Cycle and reaction times
5.5 Interrupt response time
CPU 31xC and CPU 31x, Technical Data
Manual, 01/2006 Edition, A5E00105475-06
5-21
Calculation
The formula below show how you can calculate the minimum and maximum interrupt
response times.
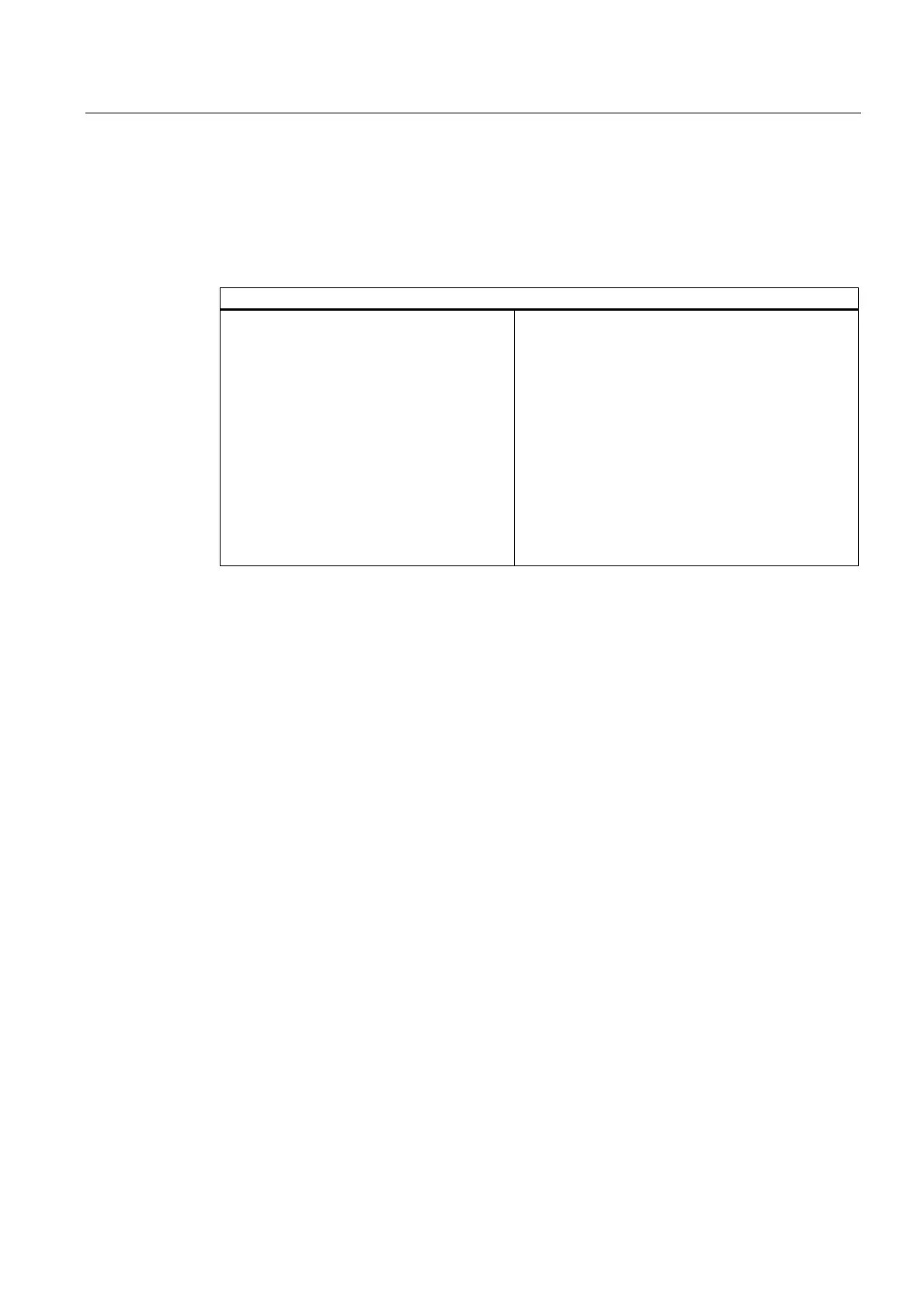
Table 5-14 Process and diagnostic interrupt response times
Calculation of the minimum and maximum interrupt reaction time
Minimum interrupt reaction time of the CPU
+ Minimum interrupt reaction time of the
signal modules
+ PROFINET IO update time (only if
PROFINET IO is used.)
+ DP cycle time on PROFIBUS DP (only if
PROFIBUS DP is used.)
= Quickest interrupt reaction time
Maximum interrupt reaction time of the CPU
+ Maximum interrupt reaction time of the signal
modules
+ 2 x PROFINET IO update time (only if PROFINET
IO is used.)
+ 2 x DP cycle time on PROFIBUS DP (only if
PROFIBUS DP is used.)
The maximum interrupt reaction time is longer when
the communication functions are active. The extra
time is calculated using the following formula:
tv: 200 μs + 1000 μs x n%
n = Setting of the cycle load as a result of
communication
Signal modules
The process interrupt response time of signal modules is determined by the following factors:
• Digital input modules
Process interrupt response time = internal interrupt preparation time + input delay
You will find these times in the data sheet for the respective digital input module.
• Analog input modules
Process interrupt response time = internal interrupt preparation time + input delay
The internal interrupt preparation time for analog input modules can be neglected. The
conversion times can be found in the data sheet for the individual analog input modules.
The diagnostic interrupt response time of signal modules is equivalent to the period that
expires between the time a signal module detects a diagnostic event and the time this signal
module triggers the diagnostic interrupt. This short time can be neglected.
Process interrupt processing
Process interrupt processing begins after process interrupt OB40 is called. Higher-priority
interrupts stop process interrupt processing. Direct I/O access is executed during runtime of
the instruction. After process interrupt processing has terminated, cyclic program execution
continues or further interrupt OBs of equal or lower priority are called and processed.
See also
Overview (Page 5-1)

 Loading...
Loading...






















