Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data Sheets
EN 63LC8.1E LB 9.
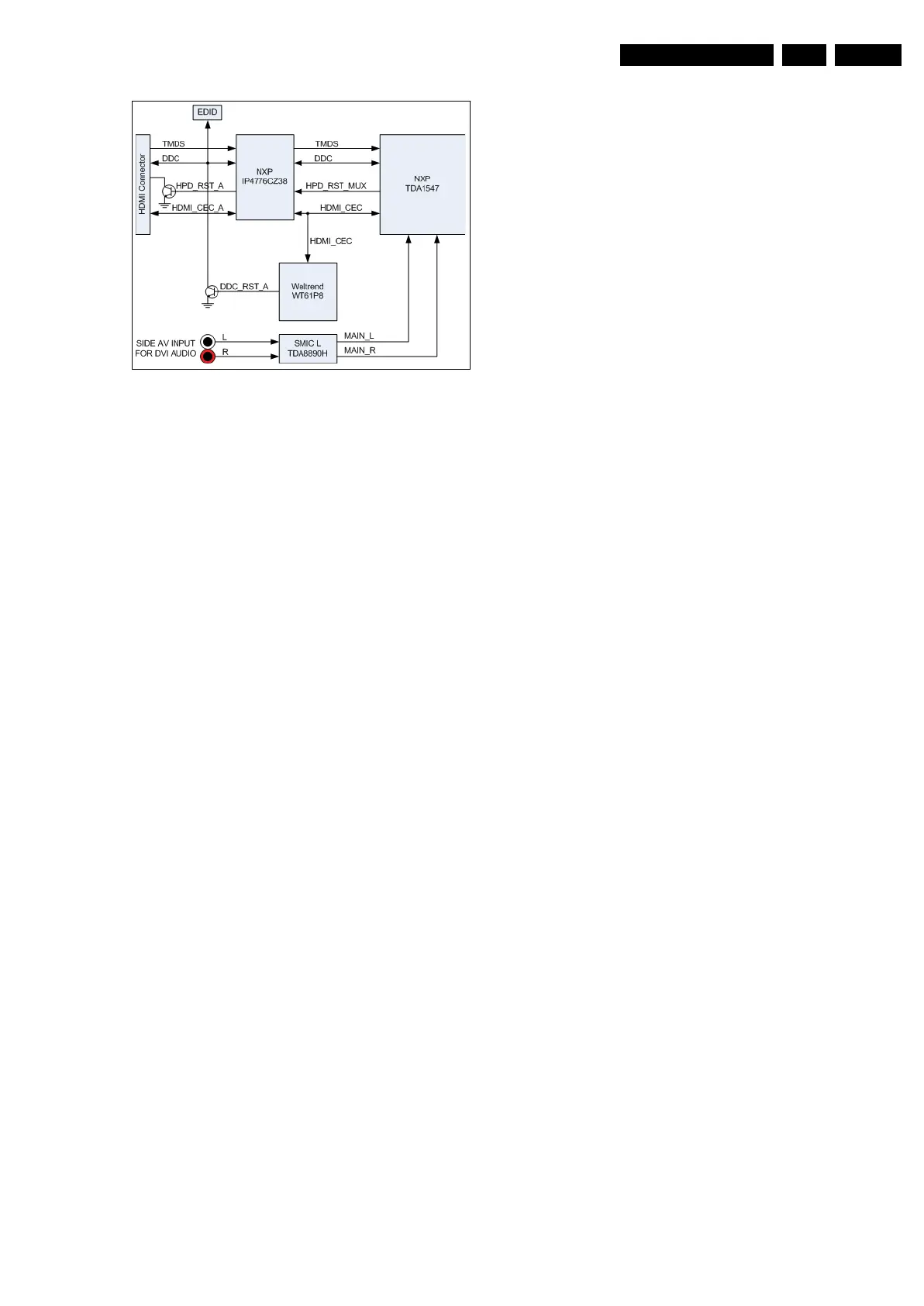
Figure 9-14 HDMI implementation
The description of the lines is as follows:
• TMDS (Time Minimized Differential Signal): the actual
HDMI signal
• DDC (Digital Data Channel): the bus used by the source to
read EDID data in the EEPROM and HDCP
authentification
• HPD_RST_A (Hotplug Detect Reset signal): used to pull-
down the HPD signal level at the connector when switching
in/out of HDMI mode; the duration of the pulse is around
500-550 ms
• DDC_RST_A has the same behaviour as the HPD_RST_A
signal. It is used to pull-down the I
2
C clock line to prevent
some problems with certain video graphic cards
• HDMI_CEC_A is the Consumer Electronic Control remote
control signal bus.
