6Tutorial
172 E364xA User’s and Service Guide
Overview of the Power Supply Operation
The basic design technique, which has not changed over the years, consists of
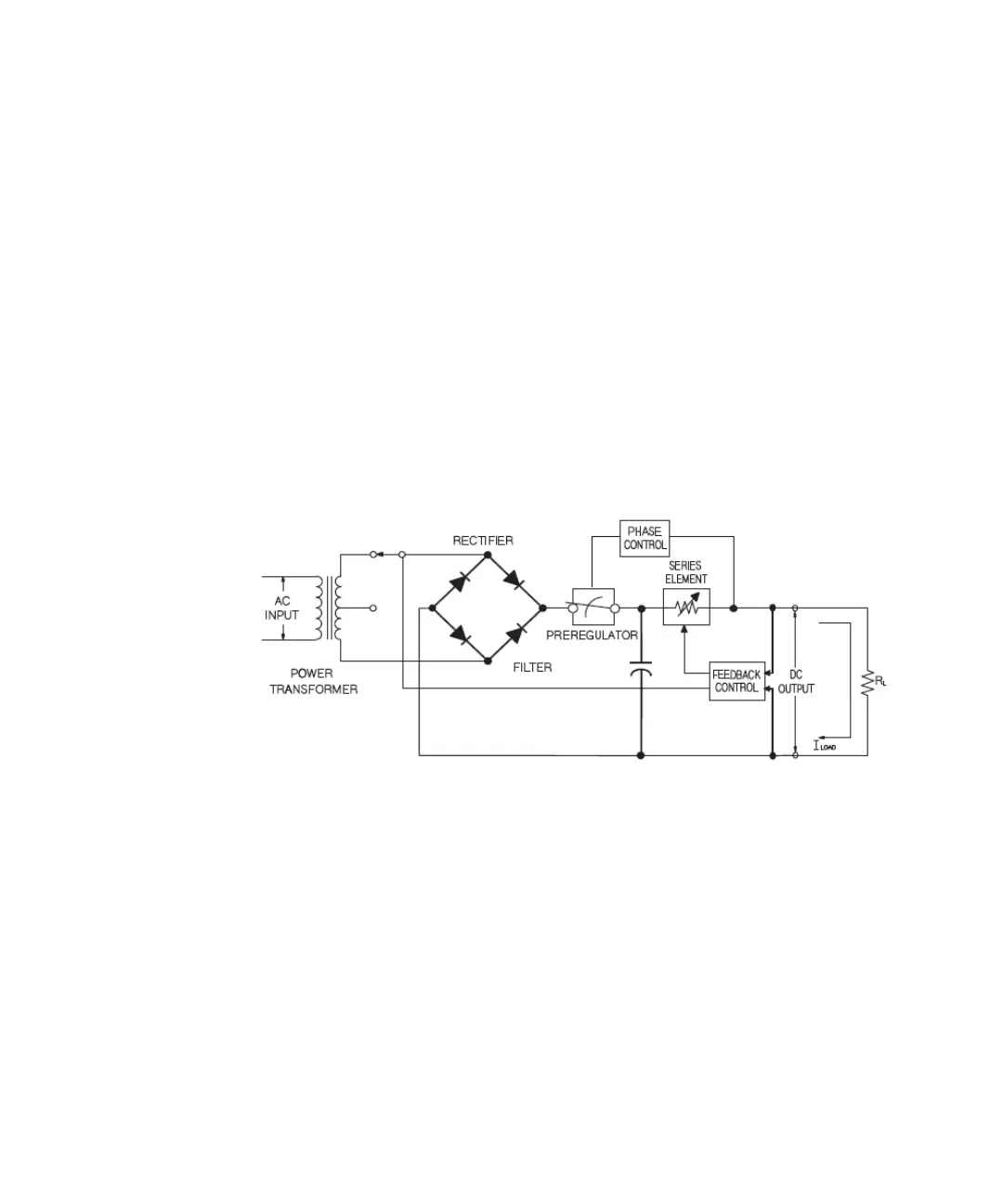
placing a control element in series with the rectifier and load device. Figure 6-1
shows a simplified schematic of a series regulated supply with the
phase-controlled pre-regulator described as a power switch and the series
element depicted as a variable resistor. The phase-controlled pre-regulator
minimizes the power dissipated at the series element by maintaining the voltage
drop across the series element at a low and constant. Feedback control circuits
continuously monitor the output and adjust the series resistance to maintain a
constant output voltage. Because the variable resistance of Figure 6-1 is actually
one or more power transistor operating in the linear (class A) mode, supplies with
this type of regulator are often called linear power supplies. Linear power supplies
have many advantages and usually provide the simplest most effective means of
satisfying high performance and low power requirements.
Figure 6-1 Diagram of a simple series power supply
This power supply has two ranges, allowing more voltage at a lower current or
more current at a lower voltage. Single range supplies can only output maximum
power at full scale voltages and full scale current. This supply can provide output
power that is close to maximum at full scale for both ranges. The pre-regulator in
this power supply uses solid state transformer tap switches on the secondary
winding of the power transformer. This technique is very effective in reducing the
power dissipated in the series element.

 Loading...
Loading...











