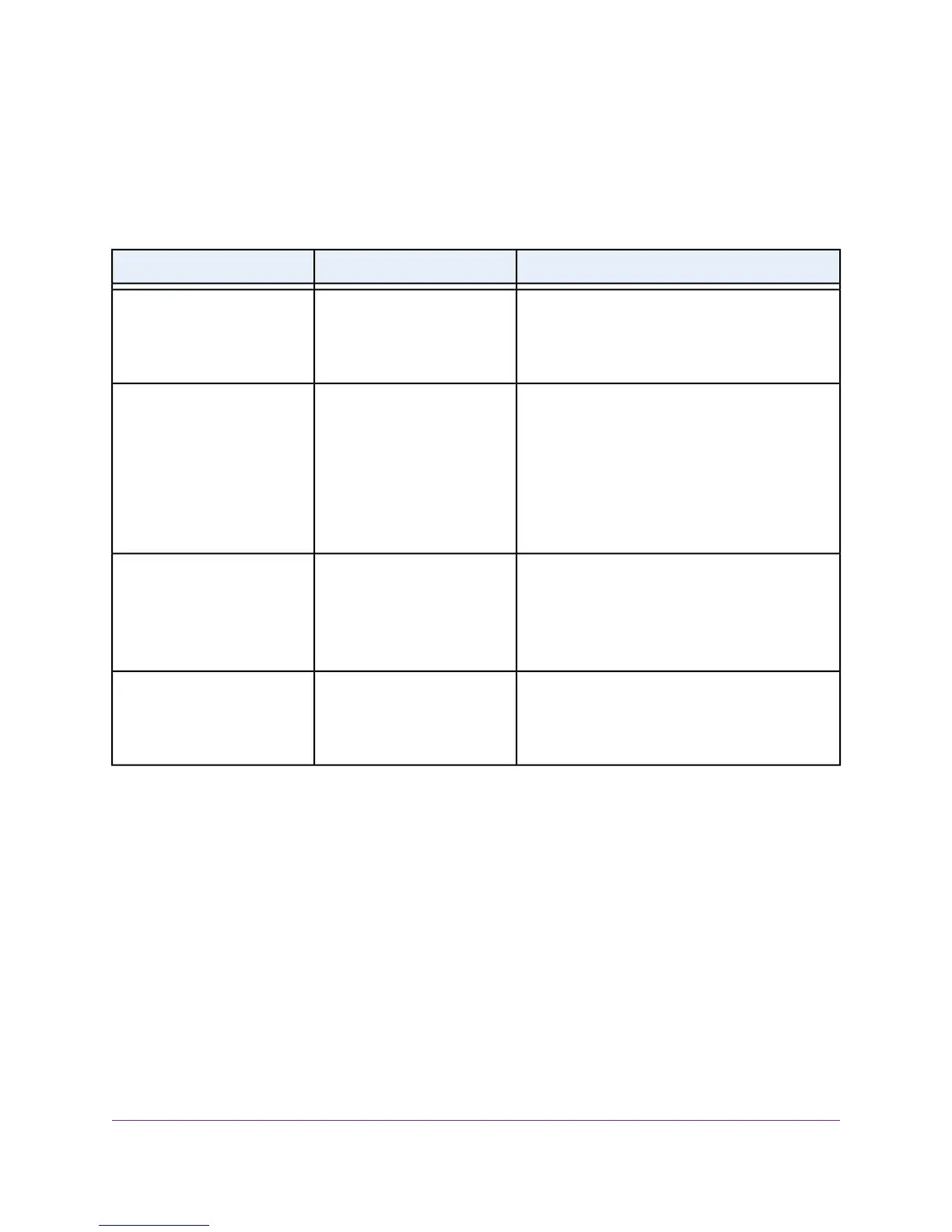
Troubleshooting Chart
The following table lists symptoms, possible causes, and possible solutions for problems that might occur.
Table 5.Troubleshooting chart
Possible SolutionPossible CauseSymptom
Check the power cable connections at the switch
and the power source.
Make sure that all cables are used correctly and
comply with the Ethernet specifications.
Power is not supplied to the
switch.
Power LED is off.
Check the crimp on the connectors and make sure
that the plug is properly inserted and locked into the
port at both the switch and the connecting device.
Make sure that all cables are used correctly and
comply with the Ethernet specifications.
Check for a defective port, cable, or module by
testing them in an alternate environment where all
products are functioning.
Port connection is not working.Combined speed and activity
LED is off when the port is
connected to a device.
Break the loop by making sure that only one path
exists from any networked device to any other
networked device. After you connect to the switch
web management interface, you can configure the
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to prevent network
loops.
One possible cause is that a
broadcast storm occurred and
that a network loop (redundant
path) was created.
File transfer is slow or
performance is degraded.
Verify that the cabling is correct.
Make sure that all connectors are securely positioned
in the required ports. It is possible that equipment
was accidentally disconnected.
One or more devices are not
properly connected, or cabling
does not meet Ethernet
guidelines.
A segment or device is not
recognized as part of the
network.
Troubleshooting
31
8-Port, 12-Port, and 16-Port Gigabit Smart Managed Pro Switch
 Loading...
Loading...











