30 Publication 1756-PM004C-EN-P - October 2009
Chapter 2 Organize Tags
Avoid using the same name for both a controller tag and a program tag. Within
a program, you cannot reference a controller tag if a tag of the same name
exists as a program tag for that program.
Certain tags must be controller scope (controller tag).
Guidelines for Tags
Use the following guidelines to create tags for a Logix5000 project.
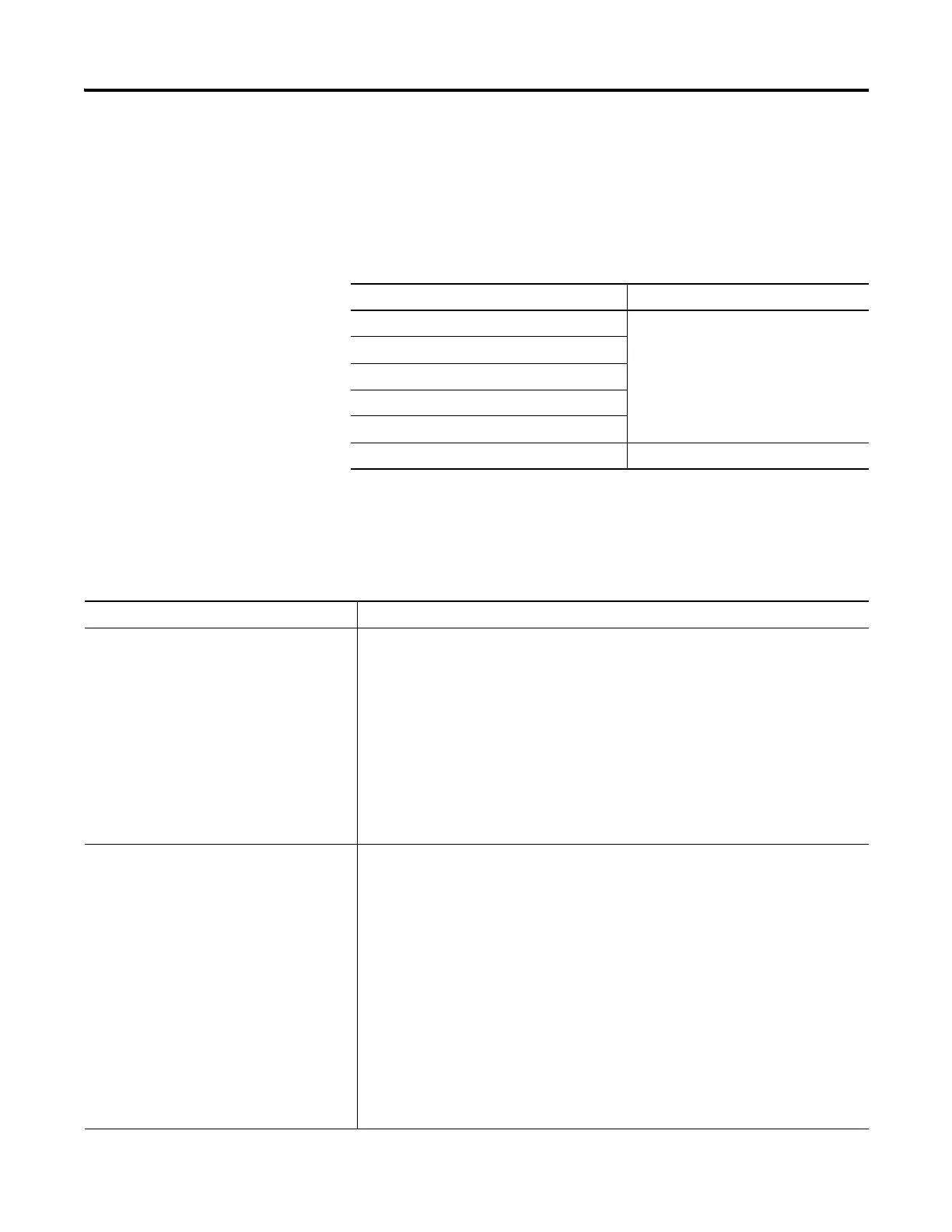
Controller Scope Tags
If you want to use the tag Then assign this scope
In more than one program in the project
Controller scope (controller tags)
In a Message (MSG) instruction
To produce or consume data
In any of the seven AXIS data types
To communicate with a PanelView terminal
None of the above Program scope (program tags)
Tag Guidelines
Guideline Details
Create user-defined data types User-defined data types (structures) let you organize data to match your machine or
process. A user-defined data type provides these advantages:
• One tag contains all the data related to a specific aspect of your system. This keeps
related data together and easy to locate, regardless of its data type.
• Each individual piece of data (member) gets a descriptive name. This automatically
creates an initial level of documentation for your logic.
• You can use the data type to create multiple tags with the same data layout.
For example, use a user-defined data type to store all the parameters for a tank, including
temperatures, pressures, valve positions, and preset values. Then create a tag for each of
your tanks based on that data type.
Use arrays to quickly create a group
of similar tags
An array creates multiple instances of a data type under a common tag name.
• Arrays let you organize a block of tags that use the same data type and perform a
similar function.
• You organize the data in one, two, or three dimensions to match what the data
represents.
For example, use a two-dimensional array to organize the data for a tank farm. Each
element of the array represents a single tank. The location of the element within the
array represents the geographic location of the tank.
Important: Minimize the use of BOOL arrays. Many array instructions do not operate on
BOOL arrays. This makes it more difficult to initialize and clear an array of BOOL data.
• Typically, use a BOOL array for the bit-level objects of a PanelView screen.
• Otherwise, use the individual bits of a DINT tag or an array of DINTs.

 Loading...
Loading...











