10
FEM630 | ELECTROMAGNETIC FLOWMETER | OI/FEM630-EN REV. A
2 ...Design and function
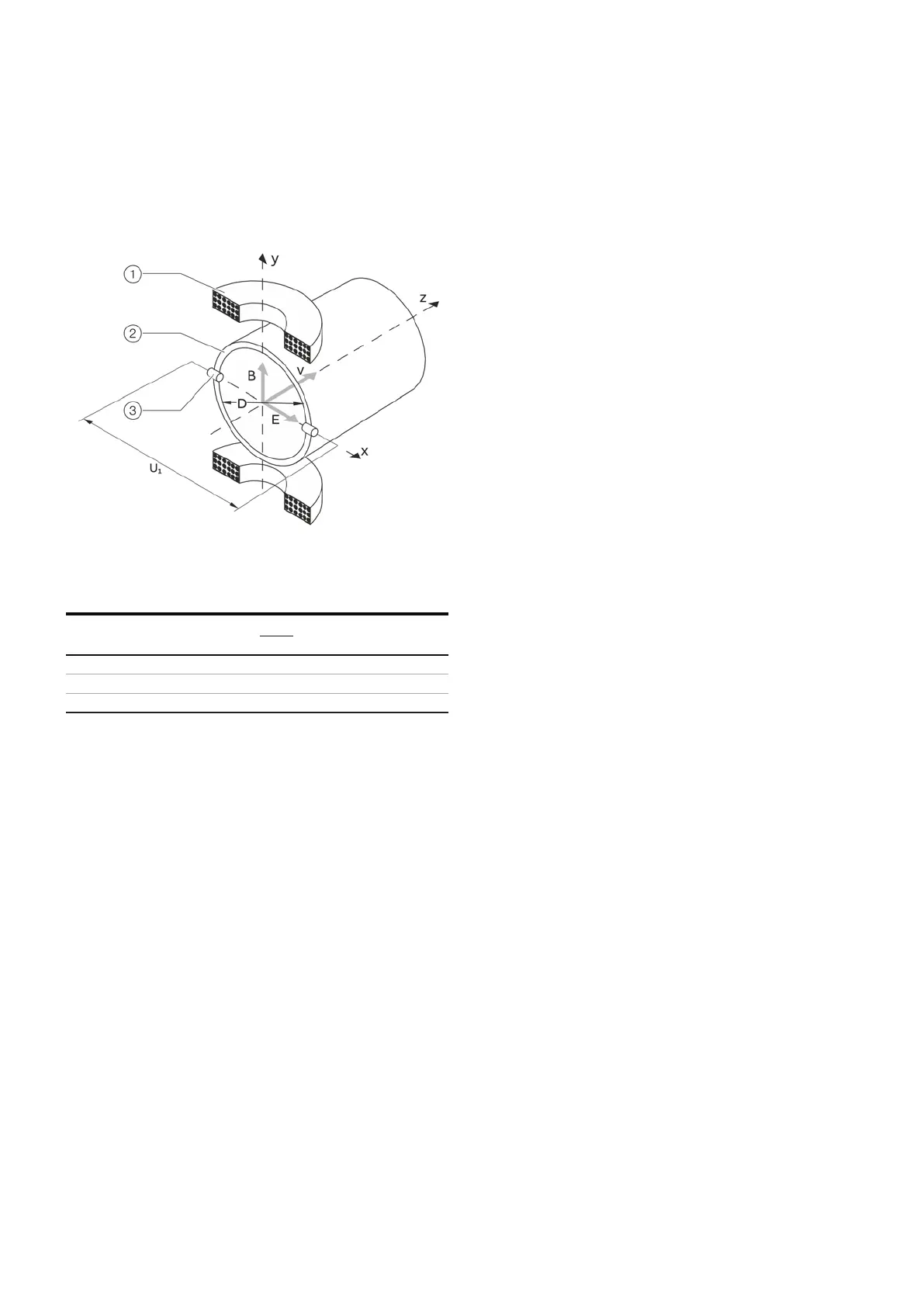
U
Measuring span
v Average flow velocity
B Magnetic induction
qv Volume flow rate
D Electrode spacing
Measuring principle
Measurements performed by the electromagnetic flowmeter
are based on Faraday’s law of induction. A voltage is
generated in a conductor when it moves through a magnetic
field.
With the device-relevant application of this measuring
principle, a conductive measuring medium flows through a
tube in which a magnetic field is generated perpendicular to
the flow direction (see Figure 3).
The voltage induced in the measuring medium is tapped by
two diametrically opposed electrodes. This measurement
voltage is proportional to the magnetic induction, the
electrode spacing and the average medium velocity v.
Taking into account that the magnetic induction and the
electrode spacing are constant values results in a proportion
between the measurement voltage U1 and the average
medium velocity.
From the calculation of the volume flow rate follows that the
measurement voltage is linear and proportional to the volume
flow rate.
The induced voltage is converted by the transmitter to
standardized, analog and digital signals.
1 Magnet coil
2 Measuring tube in electrode plane
3 Measuring electrode
Figure 3 Electromagnetic flowmeter diagram
U
1
~ B x D x v qv =
D
2
x π
x v U
1
~ qv

 Loading...
Loading...











