User Manual for BPS-2000
www.levitronix.com
PL-4021-00, Rev02, DCO# 15-235
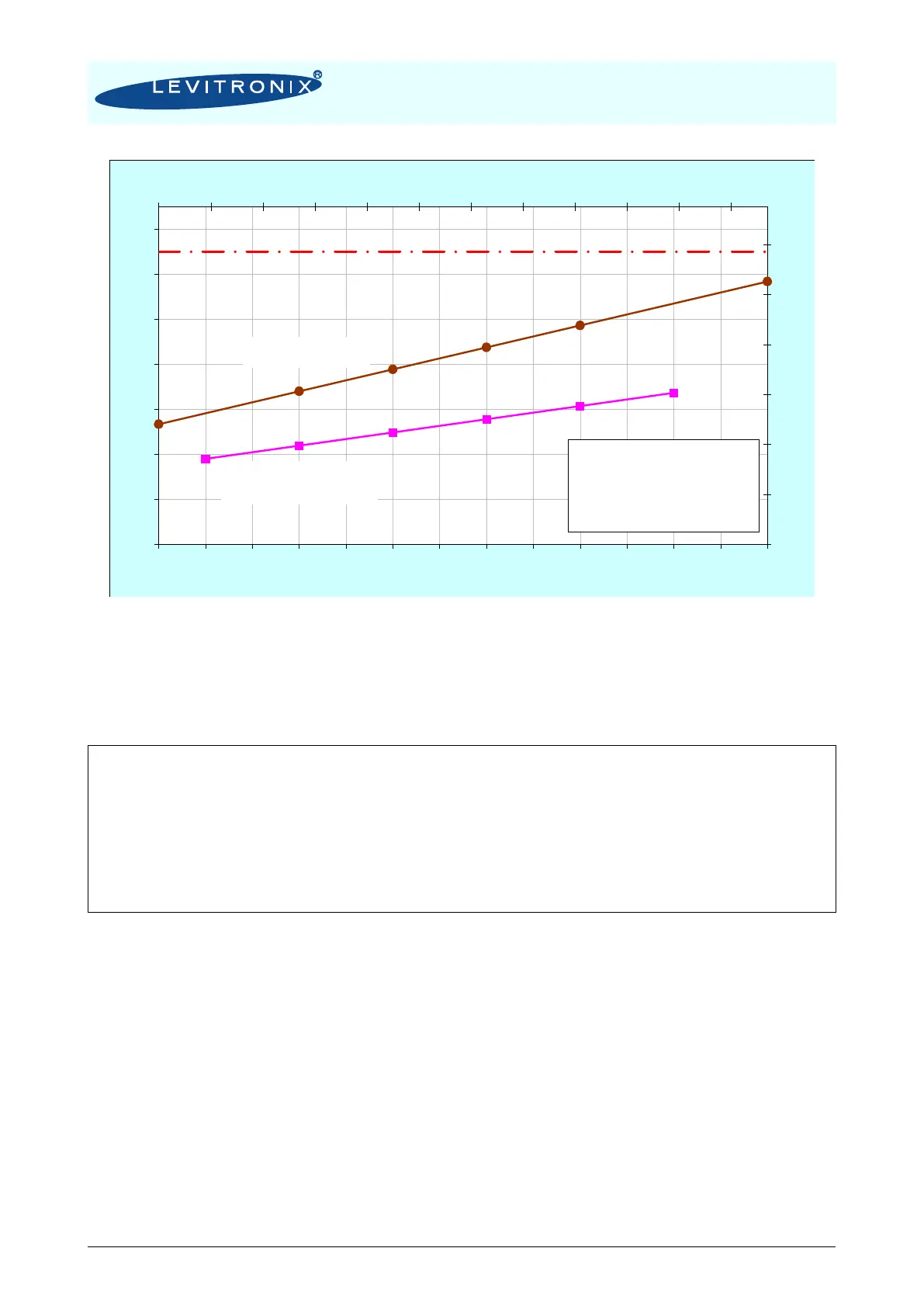
Figure 23: Influence of liquid temperature on motor temperature
(Measurement at 6000 rpm 50 lpm with LPP-2000.7, but gradients are representative for other operational points and the same for LPP-2000.6)
The above curves are measurements of the motor temperature at certain liquid and ambient temperatures.
Equation (Eq. 1) shows how to calculate the motor temperature for other liquid and ambient temperatures
based on these curves.
orliquid/mot gradient eTemperaturtgetemperatur AmbientT
etemperatur LiquidTetemperatur MotorT
CTtgCTCTCTTTTT
LMA
LM
ALMLALMALM
23 Figure see
21 Figure see
)25()25()25,25(),(
0000
In order to account for thermal variations (like ambient temperature, closed chemical cabinets or corners
without ventilations) and to not significantly reduce the MTBF of the motor it is recommended to keep about
10 to 20°C safety distance to the absolute thermal limit of the motor (90°C) when designing the thermal
concept of the pump system.
77
97
117
137
157
177
197
77 87 97 107 117 127 137 147 157 167 177 187
25
35
45
55
65
75
85
95
25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90
[°F]
[°F]
[
0
C]
Liquid Temperature in [°C]
Specific gravity = 1 g/cm3
Viscosity = 0.7 cP
Gradients measured for 6000 rpm /50
l/min but representative also for other
No Active Cooling:
Temp. Gradient = 0.49
Active Cooling with ACM-4.2:
Cooling Pressure = 1 bar
 Loading...
Loading...






