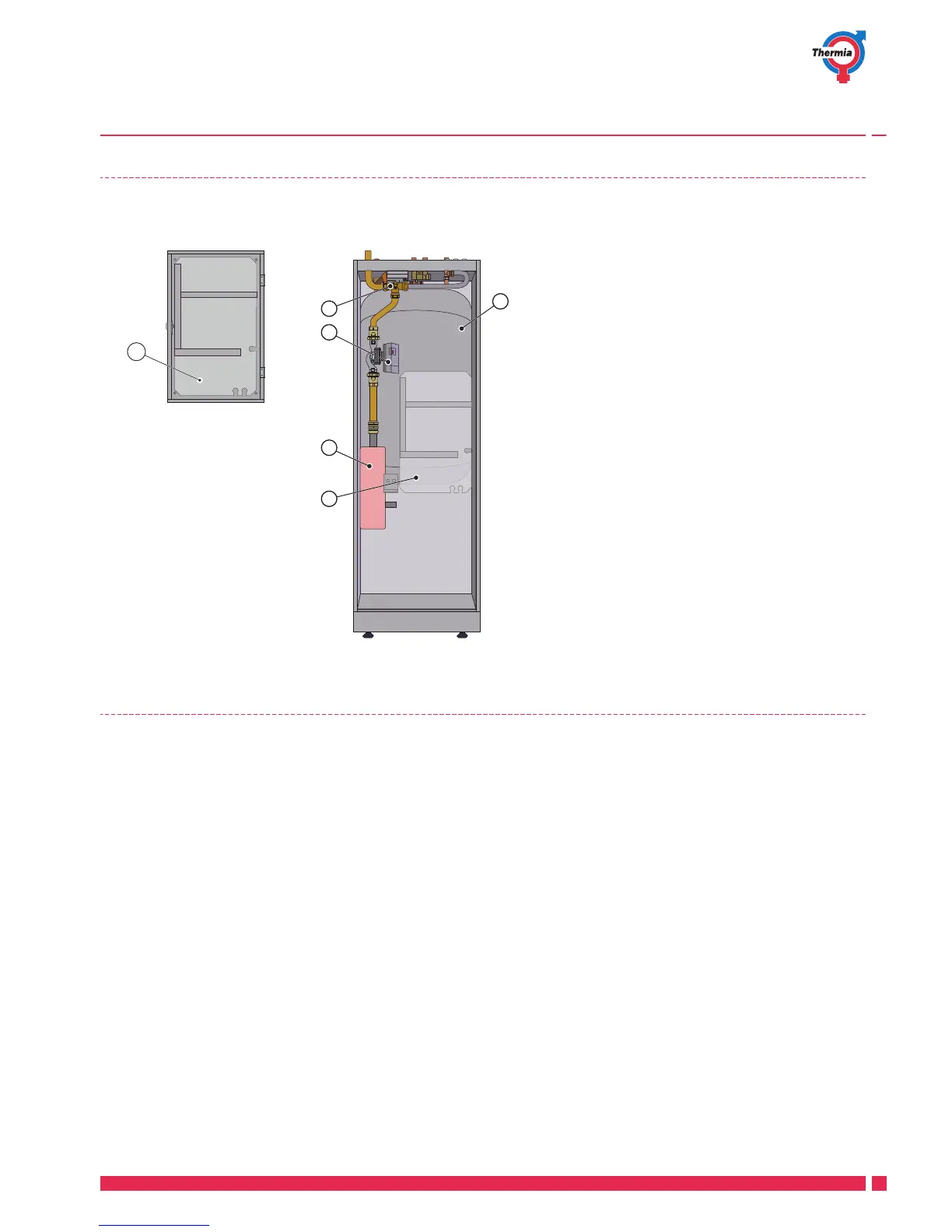
1 Control module (transparent in im-
age)
2 Immersion heater
3 Reversing valve
4 Circulation pump
5 Water heater
3.1.3 Heating
The heat pump can produce heat for heating (house, pool) and hot water.
The hot water requirement is prioritised before the heating requirement. The heating requirement is calculated
from outdoor temperature and set heat curve. An auxiliary heater starts automatically on demand.
Heat production is as follows;
▪
A fan draws the outdoor air through an air heat exchanger, which heats up the cold refrigerant, which
evaporates into a gas.
▪
The refrigerant that is now supplied with energy in the form of heat is transferred via the 4 way valve to
the compressor, where its temperature and pressure are increased.
▪
The extremely hot refrigerant continues to the flat heat exchanger . Here, the refrigerant is cooled and
releases its heat energy to the heating system. The refrigerant’s temperature drops and condenses to a
liquid state.
▪
The heating system transports the heating energy out to the water heater or the heating system of the
house.
▪
The refrigerant then passes through the drying filter to the electronic expansion valve where the pressure
and temperature drop and the process starts again.
User Guide
iTec
Thermia Värmepumpar VUJSI102
9
 Loading...
Loading...











