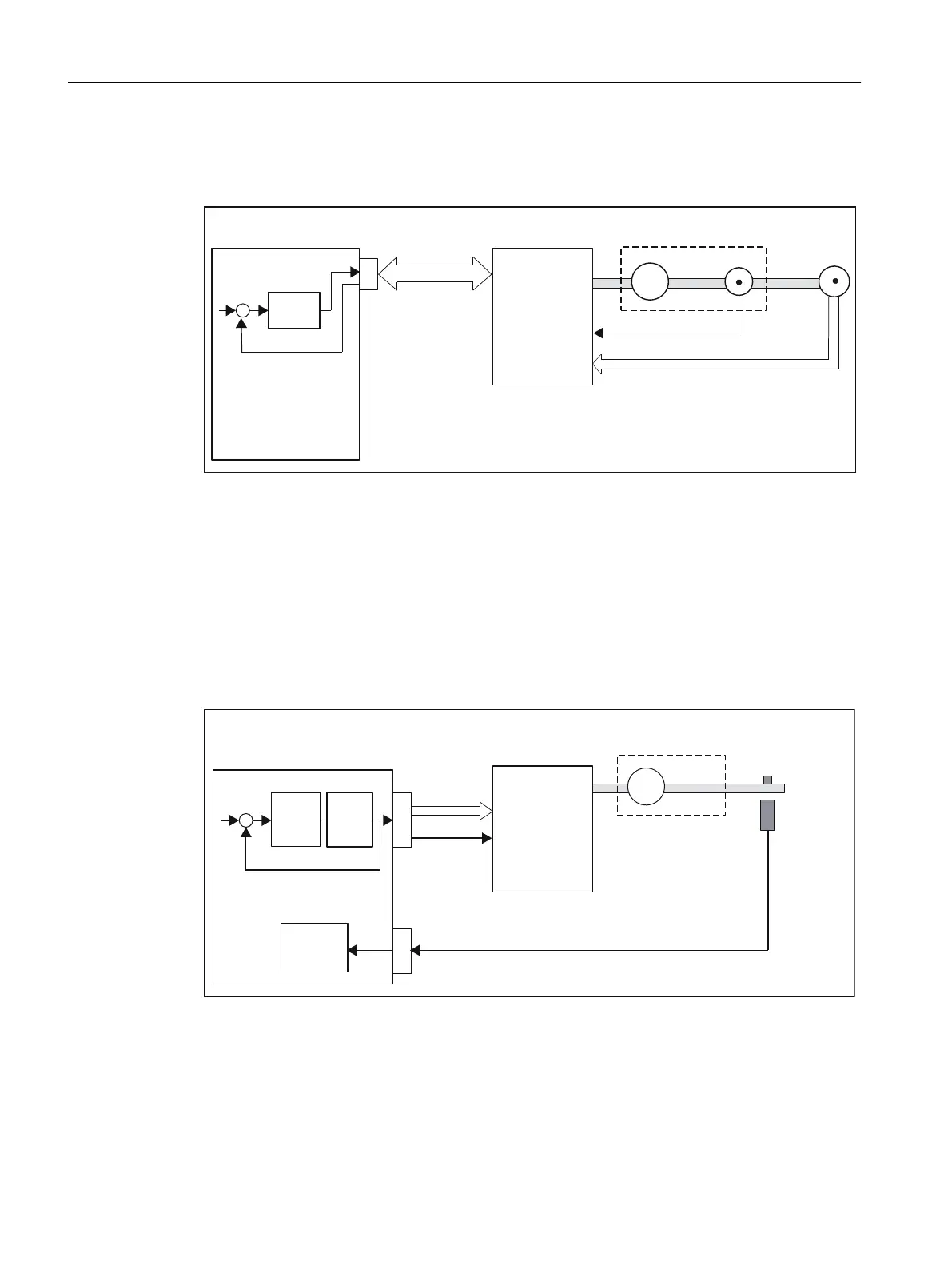
Position-controlled motion control for servo axes (PROFIBUS DP)
SIMOTION C enables position-controlled motion control of axes via PROFIBUS DP.
3RVLWLRQ
FRQWUROOHU
6SHHGVHWSRLQW
3RZHUXQLW
&XUUHQW
FRQWUROOHU
6SHHG
FRQWUROOHU
6HUYRPRWRU
$FWXDOVSHHGYDOXH
(QFRGHU
$FWXDOSRVLWLRQYDOXH]HURPDUN
&RQYHUWHU
$FWXDOSRVLWLRQ
YDOXH
352),%86'3
0
a
;
&&&31
Figure 2-6 Servo system with converter, for example SIMODRIVE 611 Universal
Stepper motor control (C230-2, C240)
In addition to the analog setpoint outputs, the C230-2/C240 has pulse outputs for up to four
stepper motor axes. The stepper motor is controlled by means of cycle clocks, the number of
which determines the position and the frequency of which determines the rotational speed
(velocity). The actual position value is not measured during controlled operation; the position
controller takes the number of pulses output (position setpoint) as the actual value. With this
type of control circuit, the motor cannot lose any steps in order to enable exact positioning.
3RVLWLRQ
FRQWUROOHU
&\FOHFORFN
GLUHFWLRQ
UHOHDVH
&RQWURO
3RZHUXQLW
60
3XOVH
HQFRGHU
5LQJFRXQWHU
3KDVHFXUUHQW
FRQWUROOHU
([WHUQDO
]HURSXOVH
5RWDWLRQ
PRQLWRULQJ
&&
;
;
%%
6,0267(3
Figure 2-7 Controlled stepper motor system with control circuit
Description
2.3 The fundamentals of motion control
SIMOTION C
24 Operating Instructions, 11/2016, A5E33441428B
 Loading...
Loading...











