VRRP
Entry-ID: 109798556, V1.0, 09/2021
© Siemens AG
2021 All rights reserved
6.3 Tracking process
Using the tracking process, you can monitor the interfaces and thus modify the
VRRP priority. The tracking methods available to you are interface tracking, VRID
tracking and address monitoring.
6.3.1 Interface tracking
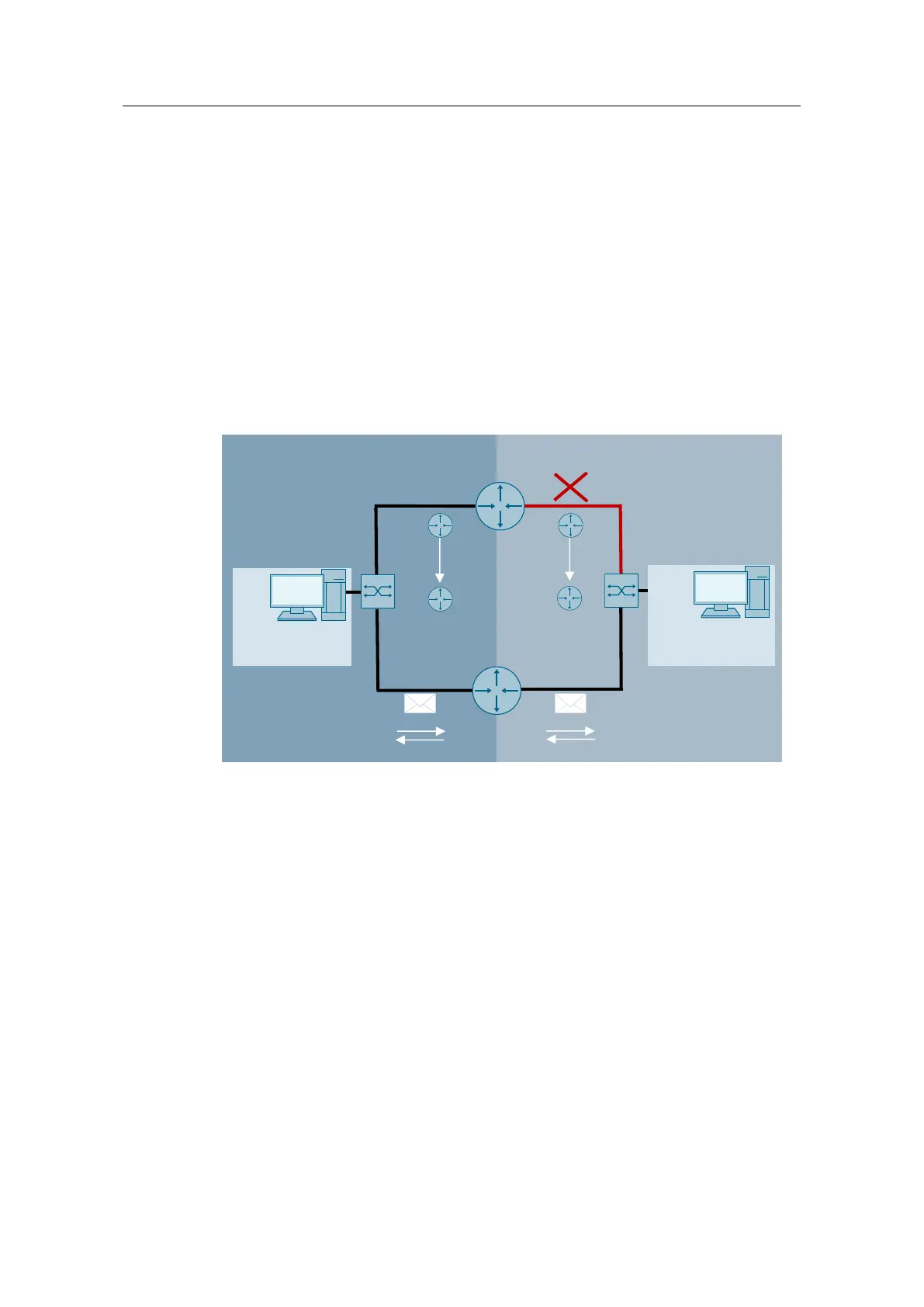
With interface tracking, the VRRP priorities of the router can be modified so that
the switchover happens synchronously. In this case, a failure of an interface will
cause the VRRP priority of the remaining VRRP instances to be decremented by a
fixed value, thus triggering a switchover.
Figure 6-4
Subnet A
Router 1
PC 1
PC 2
Router 2
Subnet B
Virtual router
Shared IP:
192.168.0.1
Virtual Router ID
(VRID): 1
192.168.0.100
255.255.2550
Router: 192.168.0.1
192.168.1.100
255.255.255.0
Router: 192.168.1.1
Virtual router
Shared IP:
192.168.1.1
Virtual Router ID
(VRID): 2
Master → Backup
Master → Backup
Backup → Master
Backup → Master
1. Failure
Connection
2. Interface
Tracking
ping ping
6.3.2 VRID tracking
If VRID tracking is enabled, all interfaces of a VRID will be monitored. When the
link of an interface changes from "up" to "down", the priority of all VRRP interfaces
with the same VRID will be reduced to the value "0". When the link of an interface
changes from "down" back to "up", the original priority of the VRRP interface is
restored.
6.3.3 Address monitoring
Within the specified time period, the router sends a ping request to each of the
configured IP addresses. If it does not receive an answer within a specific time
period, the VRRP priority of the corresponding interface will be reduced.

 Loading...
Loading...











