VINX-1x0-HDMI Extenders – User's Manual 88
9.2. Video Over IP
Basics
Beside the traditional AV matrix switchers and extenders the video over IP or networked AV system is the
biggest leading technology in the AV industry. The spreading of the technology speeds up the general
homes.
The main difference compared with the traditional AV technologies is the method of the signal transmission:
the signal bandwidth and the distance between the source and sink devices.
DEFINITION:
protocols used to interconnect network devices on the Internet or in a private network.
identify how it should be broken into packets, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination.
recover automatically from the failure of any device on the network. *
can create channels of communication across a network. It also manages how a message is assembled
into smaller packets before they are then transmitted over the Internet and reassembled in the right order at
the destination address. *
computer on the network checks this IP address to determine where to forward the message. *
* Source:
9.3. HDCP Management
to solve HDCP related problems. Complex AV systems often have both HDCP and non-HDCP components.
The matrix allows transmitting HDCP encrypted and unencrypted signals. The devices will be still HDCP
compliant as they will never output an encrypted signal to a non-HDCP compliant display device. If an
encrypted signal is switched to a non-compliant output, a red screen alert or muted screen will appear.
9.3.1. Protected and Unprotected Content
Many video sources send HDCP protected signal if they detect that the sink is HDCP capable – even if
the content is not copyrighted. This can cause trouble if an HDCP capable device is connected between
the source and the display. In this case, the content cannot be viewed on non-HDCP capable displays and
interfaces like event controllers. Rental and staging technicians often complain about certain laptops, which
are always sending HDCP encrypted signals if the receiver device (display, matrix router, etc.) reports HDCP
compliancy. However, HDCP encryption is not required all the time e.g. computer desktop image, certain
laptops still do that.
detect that the sink is not HDCP capable, and turn off authentication.
9.3.2. Disable Unnecessary Encryption
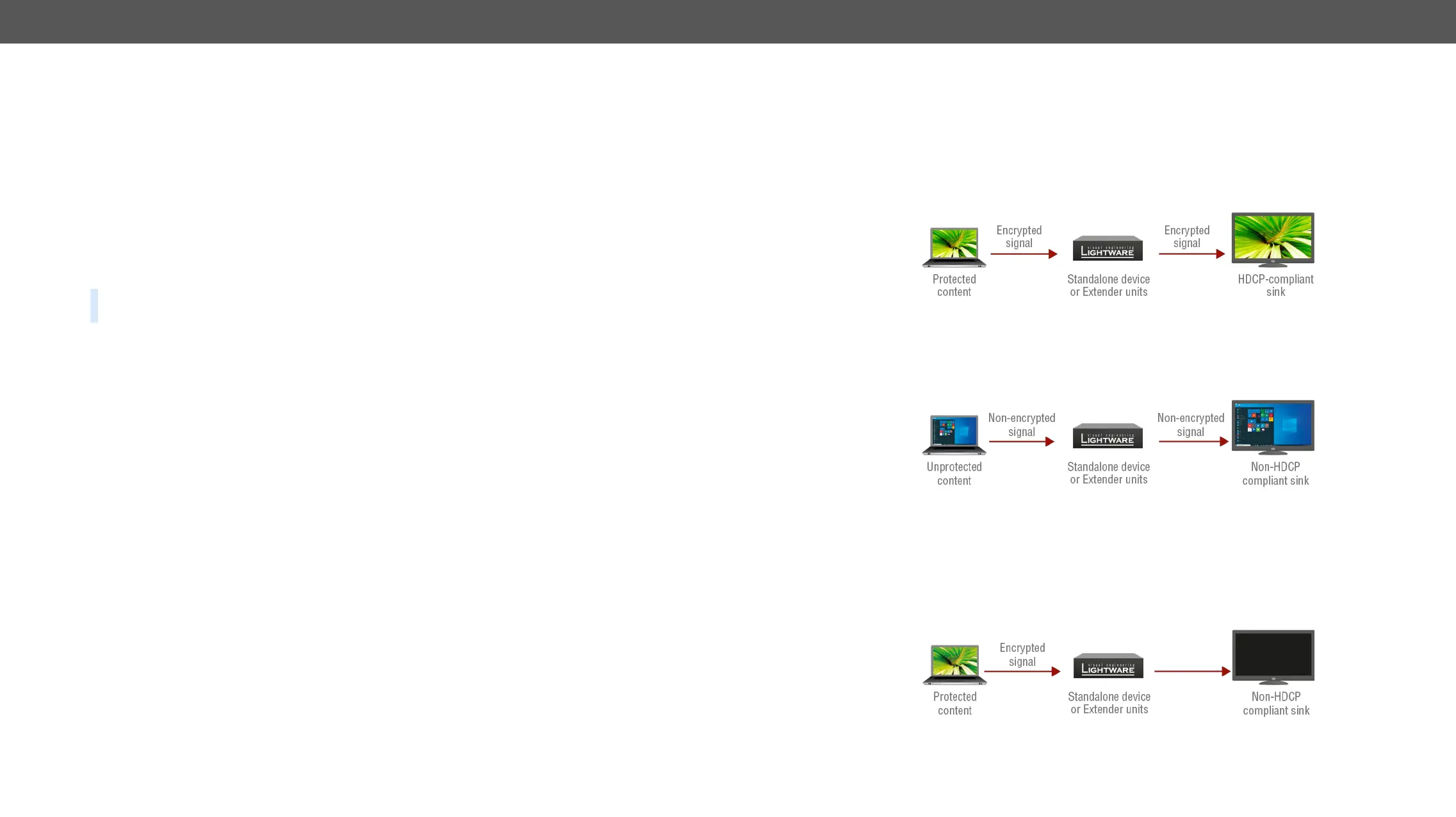
HDCP Compliant Sink
All the devices are HDCP-compliant, no manual setting is required, both protected and unprotected contents
are transmitted and displayed on the sink.
Not HDCP-compliant Sink 1.
Not-HDCP compliant sink is connected to the matrix. Some sources (e.g. computers) always send HDCP
encrypted signals if the receiver device reports HDCP compliancy, however, HDCP encryption is not required
all the time (e.g. computer desktop image). If HDCP is enabled in the matrix, the image will not be displayed
on the sink.
Setting the HDCP parameter to Auto on the output port and disable HDCP on the input port, the transmitted
signal will not be encrypted if the content is not protected. Thus, non-HDCP compliant sinks will display non-
encrypted signal.
Not HDCP-compliant Sink 2.
The layout is the same as in the previous case: non-HDCP compliant display device is connected to the
matrix but the source would send protected content with encryption. If HDCP is enabled on the input port of
the matrix, the source will send encrypted signal.
The sink is not HDCP compliant, thus, it will not display the video signal but blank screen is shown. If HDCP
is disabled on the input port of the matrix, the source will not send the signal. The solution is to replace the
display device to an HDCP-capable one.

 Loading...
Loading...











