Structure of a CPU 41x
2.2 Monitoring functions of the CPU
S7-400 Automation System, CPU Specifications
2-6 Manual, 10/2006, 6ES7498-8AA04-8BA0
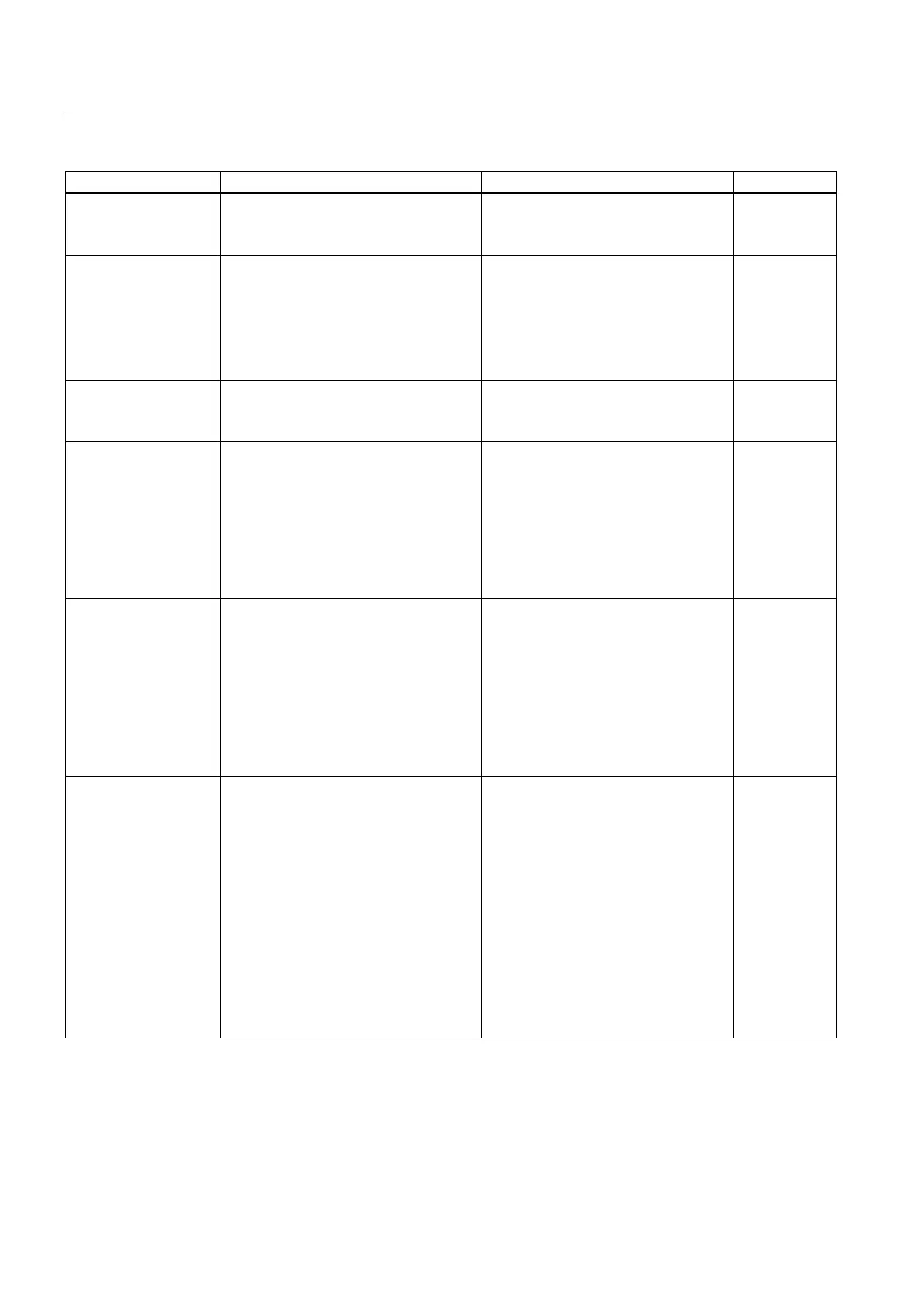
Type of error Cause of error Response of the operating system Fault LED
Diagnostic interrupt
(entering and exiting
state)
An I/O module with interrupt capability
reports a diagnostic interrupt
OB 82 call
If the OB is not loaded: The CPU
changes to STOP
EXTF
Remove/insert module
interrupt
(entering and exiting
state)
Removal or insertion of an SM and
insertion of the wrong module type. The
LED EXTF does not light up if only one
SM is installed and then removed while
the CPU is in STOP (default setting).
The LED lights up briefly when the SM
is inserted again.
OB 83 call
If the OB is not loaded: The CPU
changes to STOP
EXTF
CPU Hardware
error
(entering state)
• A memory error was
detected and
eliminated
OB 84 call
If the OB is not loaded: The CPU
remains in RUN.
INTF
Priority class error
(Only entering state,
depending on OB85
mode)
• A priority class is
called, but the
corresponding OB is
not present.
• In the case of an SFB
call: The instance DB
is missing or bad.
• Error while updating
the process image
OB 85 call
If the OB is not loaded: The CPU
changes to STOP
INTF
EXTF
Rack / station failure
(entering and exiting
state)
• Power failure on an
expansion module
• PROFINET DP chain
failure
• PROFINET IO
subsystem failure
• Failure of a coupling
chain: missing or
defective IM, cable
break)
OB 86 call
If the OB is not loaded: The CPU
changes to STOP
EXTF
Communication error
(entering state)
• Unable to enter
status information in
the DB (shared data
communication)
• Incorrect message
frame (shared data
communication)
• Incorrect message
length (shared data
communication)
• Error in the structure
of the shared data
frame (shared data
communication)
• DB access error
OB 87 call INTF

 Loading...
Loading...




















