NI cDAQ-9178/9174 User Guide and Specifications 56 ni.com
Figure 51. Finite Implicit Buffered Pulse Train Generation
Continuous Buffered Implicit Pulse Train Generation
This function generates a continuous train of pulses with variable idle and active times. Instead of
generating a set number of data samples and stopping, a continuous generation continues until you stop
the operation. Each point you write generates a single pulse. All points are generated back to back to
create a user defined pulse train.
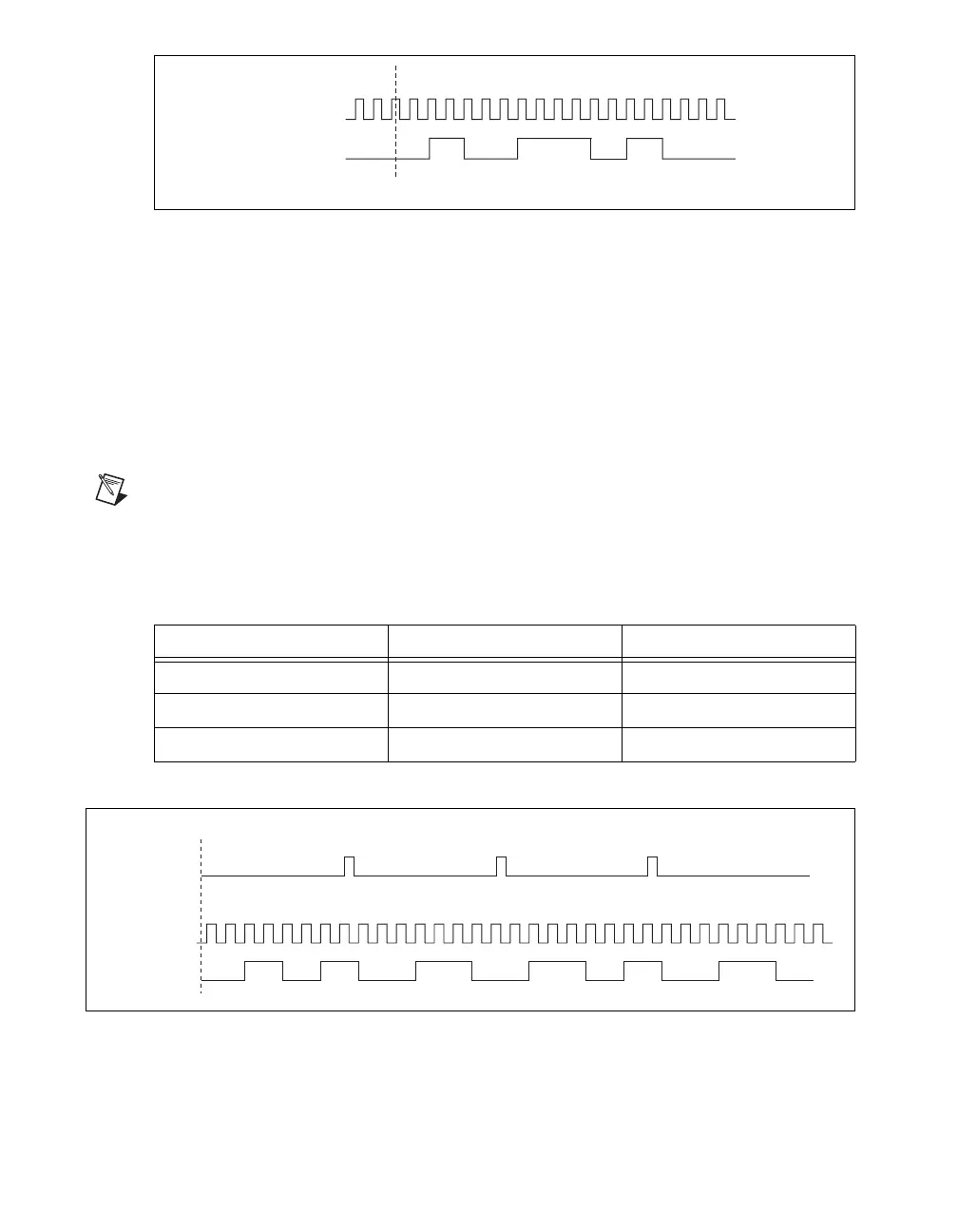
Finite Buffered Sample Clocked Pulse Train Generation
This function generates a predetermined number of pulse train updates. Each point you write defines
pulse specifications that are updated with each sample clock. When a sample clock occurs, the current
pulse (idle followed by active) finishes generation and the next pulse updates with the next sample
specifications.
Note When the last sample is generated, the pulse train continues to generate with these
specifications until the task is stopped.
Table 10 and Figure 52 detail a finite sample clocked generation of three samples where the pulse
specifications from the create channel are two ticks idle, two ticks active, and three ticks initial delay.
Figure 52. Finite Buffered Sample Clocked Pulse Train Generation
There are several different methods of continuous generation that control what data is written. These
methods are regeneration, FIFO regeneration, and non-regeneration modes.
Table 10. Finite Buffered Sample Clocked Pulse Train Generation
Sample Idle Ticks Active Ticks
1 3 3
2 2 2
3 3 3
SOURCE
OUT
Counter Armed
22 3 422
Source
Out
Counter Armed
Sample
Clock
Counter
Load Values
21010101 2102100 21021010 02102110
3 222 33332 332
 Loading...
Loading...