92
Shifting Input Values Section 4-1
Method for a 2-point
Shift
Use a 2-point input shift if you want to increase the accuracy of the readout
values across the range of the Sensor.
1,2,3... 1. Shift the Controller readout at two points, near room temperature and near
the value at which the temperature of the control target is to be controlled.
For this reason, check the thermometer temperature (B) and Controller
readout (A) with the thermometer temperature near room temperature and
near the set point.
2.
• Y1 is the Controller readout at room temperature before shifting and
X1 is the Controller readout at room temperature after shifting.
• Y2 is the Controller readout at the set temperature before shifting and
X2 is the Controller readout at the set temperature after shifting.
• Set the upper-limit temperature input shift and the lower-limit temper-
ature input shift using the following formulas based on the tempera-
tures before shifting (Y1 and Y2), the temperatures after shifting (X1
and X2), the set temperature upper limit (YH), and the set temperature
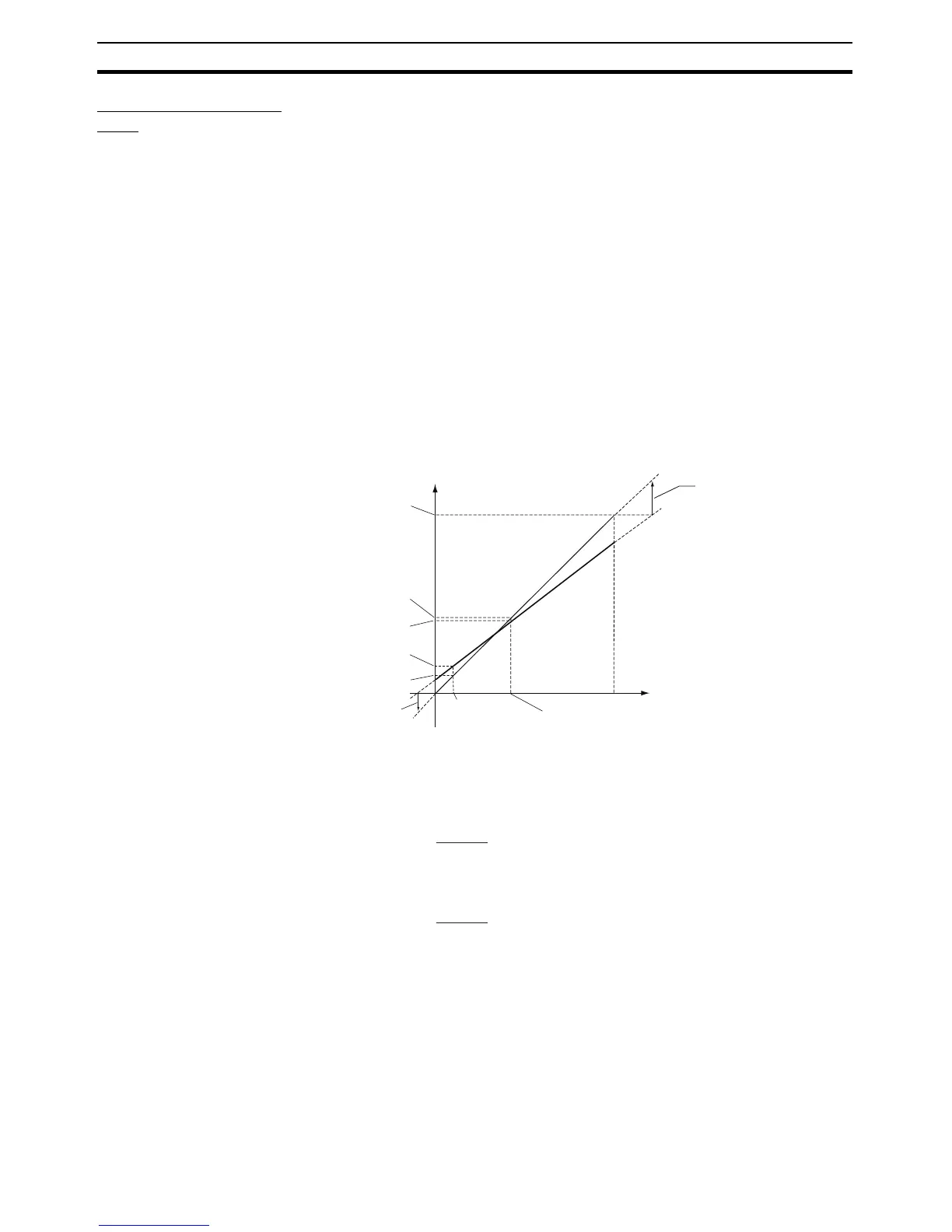
lower limit (YL). The shift is illustrated in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Illustration of 2-Point Shift
a. Lower-limit temperature input shift value
b. Upper-limit temperature input shift value
3. After setting the calculated values to insl and insh, check the Controller
readout (A) and thermometer temperature (B).
4. Here, offsets are set at two points, near room temperature and near the set
point. To improve accuracy within the measurement temperature range,
another point in the measurement temperature range other than the set
point should be set instead of room temperature.
0
Controller readout (A)
YH: Set temperature upper limit
(e.g., 260°C)
X2: Controller readout after shifting
(e.g., 110°C)
Y2: Controller readout before shifting
(e.g., 105°C)
Y1: Controller readout before shifting
(e.g., 40°C)
X1: Controller readout after shifting
(e.g., 25°C)
After shifting
Upper-limit temperature input
shift value (e.g., 52.7°C) insh
Before shifting
X1: Room temper-
ature (e.g., 25°C)
Control target temperature (B)
Lower-limit temperature input
shift value (e.g., −27.3°C) insl
YL: Set temperature lower limit
(e.g., 0°C)
X2: Near set point (e.g., 110°C)
260°C
insl =
YL − Y1
Y2 − Y1
× {(X2 − Y2) − (X1 − Y1)} + (X1 − Y1)
insh =
YH − Y1
Y2 − Y1
× {(X2 − Y2) − (X1 − Y1)} + (X1 − Y1)
 Loading...
Loading...