OM-2240 Page 69
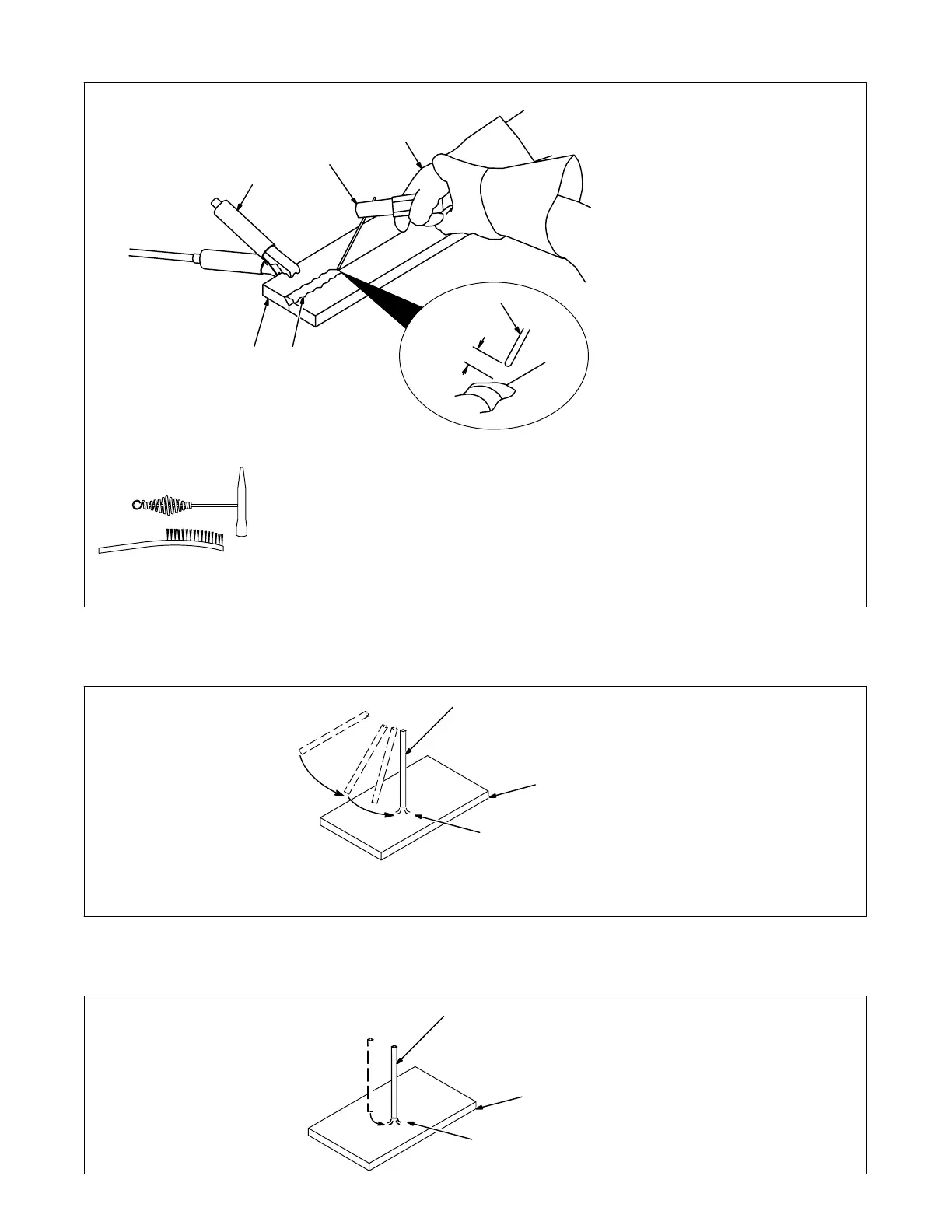
12-3. Stick Welding Procedure
stick 12/96 − ST-151 593
Y Weld current starts when
electrode touches work-
piece.
Y Weld current can damage
electronic parts in vehicles.
Disconnect both battery
cables before welding on a
vehicle. Place work clamp as
close to the weld as possible.
1 Workpiece
Make sure workpiece is clean be-
fore welding.
2 Work Clamp
3 Electrode
A small diameter electrode requires
less current than a large one. Fol-
low electrode manufacturer’s
instructions when setting weld am-
perage (see Section 12-2).
4 Insulated Electrode Holder
5 Electrode Holder Position
6 Arc Length
Arc length is the distance from the
electrode to the workpiece. A short
arc with correct amperage will give
a sharp, crackling sound.
7 Slag
Use a chipping hammer and wire
brush to remove slag. Remove slag
and check weld bead before mak-
ing another weld pass.
Tools Needed:
1
4
3
5
2
7
6
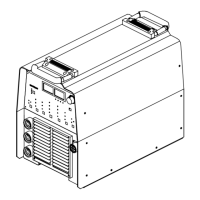
12-4. Striking an Arc − Scratch Start Technique
S-0049
1 Electrode
2 Workpiece
3 Arc
Drag electrode across workpiece
like striking a match; lift electrode
slightly after touching work. If arc
goes out electrode was lifted too
high. If electrode sticks to work-
piece, use a quick twist to free it.
Y Normal open-circuit voltage
(80 volts) is present if normal
open-circuit voltage is se-
lected (see Section 6-6).
1
2
3
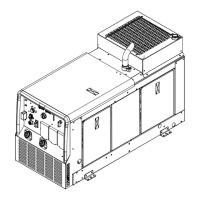
12-5. Striking an Arc − Tapping Technique
S-0050
1 Electrode
2 Workpiece
3 Arc
Bring electrode straight down to
workpiece; then lift slightly to start
arc. If arc goes out, electrode was
lifted too high. If electrode sticks to
workpiece, use a quick twist to free it.
1
3
2