S7-400 cycle and response times
19.8 Interrupt response time
S7-400H
System Manual, 03/2012, A5E00267695-11
379
19.8 Interrupt response time
Definition of interrupt response time
The interrupt response time is the time from the first occurrence of an interrupt signal to the
call of the first instruction in the interrupt OB.
General rule: Higher priority interrupts are handled first. This means the interrupt response
time is increased by the program execution time of the higher-priority interrupt OBs, and by
previous interrupt OBs of the same priority which have not yet been processed (queue).
Note that any update of the standby CPU extends the interrupt response time.
Calculating the interrupt response time
Minimum interrupt response time of the CPU
+ minimum interrupt response time of the
signal modules
+ PROFIBUS DP cycle time on PROFINET
= Shortest interrupt response time
Minimum interrupt response time of the CPU
+ maximum interrupt response time of the
signal modules
+ 2 * cycle time on PROFIBUS DP or PROFINET
= Longest interrupt response time
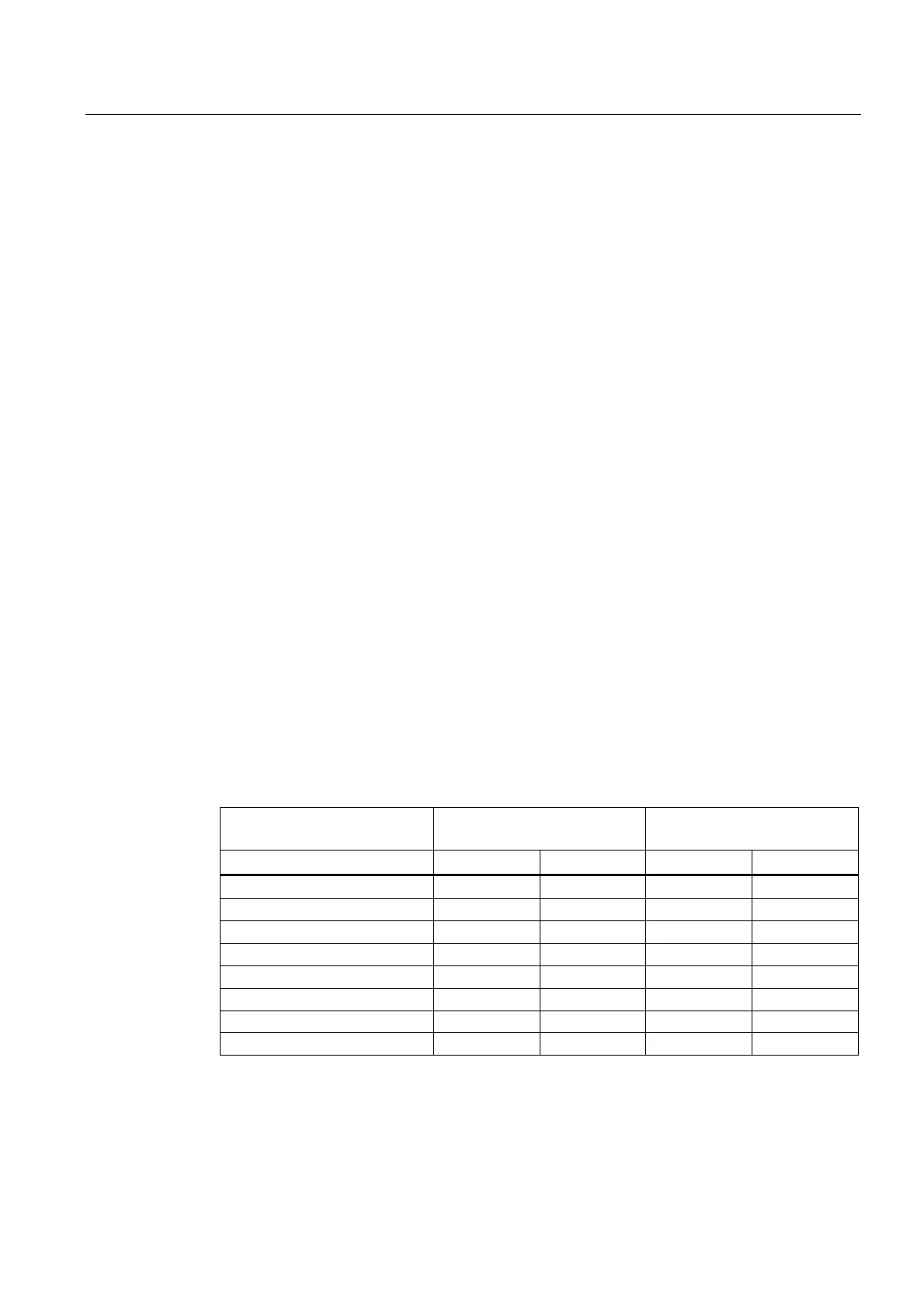
Process and diagnostic interrupt response times of the CPUs
Table 19- 14 Process and interrupt response times; maximum interrupt response time without
communication
CPU Hardware interrupt response
times
Diagnostic interrupt response
times
min. max. min. max.
412-5H stand-alone mode 190 µs 370 µs 200 µs 390 µs
412–5H redundant 370 µs 850 µs 410 µs 690 µs
414–5H stand-alone mode 140 µs 200 µs 150 µs 330 µs
414–5H redundant 330 µs 620 µs 290 µs 490 µs
416–5H stand-alone mode 90 µs 140 µs 90 µs 200 µs
416–5H redundant 240 µs 500 µs 200 µs 400 µs
417–5H stand-alone mode 80 µs 90 µs 80 µs 90 µs
417–5H redundant 160 µs 310 µs 140 µs 250 µs

 Loading...
Loading...











