Theory of Operation—2465B/2467B Service
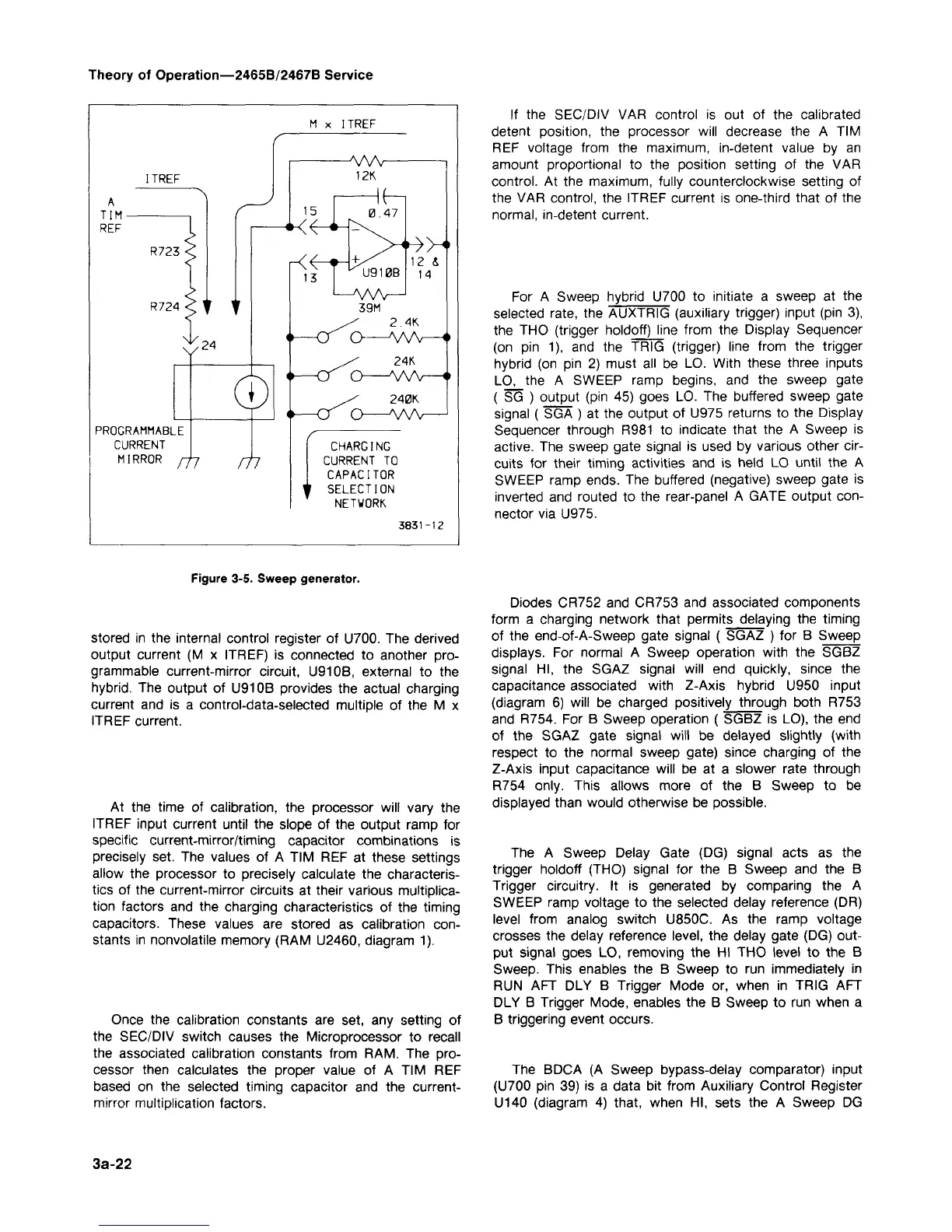
M x ITREF
ITREF
PROGRAMMABLE
CURRENT
MIRROR ffj
CHARGING
CURRENT TO
CAPACITOR
* SELECTION
NETWORK
3831-12
If the SEC/DIV VAR control is out of the calibrated
detent position, the processor will decrease the A TIM
REF voltage from the maximum, in-detent value by an
amount proportional to the position setting of the VAR
control.
At the maximum, fully counterclockwise setting of
the VAR control, the ITREF current is one-third that of the
normal,
in-detent current.
For A Sweep hybrid U700 to initiate a sweep at the
selected rate, the AUXTRIG (auxiliary trigger) input (pin 3),
the THO (trigger holdoff) line from the Display Sequencer
(on pin 1), and the TRIG (trigger) line from the trigger
hybrid (on pin 2) must all be LO. With these three inputs
LO,
the A SWEEP ramp begins, and the sweep gate
( SG ) output (pin 45) goes LO. The buffered sweep gate
signal ( SGA ) at the output of U975 returns to the Display
Sequencer through R981 to indicate that the A Sweep is
active.
The sweep gate signal is used by various other cir-
cuits for their timing activities and is held LO until the A
SWEEP ramp ends. The buffered (negative) sweep gate is
inverted and routed to the rear-panel A GATE output
con-
nector via U975.
Figure 3-5. Sweep generator.
stored in the internal control register of U700. The derived
output current (M x ITREF) is connected to another pro-
grammable current-mirror circuit, U910B, external to the
hybrid.
The output of U910B provides the actual charging
current and is a control-data-selected multiple of the M x
ITREF current.
At the time of calibration, the processor will vary the
ITREF input current until the slope of the output ramp for
specific current-mirror/timing capacitor combinations is
precisely set. The values of A TIM REF at these settings
allow the processor to precisely calculate the characteris-
tics of the current-mirror circuits at their various multiplica-
tion factors and the charging characteristics of the timing
capacitors. These values are stored as calibration
con-
stants in nonvolatile memory (RAM U2460, diagram 1).
Once the calibration constants are set, any setting of
the SEC/DIV switch causes the Microprocessor to recall
the associated calibration constants from RAM. The pro-
cessor then calculates the proper value of A TIM REF
based on the selected timing capacitor and the current-
mirror multiplication factors.
Diodes CR752 and CR753 and associated components
form a charging network that permits delaying the timing
of the end-of-A-Sweep gate signal ( SGAZ ) for B Sweep
displays. For normal A Sweep operation with the SGBZ
signal HI, the SGAZ signal will end quickly, since the
capacitance associated with Z-Axis hybrid U950 input
(diagram 6) will be charged positively through both R753
and R754. For B Sweep operation ( SGBZ is LO), the end
of the SGAZ gate signal will be delayed slightly (with
respect to the normal sweep gate) since charging of the
Z-Axis input capacitance will be at a slower rate through
R754 only. This allows more of the B Sweep to be
displayed than would otherwise be possible.
The A Sweep Delay Gate (DG) signal acts as the
trigger holdoff (THO) signal for the B Sweep and the B
Trigger circuitry. It is generated by comparing the A
SWEEP ramp voltage to the selected delay reference (DR)
level from analog switch U850C. As the ramp voltage
crosses the delay reference level, the delay gate (DG) out-
put signal goes LO, removing the HI THO level to the B
Sweep. This enables the B Sweep to run immediately in
RUN AFT DLY B Trigger Mode or, when in TRIG AFT
DLY B Trigger Mode, enables the B Sweep to run when a
B triggering event occurs.
The BDCA (A Sweep bypass-delay comparator) input
(U700 pin 39) is a data bit from Auxiliary Control Register
U140 (diagram 4) that, when HI, sets the A Sweep DG
3a-22
 Loading...
Loading...