The ac input to each output board is rectified, filtered, and
applied to the power module regulator. Each output board
employs series regulation techniques. The regulator element
is connected in series with the load and operates in the
linear region (between saturation and cutoff) of the
transistor characteristic curve. Regulation is achieved by
varying the conduction of the series element in response to
changes in the line voltage or the load. The constant voltage
CV control circuit compares the voltage at the output with a
reference voltage and generates a control signal which
varies the conduction of the series regulator to raise or
lower the output voltage as required. The constant current
CC control circuit compares the voltage at the current
monitor resistor with a reference and likewise varies the
conduction of the series regulator.
The interface circuit on the output board receives digital
signals (reference voltages) which are sent to the control
circuit to program the output voltage and current.
The output boards can be commanded to send
and/or to the display on the front panel. The data is sent
back via the secondary interface circuit and the appropriate
The output board is able to sink current as well as source
current. Current sink limits are fixed at values
approximately ten percent higher than the maximum
current source limit for the particular output voltage
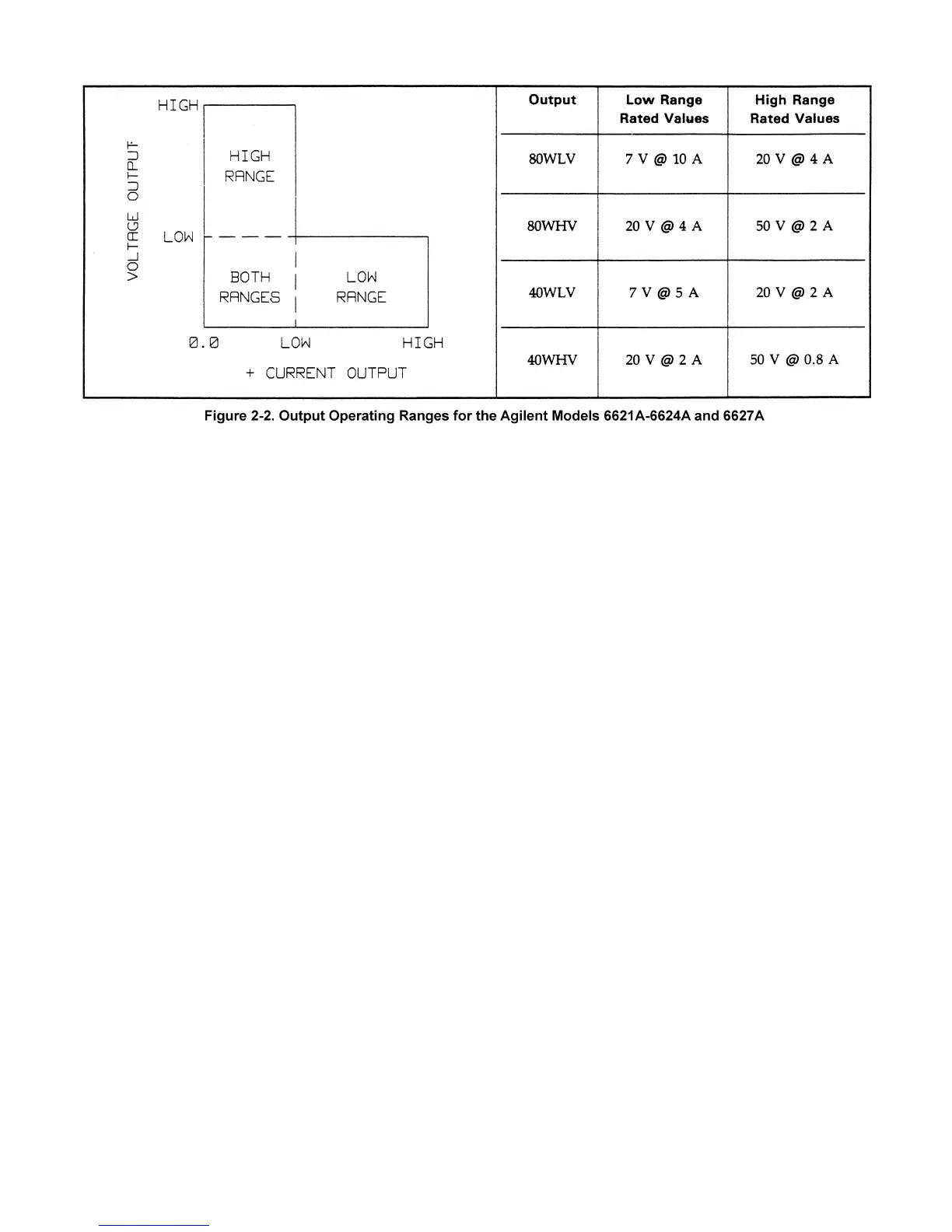
operating point. See Figure 2-7 for typical current source
and sink characteristics. The output board circuits are
described in greater detail in paragraph 2-24.
2-7
Figure 2-3 illustrates the major circuits and signal flow on
functional schematic, Figure 6-2, in the rear of this manual.
The functional names on the block diagram correspond with
those on the schematic so that the diagrams can be
correlated. As shown in Figure 2-3, the major circuits consist
output boards interface, and the front panel interface circuit.
transceivers (U203) for the 8 data lines and 8 control lines,
handles data transfer between the microprocessor and the
the data bus and appears as memory locations to the
microprocessor.
for the transfer of data and other messages in a byte serial,
bit parallel manner. Data and message transfer is
asynchronous, coordinated by the three handshake lines
(DAV, NRFD, and NDAC). The power supply can be a
true and sending talk or listen addresses on the data lines
the EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable memory)
chip along with other system variables. You can find out
key as described in the operating manual. As shipped from
the factory, the power supply's address is set to 5. Any
address from 0 through 30 is a valid address.
2-3
of the GPIB interface, the system micro-computer, the
2-8 GPIB Interface
These circuits consist of the GPIB bus connector (J201),
and the GPIB talker/listener chip (U202). All GPIB (IEEE-
488) functions are implemented by the GPIB chip which
GPIB, handshake protocol, and talker/listener addressing
procedures. The GPIB talker/listener chip is connected to
The eight data lines (DI01-DI08) of the GPIB are reserved for
signals from the GPIB board and converts them to analog
measurement and status data back to the GPIB controller
circuits on the GPIB board.
talker or a listener on the GPIB. The controller dictates the
role of an GPIB device by setting the ATN (attention) line
(DI01-DI08). The power supply's GPIB address is stored in
your supply's GPIB address by using the front panel ADDR
There are five GPIB control lines: ATN, IFC, REN, SRQ, and
EOI (IEEE-488). When the controller sets the ATN line true,
all devices on the bus must "listen" to the addresses and
universal commands placed on the bus. When ATN is false,
only devices that are addressed will actively send or receive
data. All unaddressed devices will ignore the data lines
when ATN is false.
GPIB BOARD (FIGURE 2-3)
the GPIB board. Complete circuit details are shown on the
 Loading...
Loading...











