SARA-G450 - System integration manual
UBX-18046432 - R08 Design-in Page 57 of 143
C1-Public
SARA-G450 modules must be supplied through the VCC pins by a clean DC power supply that should
comply with the module VCC requirements summarized in Table 6.
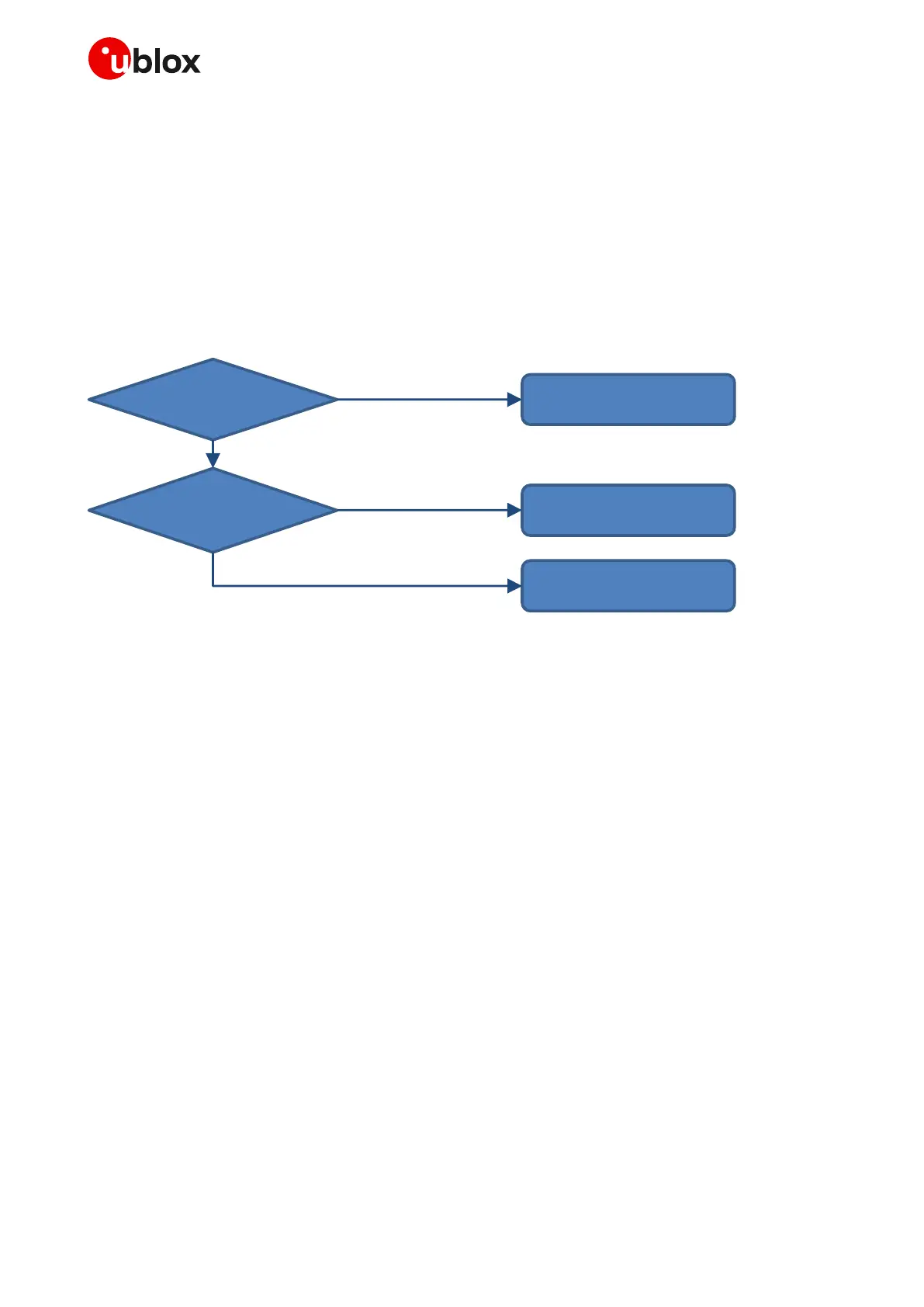
The appropriate DC power supply can be selected according to the application requirements (see
Figure 22) between the different possible supply sources types, which most common ones are the
following:
Switching regulator
Low Drop-Out (LDO) linear regulator
Rechargeable Lithium-ion (Li-Ion) or Lithium-ion polymer (Li-Pol) battery
Primary (disposable) battery
Main supply
available?
Battery
Li-Ion 3.7 V
Linear LDO
regulator
Main supply
voltage > 5V?
Switching step-down
regulator
No, portable device
No, less than 5 V
Yes, greater than 5 V
Yes, always available
Figure 22: VCC supply concept selection
The DC-DC switching step-down regulator is the typical choice when the available primary supply
source has a nominal voltage much higher (e.g. greater than 5 V) than the modules VCC operating
supply voltage. The use of switching step-down provides the best power efficiency for the overall
application and minimizes current drawn from the main supply source. See sections 2.2.1.2, 2.2.1.6,
2.2.1.10 and 2.2.1.11 for specific design-in.
The use of an LDO linear regulator becomes convenient for a primary supply with a relatively low
voltage (e.g. less than 5 V). In this case the typical 90% efficiency of the switching regulator
diminishes the benefit of voltage step-down and no true advantage is gained in input current savings.
On the opposite side, linear regulators are not recommended for high voltage step-down as they
dissipate a considerable amount of energy in thermal power. See sections 2.2.1.3, 2.2.1.6, 2.2.1.10 and
2.2.1.11 for specific design-in.
If the modules are deployed in a mobile unit where no permanent primary supply source is available,
then a battery will be required to provide VCC. A standard 3-cell Li-Ion or Li-Pol battery pack directly
connected to VCC is the usual choice for battery-powered devices. During charging, batteries with
Ni-MH chemistry typically reach a maximum voltage that is above the maximum rating for VCC, and
should therefore be avoided. See sections 2.2.1.4, 2.2.1.6, 2.2.1.10 and 2.2.1.11 for specific design-in.

 Loading...
Loading...