86 Rockwell Automation Publication 750-RM100A-EN-P - August 2019
Chapter 9 Reference Motion Planners
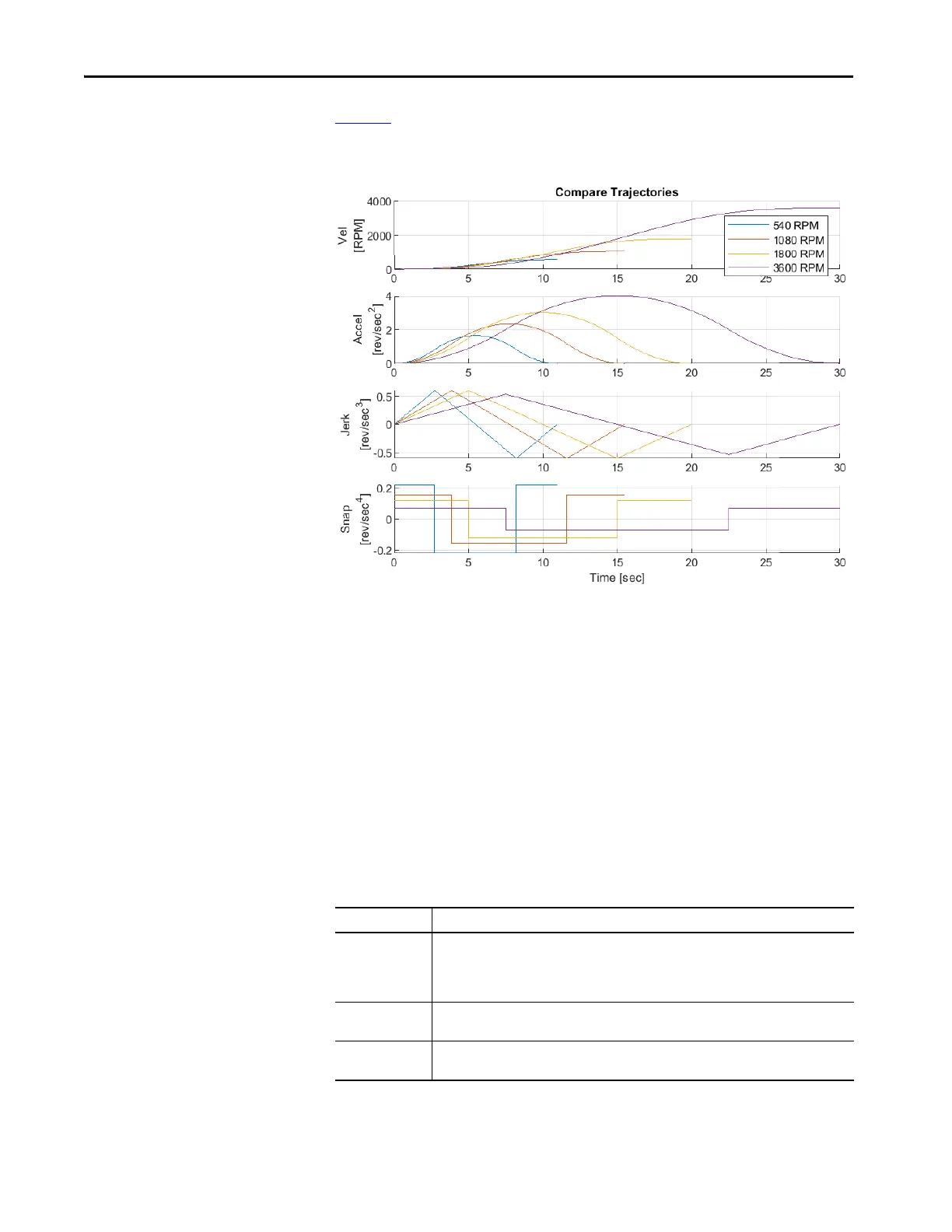
Figure 30 shows different target velocities for a LinScurve velocity move with a 10 second
acceleration time.
Figure 30 - Rate Based Velocity Moves with Different Distances
Note the following relationships:
• Acceleration and deceleration times are calculated based on a constant
maximum jerk (acceleration rate).
• Rate based move times are good when continually indexing to various
target velocities.
Time Based Move
When 10/11:933 [Ref Time Base] = ‘Time’, you can enter acceleration and deceleration
times directly using parameters in the following table. However, this only affects
commands that are generated when 10/11:931 [Ref Move Type] = ‘SineSquared’, ‘Poly5’,
or ‘Cubic’. Rate based calculations are always applied when 10/11:931 [Ref Move Type]
= ‘LinScurve’.
Table 32 - Velocity Reference Time Based Move Parameters
Parameter Description
10/11:933
[Ref Time Base]
Select how acceleration and deceleration times are calculated for position and velocity reference
commands.
‘Time’ (1) – 10/11:934 [Ref Accel Time] and P935 [Ref Decel Time] are applied directly as
acceleration and deceleration times.
10/11:934
[Ref Accel Time]
Enter the acceleration time that is directly applied to position and velocity reference commands
when 10/11:933 [Ref Time Base] = ‘Time’.
10/11:935
[Ref Decel Time]
Enter the deceleration time that is directly applied to position and velocity reference commands
when 10/11:933 [Ref Time Base] = ‘Time’.

 Loading...
Loading...
















