IM 12D7B3-E-E
6-1 Calibration
6. CALIBRATION
6-1 When is calibration necessary?
Calibration of conductivity/resistivity instruments is normally not required, since Yokogawa delivers a wide
range of sensors, which are factory calibrated traceable to NIST standards. The cell constant values are
normally indicated on the top of the sensor or on the integral cable. These values can be entered directly
in service code 03 (section 5-3-1). If the cell has been subjected to abrasion (erosion or coating) calibration
may be necessary. In the next section two examples are given. Alternatively calibration may be carried out
with a simulator to check the electronics only.
NOTE:
During calibration the temperature compensation is still active. This means that the readings are referred to
the reference temperature as chosen in service code 20 (section 5-3-4, default 25 °C).
Calibration is normally carried out by measuring a solution with a known conductivity value at a known
temperature. The measured value is adjusted in the calibration mode. On the next pages the handling
sequence for this action is visualized. Calibration solutions can be made up in a laboratory. An amount of
salt is dissolved in water to give a precise concentration with the temperature stabilized to the adjusted
reference temperature of the instrument (default 25 °C). The conductivity of the solution is taken from
literature tables or the table on this page.
Alternatively the instrument may be calibrated in an unspecified solution against a standard instrument.
Care should be taken to make a measurement at the reference temperature since differences in the type of
temperature compensation of the instrument may cause an error.
NOTE:
The standard instrument used as a reference must be accurate and based on an identical temperature
compensation algorithm. Therefore the Model SC82 Personal Conductivity Meter of Yokogawa is
recommended.
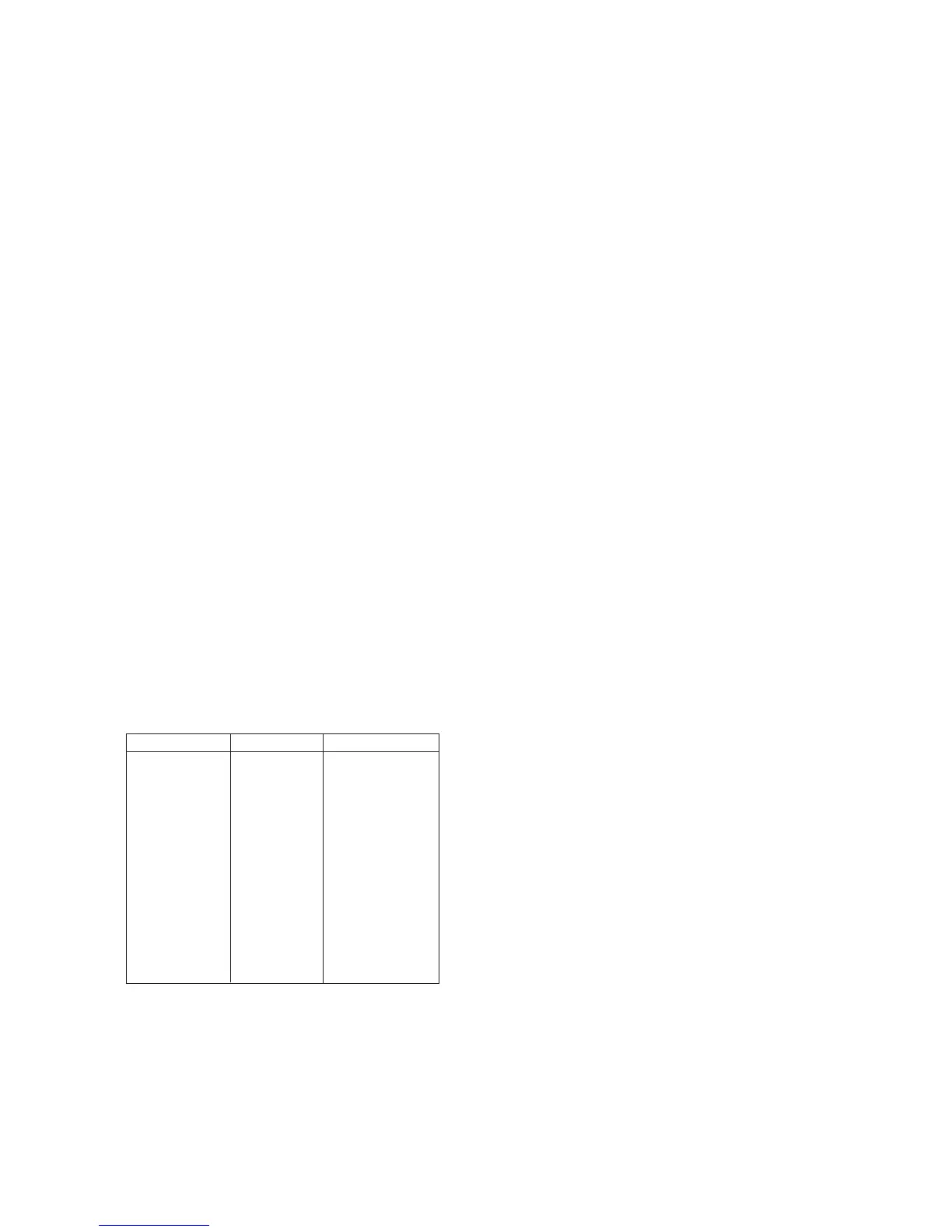
Typical calibration solutions.
The table shows some typical conductivity values for sodium-chloride (NaCl) solutions which can be made
up in a laboratory.
Table 6-1. NaCl values at 25 °C
Weight % mg/kg Conductivity
0.001 10 21.4 µS/cm
0.003 30 64.0 µS/cm
0.005 50 106 µS/cm
0.01 100 210 µS/cm
0.03 300 617 µS/cm
0.05 500 1.03 mS/cm
0.1 1000 1.99 mS/cm
0.3 3000 5.69 mS/cm
0.5 5000 9.48 mS/cm
1 10000 17.6 mS/cm
3 30000 48.6 mS/cm
5 50000 81.0 mS/cm
10 100000 140 mS/cm
NOTE:
For resistivity measurement the standard resistivity
units of the calibration solution can be calculated as
follows:
R = 1000/G (kΩ.cm if G = µS/cm)
Example:
0.001% weight
R = 1000/21.4 = 46.7 kΩ.cm

 Loading...
Loading...