Structure of a CPU 41x
2.2 Monitoring functions of the CPU
S7-400 Automation System, CPU Specifications
Manual, 10/2006, 6ES7498-8AA04-8BA0
2-7
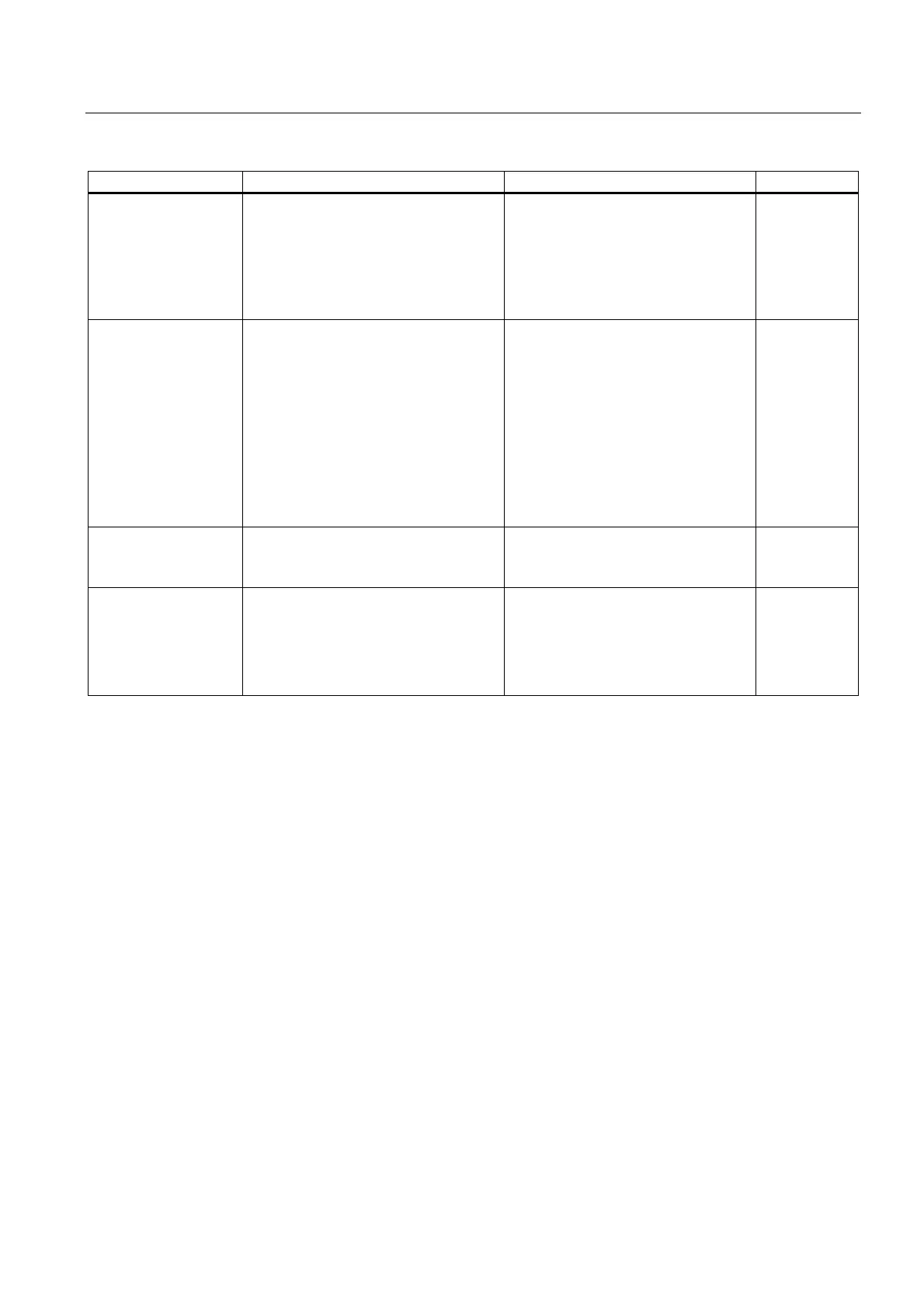
Type of error Cause of error Response of the operating system Fault LED
Execution abort
(entering state)
• Synchronous error
nesting depth
exceeded
• Too many nested
block calls (B stack)
• Error when allocating
local data
OB 88 call
If the OB is not loaded: The CPU
changes to STOP
INTF
Programming error
(entering state)
Errors in the user program
• BCD conversion error
• Range length error
• Range error
• Alignment error
• Write error
• Timer number error
• Counter number error
• Block number error
• Block not loaded
OB 121 call
If the OB is not loaded: The CPU
changes to STOP
INTF
Code error
(entering state)
Error in the compiled user program (for
example, illegal OP code or a jump
beyond block end)
The CPU changes to STOP
Restart or CPU memory reset
required.
INTF
Loss of the clock
signal
(entering state)
When using isochronous mode: Clock
pulses were lost either because OB61
... 64 was not started due to higher
priorities, or because additional
asynchronous bus loads suppressed the
bus clock pulses.
OB 80 call
If the OB is not loaded: The CPU
changes to STOP
Call of OB 61..64 at the next pulse.
INTF
Further test and information functions are available in each CPU and you can invoke these in
STEP 7.

 Loading...
Loading...




















