36
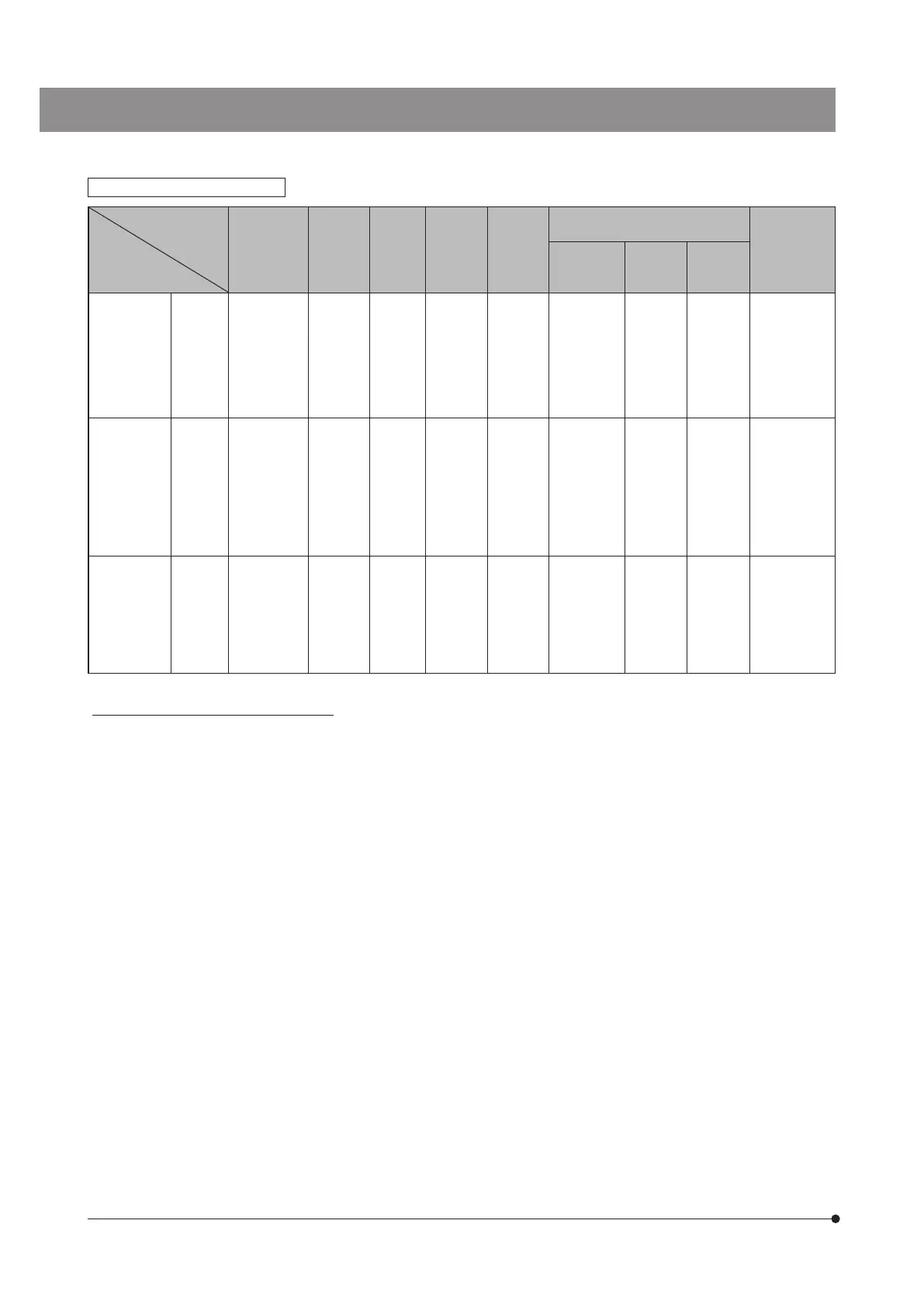
Basic information by objective
Optical performance
Objective
Notation
Magnification
Numerical
aperture
NA
Working
distance
(WD)
(mm)
Cover
glass
thickness
(mm)
Resolution
(µm)
WHB10x/WHB10x-H-2
(Field number: 20)
Notes
Total
magnification
Focal depth
(µm)
Actual field
of view
(mm)
Plan
Achromat
PLCN
4X
10X
20X
40X
100XO
0.10
0.25
0.40
0.65
1.25
27.8
8.0
1.2
0.6
0.13
-
-
0.17
0.17
-
3.36
1.34
0.84
0.52
0.27
40X
100X
200X
400X
1000X
175.0
28.0
9.27
3.04
0.69
5.0
2.0
1.1
0.5
0.2
Oil immersed
For
polarization
Plan
Achromat
Achromat
PLN (P)
4X 0.10 18.5 - 3.36 40X 180.0 5.5
ACHN
(P)
10X
20X
40X
100XO
0.25
0.40
0.65
1.25
6.0
3.0
0.45
0.13
-
0.17
0.17
0.17
1.34
0.84
0.52
0.27
100X
200X
400X
1000X
28.0
6.09
3.04
0.69
2.2
1.1
0.5
0.2
Oil immersed
For phase
contrast
Plan
Achromat
PLCN
(PH)
10X
20X
40X
100XO
0.25
0.4
0.65
1.25
10.6
1.2
0.6
0.15
-
0.17
0.17
-
1.34
0.84
0.52
0.27
100X
200X
400X
1000X
28.0
9.27
3.04
0.69
2.2
1.1
0.55
0.22
Oil immersed
Explanation of optical performance terms
Numerical aperture:
(NA)
The numerical aperture corresponds to F-number
* of the camera and is related to the resolution. The
resolution becomes higher when the numerical aperture becomes larger.
(
*
: F-number is a value obtained by dividing the focal distance of lens by the valid aperture diameter.
This is used as an index to show the brightness of the lens.)
Working distance:
(W.D.)
Distance between the top surface of the cover glass and the tip of the objective when the specimen
is in focus.
Resolution: The resolution is the ability of an objective to resolve adjacent two points in the image to the minimum
limit, which is expressed as the distance between two points on the specimen surface.
Field number:
(FN)
The field number is the diameter of the image viewed through eyepieces, indicated in millimeters.
Total magnification: Magnification of objective x Magnification of eyepiece
Focal depth:
(Object side)
The focal depth is the depth range of the specimen focused. The depth becomes deeper by narrowing
down the aperture diaphragm and it becomes shallower by increasing the aperture diaphragm of the
objective.
Actual field of view: The actual field of view is a diameter of the field of view, expressed as the size (mm) on the specimen
surface.
 Loading...
Loading...