© Microhard Systems Inc. 126
4.0 Configuration
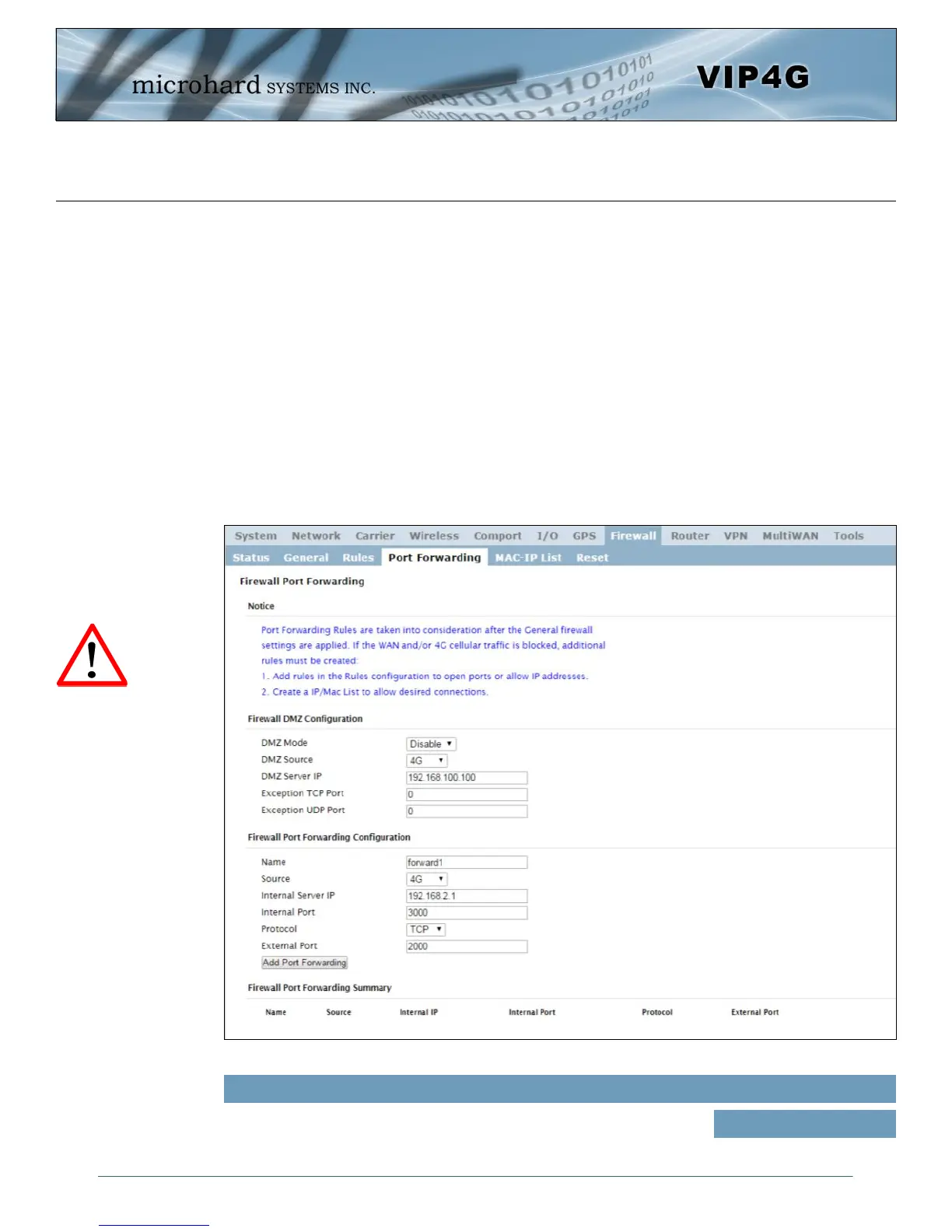
Image 4-8-4: Firewall > Port Forwarding
4.8.4 Firewall > Port Forwarding
The VIP4G can be used to provide remote access to connected devices. To access these devices a user
must define how incoming traffic is handled by the VIP4G. If all incoming traffic is intended for a specific
connected device, DMZ could be used to simplify the process, as all incoming traffic can be directed
towards a specific IP address.
In the case where there is multiple devices, or only specific ports need to be passed, Port forwarding is
used to forward traffic coming in from the WAN (Cellular) to specific IP Addresses and Ports on the LAN.
Port forwarding can be used in combination with other firewall features, but the Firewall must be enabled
for Port forwarding to be in effect. If the WAN Request is blocked on the General Tab, additional rules and/
or IP Lists must be set up to allow the port forwarding traffic to pass through the firewall.
IP-Passthrough (Carrier > Settings) is another option for passing traffic through the VIP4G, in this case all
traffic is passed to a single device connected to a RJ45 port on the VIP4G, The device must be set for
DHCP or have the WAN IP set as its static IP, as the VIP4G assigns the WAN IP to the device, and the
modem enters into a transparent mode, routing all traffic to the RJ45 port. This option bypasses all firewall
features of the VIP4G, as well as all other features of the VIP4G such as COM, VPN, GPS etc.
DMZ Mode
Enable or disable DMZ Mode. DMZ can be used to forward all traffic to a
specific IP address (DMZ Server IP) on the LAN.
Values (selection)
Disable / Enable
If DMZ is enabled and an
exception port for the WebUI
is not specified, remote
management will not be
possible. The default port for
remote management is TCP
80.
 Loading...
Loading...