It should be noted that in this chassis the HDCP-key is
embedded in the main processor (no need for a separate
Service-SSB).
9.7 Abbreviation List
1080i 1080 visible lines, interlaced
1080p 1080 visible lines, progressive scan
2CS 2 Carrier Sound
2DNR Spatial (2D) Noise Reduction
3DNR Temporal (3D) Noise Reduction
480i 480 visible lines, interlaced
480p 480 visible lines, progressive scan
AARA Automatic Aspect Ratio Adaptation:
algorithm that adapts aspect ratio to
remove horizontal black bars; keeping
up the original aspect ratio
ACI Automatic Channel Installation:
algorithm that installs TV channels
directly from a cable network by
means of a predefined TXT page
ADC analogue to Digital Converter
AFC Automatic Frequency Control: control
signal used to tune to the correct
frequency
AGC Automatic Gain Control: algorithm that
controls the video input of the feature
box
AM Amplitude Modulation
AUO Acer Unipack Optronics
AP Asia Pacific
AR Aspect Ratio: 4 by 3 or 16 by 9
ASD Automatic Standard Detection
AV Audio Video
B/G Monochrome TV system. Sound
carrier distance is 5.5 MHz
BTSC Broadcast Television System
Committee
CAM Conditional Access Module
CBA Circuit Board Assembly (or PWB)
CEC Consumer Electronics Control bus;
remote control bus on HDMI
connections
CI Common Interface; E.g PCMCIA slot
for a CAM in a set top box
CL Constant Level: audio output to
connect with an external amplifier
CLUT Colour Look Up Table
ComPair Computer aided rePair
COFDM Coded Orthogonal Frequency Division
Multiplexing; A multiplexing technique
that distributes the data to be
transmitted over many carriers
CSM Customer Service Mode
CVBS Composite Video Blanking and
Synchronisation
CVBS-MON CVBS monitor signal
CVBS-TER-OUT CVBS terrestrial out
CVI Component Video Input
DAC Digital to analogue Converter
DBE Dynamic Bass Enhancement: extra
low frequency amplification
DDC Display Data Channel; is a part of the
"Plug and Play" feature
DFU Directions For Use: owner's manual
DNR Dynamic Noise Reduction
DRAM Dynamic RAM
DSP Digital Signal Processing
DST Dealer Service Tool: special
(European) remote control designed
for service technicians
DTS Digital Theatre Sound
DVB(T) Digital Video Broadcast; An MPEG2
based standard for transmitting digital
audio and video. T= Terrestrial
DVD Digital Versatile Disc
DVI Digital Visual Interface
DW Double Window
ED Enhanced Definition: 480p, 576p
EDID Extended Display Identification Data
(VESA standard)
EEPROM Electrically Erasable and
Programmable Read Only Memory
EMC Electro Magnetic Compatibility
EU EUrope
EXT EXTernal (source), entering the set by
SCART or by cinches (jacks)
FBL Fast Blanking: DC signal
accompanying RGB signals
FBL-TXT Fast Blanking Teletext
FET Field Effect Transistor
FLASH FLASH memory
FM Field Memory / Frequency Modulation
FMR FM Radio
FRC Frame Rate Converter
FTV Flat TeleVision
H H_sync to the module
HD High Definition: 720p, 1080i, 1080p
HDCP High-bandwidth Digital Content
Protection; A "key" encoded into the
HDMI/DVI signal that prevents video
data piracy. If a source is HDCP coded
and connected via HDMI/DVI without
the proper HDCP decoding, the
picture is put into a "snow vision"
mode or changed to a low resolution.
For normal content distribution, the
source and the display device must be
enabled for HDCP "software key"
decoding
I_18170_049.eps
310708
 Loading...
Loading...