- 8 -
2. Operational Principles
The MPC Series employs Tanaka Scientific's unique air pressure system (certified as U.S. standard
ASTM D 6749) to detect pour points (solidification points). Air pressure is applied to the surface of a
specimen, with subsequent motion of the sample surface measured to detect sample flow.
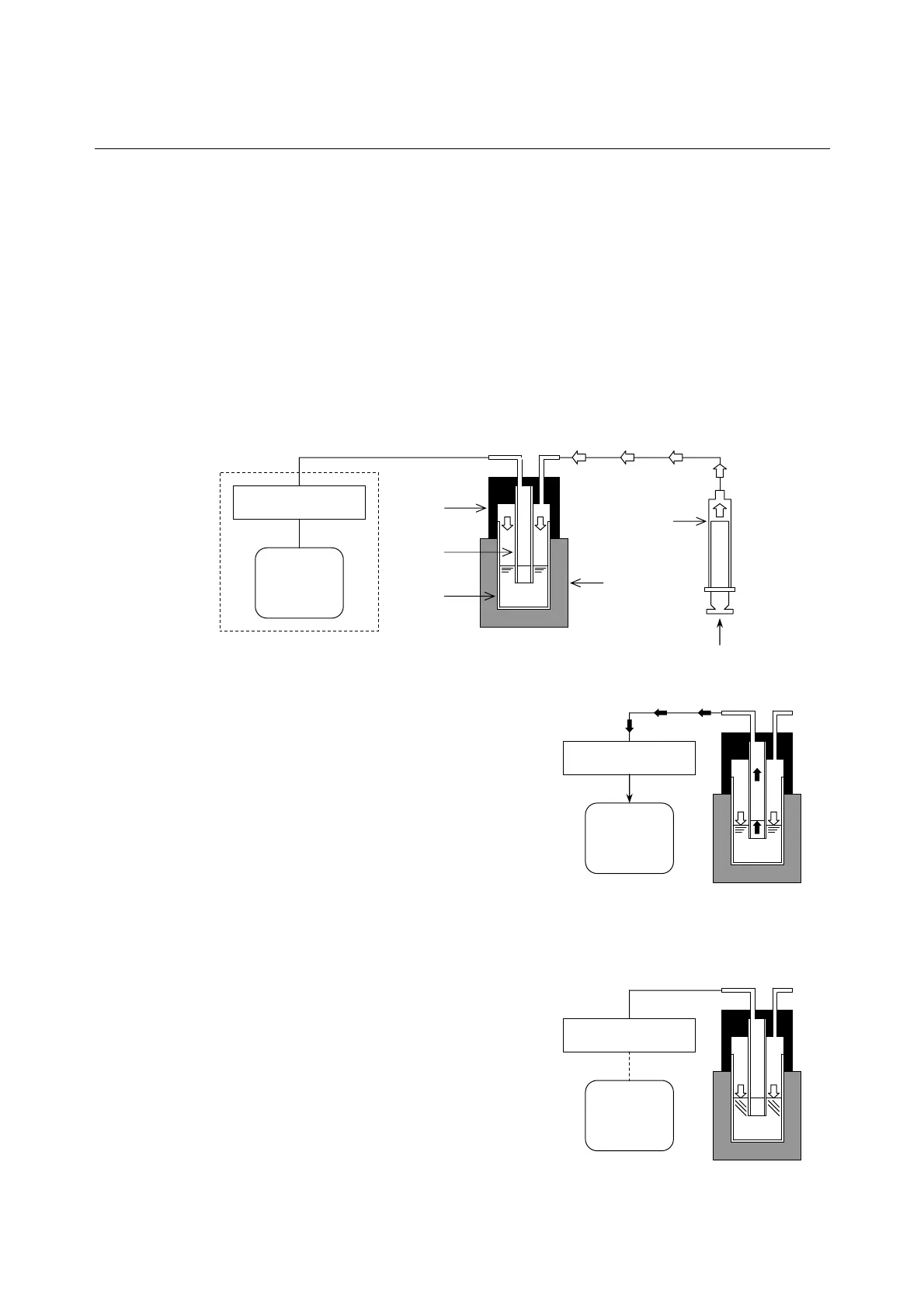
[System Outline]
The specimen chamber and specimen surface are divided into inner and outer regions by the pressure
conducting tube. Air pressure is applied to the specimen by a pressurizing syringe connected to the
outer region, creating a pressure differential between the inner and outer surfaces of the sample. Two
outcomes are then possible.
1. Specimen flow
The pressure differential causes the specimen to flow,
with the surface level inside the pressure conducting
tube rising (principle of the U-tube), causing a change in
pressure that is detected by the pressure sensor inside.
Upon a pre-determined pressure change, the pressure
switch is activated, indicating to the instrument that the
specimen is still flowing.
<Flow detected ⇒ Test continues>
2. No specimen flow
When the specimen is not flowing, the specimen surface
levels do not change despite the pressure differential.
Thus, the pressure inside the pressure conducting tube
remains unchanged and the pressure switch is not
activated. Specimen flow is assumed to have stopped if
the pressure switch is not activated within five seconds.
<<Non-Flow (solid) detected ⇒ Test completes>
ON
Pressure rise detected
Pressure
conducting
tube
Specimen
Cup
Pressurizing
Syringe
Detector
Head
Bath
Specimen
Pressure
Switch
Pressure sensor
OFF
No pressure rise
 Loading...
Loading...