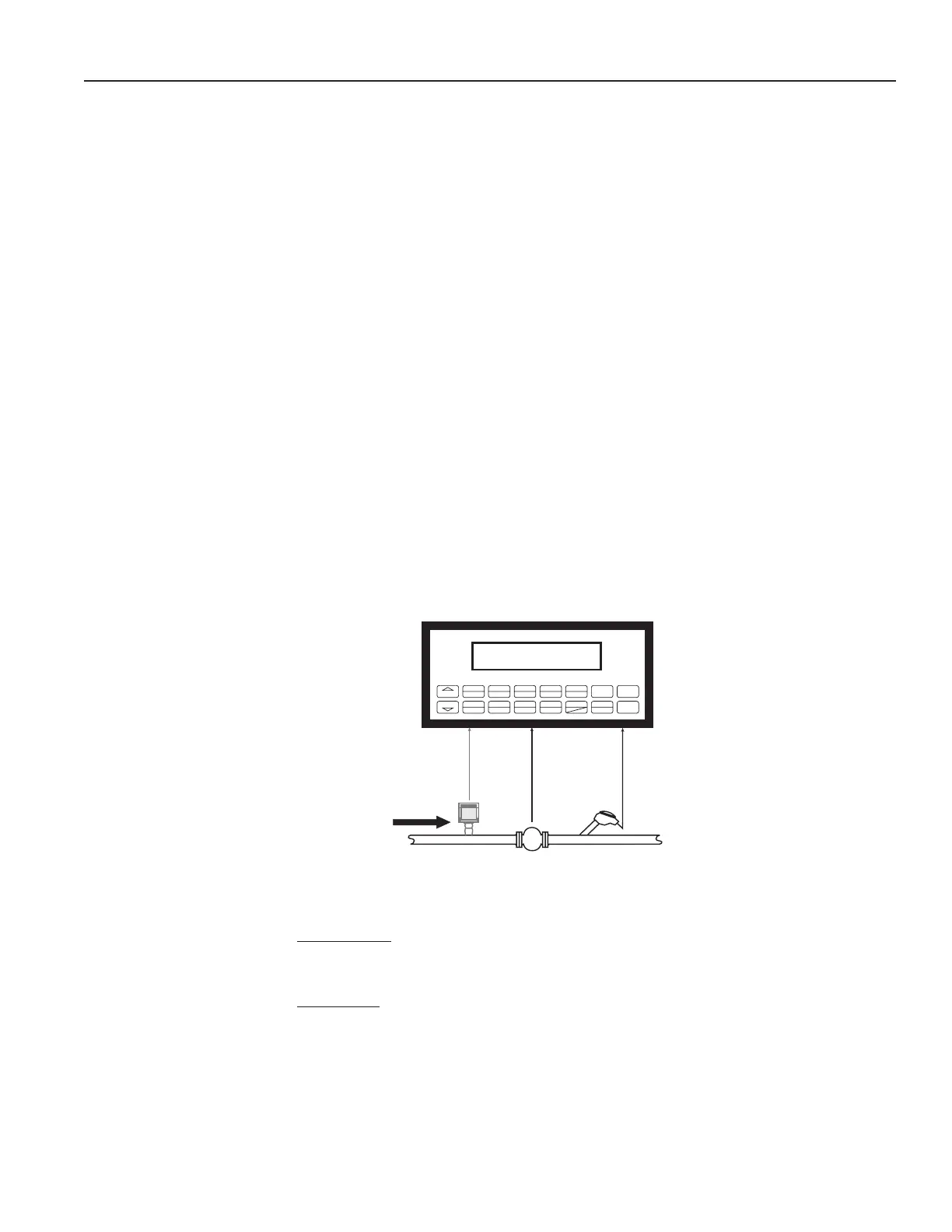
Actual volume ow is measured by the ow element (DP transmitter, Flowmeter).
Temperature is measured by the temperature transmitter. A pressure transmitter can
be used to monitor pressure. Pressure measurement does not affect the calculation. A
density transmitter may be used in place of a temperature transmitter for direct density
measurement.
Calculations:
• The density and mass ow are calculated using the reference density and the thermal
expansion coefcient of the liquid (see "FLUID DATA" submenu)
Output Results:
• Display Results
Mass or Volume Flow Rate, Resettable Total, Non-Resettable Total, Temperature,
Pressure, Density (optional: peak demand, demand last hour, time/date stamp)
• Analog Output
Mass or Volume Flow Rate, Temperature, Pressure, Density, Peak Demand,
Demand Last Hour
• Pulse Output
Mass or Volume Total
• Relay Outputs
Mass or Volume Flow Rate, Total, Temperature, Pressure, Density Alarms, Peak
Demand, Demand Last Hour
Applications:
Monitoring mass ow and total of any liquid. Flow alarms are provided via relays and
datalogging is available via analog (4-20mA) and serial outputs.
Liquid Mass
Liquid Mass
Illustration
Volume Flow
As calculated in section 3.8
Mass Flow
Mass Flow = volume ow • (1-a • (T
1
-T
ref
))
2
• ref. density
α = Thermal expansion coefcient • 10
-6
Calculations
NOTE:
A density transmitter may be used
for direct density measurement.
FlowmeterTemperature
Transmitter
PRINT
5
0
–
TIME
CLEAR
•
MENU
ENTER
HELP
TEMP
4
PRE 1
3
RATE
2
TOTAL
1
GRAND
6
SCROLL
7
PRE 2
8
DENS
9
Optional
Pressure
Transmitter
T
1
 Loading...
Loading...