Section 2 - Introduction to CCD Cameras
Page 26
transports the charge packets in a serial manner to an on-chip amplifier. The
final operating step, charge detection, is when individual charge packets are
converted to an output voltage. The voltage for each pixel can be amplified off-
chip and digitally encoded and stored in a computer to be reconstructed and
displayed on a television monitor."
1
X=1 X=M
Y=1
Y=N
Output
Readout Register
Amplifier
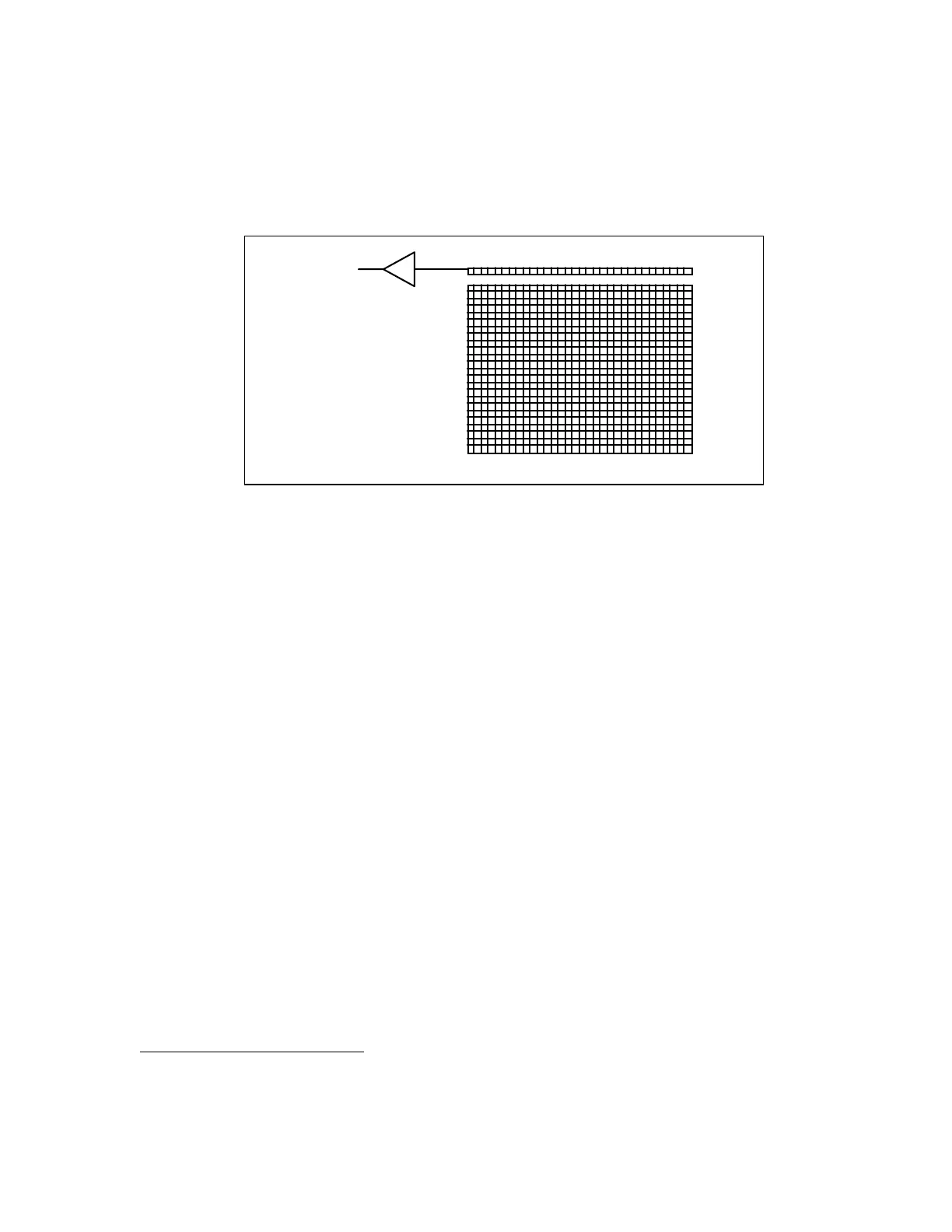
Figure 2.1 - CCD Structure
2.2.1. Full Frame and Frame Transfer / Interline CCDs
In the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE and ST-10XME, the CCD is read out electronically by
shifting each row of pixels into a readout register at the Y=0 position of the CCD (shown in
Figure 2.1), and then shifting the row out through an amplifier at the X=0 position. The entire
array shifts up one row when a row is shifted into the readout register, and a blank row is
inserted at the bottom. The electromechanical shutter built into the camera covers the CCD
during the readout to prevent streaking of the image. Without a shutter the image would be
streaked due to the fact that the pixels continue to collect light as they are being shifted out
towards the readout register. CCDs with a single active area are called Full Frame CCDs.
For reference, the ST-5C, ST-237A, STV and guiding CCDs in the ST-X series of cameras
use a different type of CCD, which is known as a Frame Transfer CCD. In these devices all
active pixels are shifted very quickly into a pixel array screened from the light by a metal layer,
and then read out. This makes it possible to take virtually streak-free images without a shutter.
This feature is typically called an electronic shutter. The interline CCD used in the ST-2000XM is
similar to a frame transfer except that the protected pixels are interlaced with the active pixels.
2.3. Camera Hardware Architecture
This section describes the ST-7XE, ST-8XE, ST-9XE, ST-10XE, ST-10XME and ST-2000XM CCD
cameras from a systems standpoint. It describes the elements that comprise a CCD camera and
the functions they provide. Please refer to Figure 2.2 below as you read through this section.
1
"History and Advancements of Large Area Array Scientific CCD Imagers", James Janesick, Tom
Elliott. Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, CCD Advanced Development
Group.

 Loading...
Loading...