Parker Hannifin
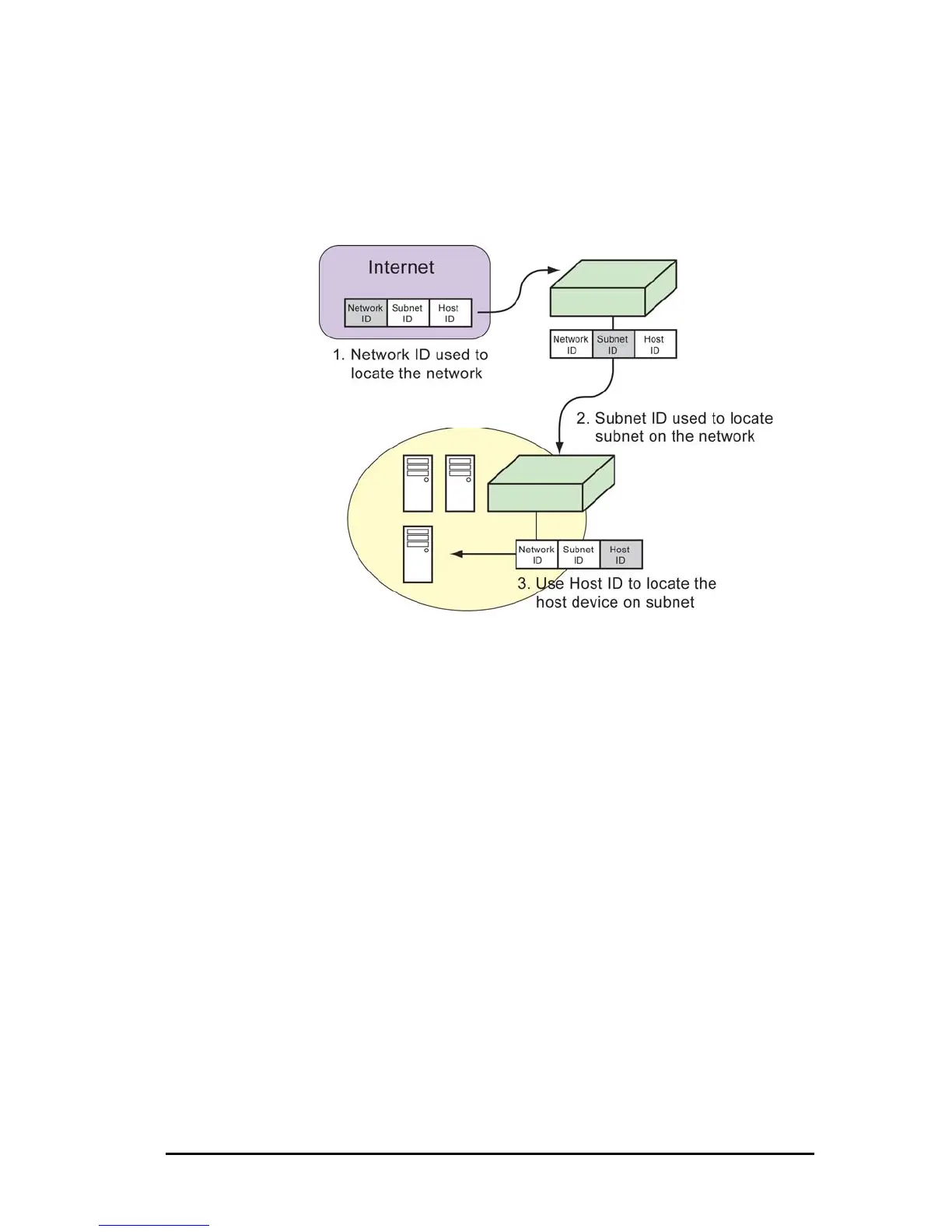
To provide another level of addressing, some of the host ID is
borrowed to create a subnet ID. The subnet ID allows you to
logically group devices together (often related to a specific
network segment). Once data arrives at the network, the subnet
ID allows routers or host devices to locate the appropriate
network segment, and then the host.
Suppose you have a class C network, comprised of 6 computers.
All share the same network ID 192.168. but are divided into two
subnets. Three computers use 192.168.10., where 10. is the subnet
ID; the remaining three use 192.168.5., where 5. is the subnet ID.
Subnet Masks
A subnet mask determines how many bits after the network ID
are used for the subnet ID. As the subnet ID increases, the
number of host IDs available for that network decrease. Similarly,
a smaller subnet ID allows you to increase the number of hosts on
the network. For simplicity, this discussion only looks at complete
octets in dotted decimal format, and does not explore
converting partial masks from binary to decimal.
170 Programmer’s Guide

 Loading...
Loading...











