NI cDAQ-9178/9174 User Guide and Specifications 46 ni.com
measured must be at least twice the sample clock rate to ensure that a full period of the frequency to be
measured occurs between sample clocks.
• Low frequency measurements with one counter is a good method for many applications. However,
the accuracy of the measurement decreases as the frequency increases.
• High frequency measurements with two counters is accurate for high frequency signals. However,
the accuracy decreases as the frequency of the signal to measure decreases. At very low
frequencies, this method may be too inaccurate for your application. Another disadvantage of this
method is that it requires two counters (if you cannot provide an external signal of known width).
An advantage of high frequency measurements with two counters is that the measurement
completes in a known amount of time.
• Measuring a large range of frequencies with two counters measures high and low frequency signals
accurately. However, it requires two counters, and it has a variable sample time and variable
error % dependent on the input signal.
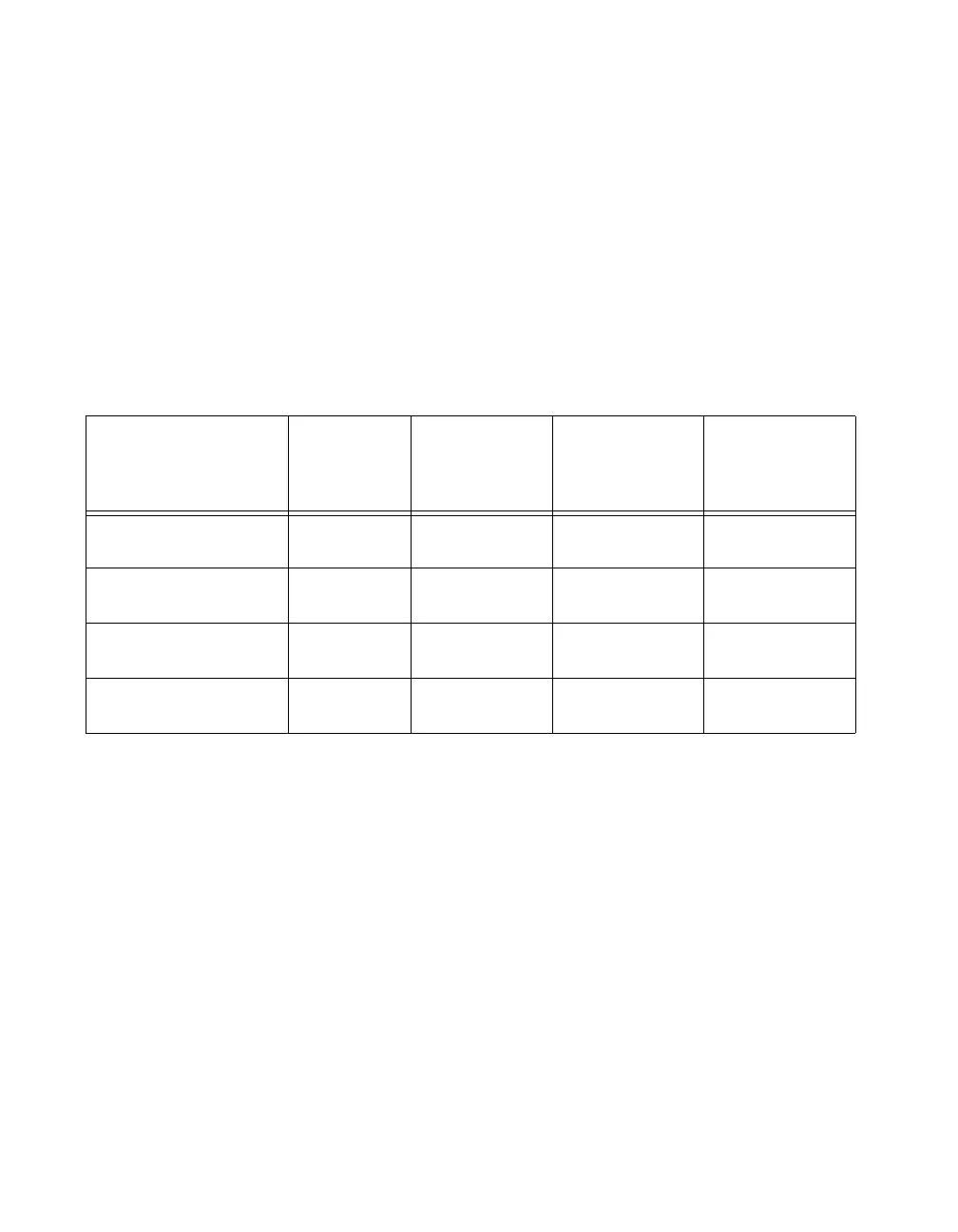
Table 8 summarizes some of the differences in methods of measuring frequency.
For information about connecting counter signals, refer to the Default Counter/Timer Routing section.
Period Measurement
In period measurements, the counter measures a period on its Gate input signal after the counter is
armed. You can configure the counter to measure the period between two rising edges or two falling
edges of the Gate input signal.
You can route an internal or external periodic clock signal (with a known period) to the Source input of
the counter. The counter counts the number of rising (or falling) edges occurring on the Source input
between the two active edges of the Gate signal.
You can calculate the period of the Gate input by multiplying the period of the Source signal by the
number of edges returned by the counter.
Period measurements return the inverse results of frequency measurements. Refer to the Frequency
Measurement section for more information.
Table 8. Frequency Measurement Method Comparison
Method
Number of
Counters
Used
Number of
Measurements
Returned
Measures High
Frequency
Signals
Accurately
Measures Low
Frequency
Signals
Accurately
Low frequency with
one counter
1 1 Poor Good
High frequency with
two counters
1 or 2 1 Good Poor
Large range of frequencies
with two counters
2 1 Good Good
Sample clocked
(averaged)
1 1 Good Good
 Loading...
Loading...