© National Instruments | 7-17
X Series User Manual
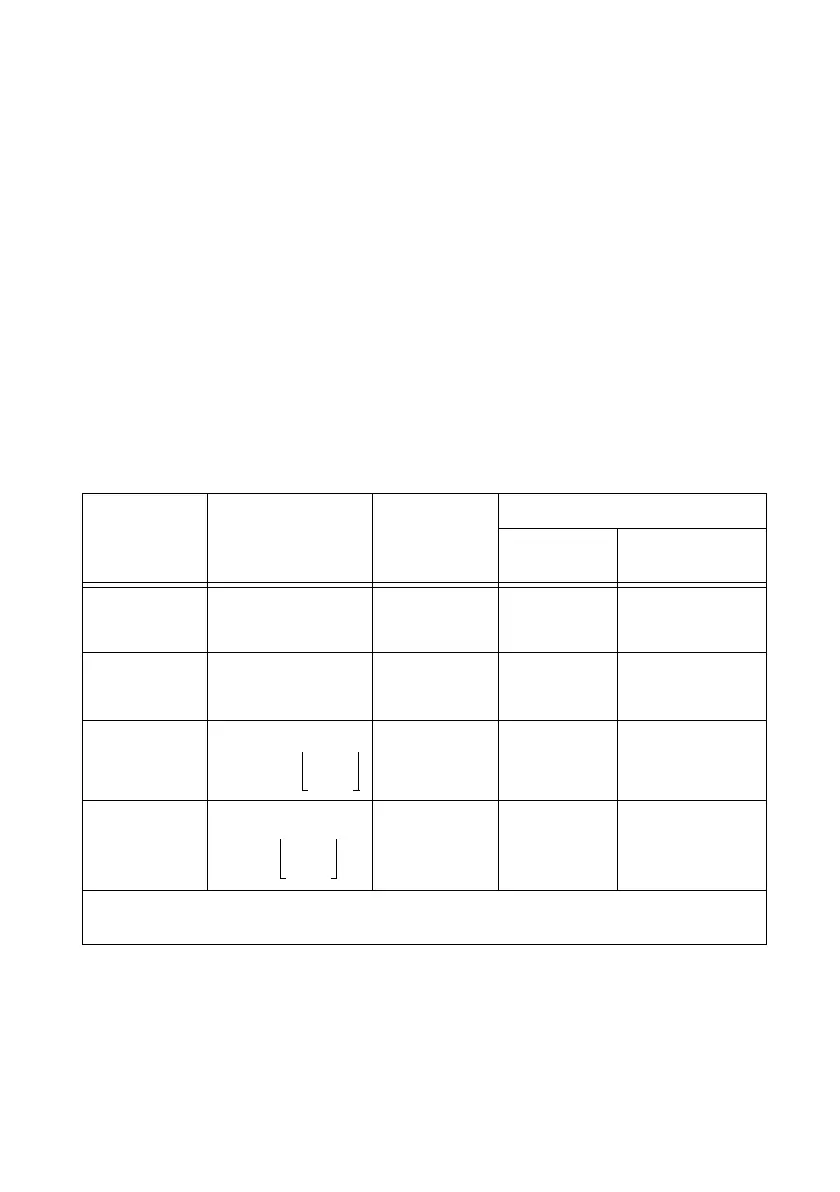
Here is how these variables apply to each method, summarized in Table 7-2.
• One counter—With one counter measurements, a known timebase is used for the source
frequency (fk). The measurement time is the period of the frequency to be measured,
or 1/fx.
• Two counter high frequency—With the two counter high frequency method, the second
counter provides a known measurement time. The gate frequency equals 1/measurement
time.
• Two counter large range—The two counter larger range measurement is the same as a one
counter measurement, but now the user has an integer divide down of the signal. An internal
timebase is still used for the source frequency (fk), but the divide down means that the
measurement time is the period of the divided down signal, or N/fx where N is the divide
down.
• Sample clocked—For sample clocked frequency measurements, a known timebase is
counted for the source frequency (fk). The measurement time is the period of the sample
clock (fs).
Table 7-2. Frequency Measurement Methods
Variable Sample Clocked One Counter
Two Counter
High
Frequency
Large Range
fk Known timebase Known
timebase
Known timebase
Measurement
time
gating period
Max.
frequency
error
fk
Max. error %
Note: Accuracy equations do not take clock stability into account. Refer to your device specifications
for clock stability.
1
gating period
-----------------------------------
fx
fx
fk
fx
fs
---- 1–
-------------------------------
fx
fx
fk fx–
---------------
fx
fx
Nfkfx–
--------------------------
fx
fk
fx
fs
---- 1–
-------------------------------
fx
Nfkfx–
--------------------------

 Loading...
Loading...











