17 APPENDIX C AquaLab
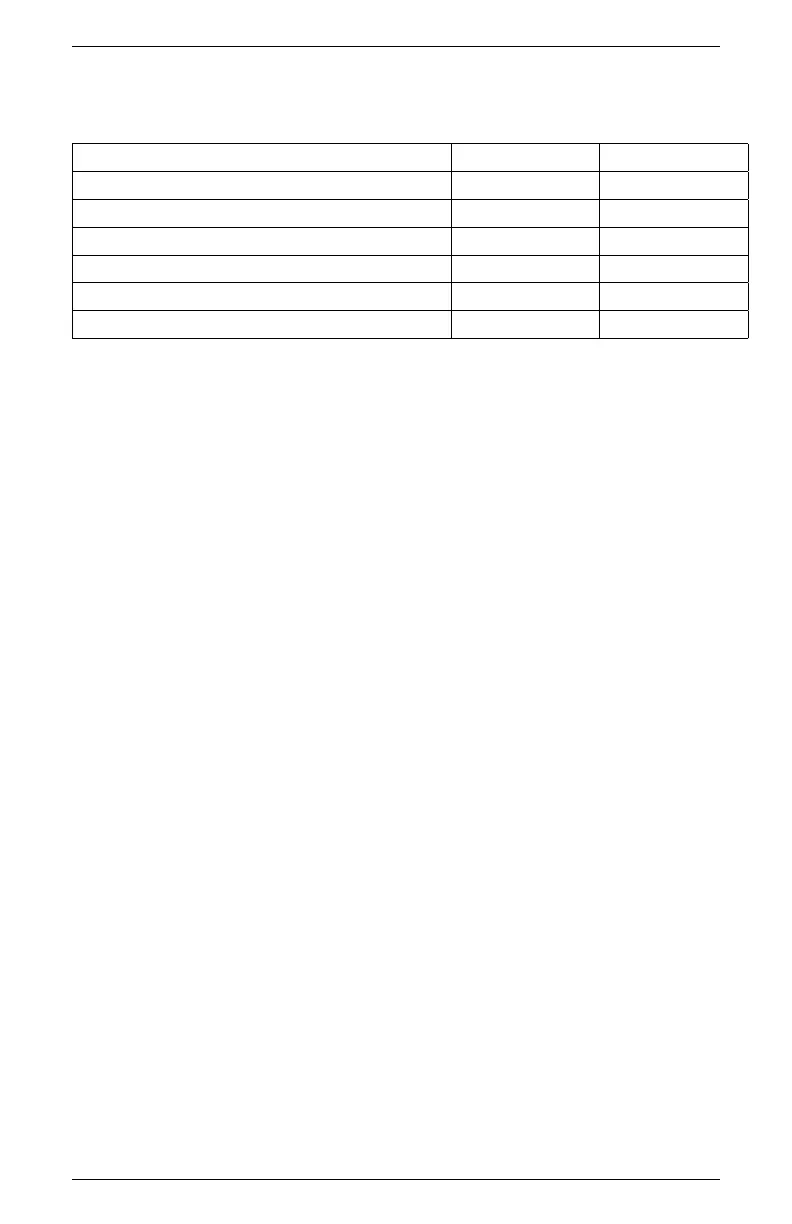
Table 6: Verification Standard Expected Values
Verification Standard Water Activity
USP Purified Water 1.000 ±0.003 1.000 ±0.015
0.50 mol/kg KCl 0.984 ±0.003 0.984 ±0.015
2.33 mol/kg NaCl 0.920 ±0.003 0.920 ±0.015
6 mol/kg NaCl 0.760 ±0.003 0.760 ±0.015
8.5 mol/kg LiCl 0.500 ±0.003 0.500 ±0.015
13.4 mol/kg LiCl 0.250 ±0.003 0.250 ±0.015
Verify the AquaLab is functioning properly with any two of these
solutions. We recommended that you choose a standard from the
range in which you are measuring and steam distilled water (or an-
other solution from the table).
1. Place the verification standard (do not start with water) in
AquaLab for measuring. When you reach a final reading, check
it against the values in Table 6. If it is within ±0.003, place
your second solution in the drawer for testing. It should read
the value ±0.003 listed in the table above. If the readings are
within the expected values your verification is complete.
2. If the first solution does not read within ±0.003 of the ex-
pected value, then you need to adjust the linear offset so that
the solution reads correctly (see Section 7). When you are fin-
ished measuring both standards, the readings should be within
±0.003 of the predicted values.
References
AOAC, Method 978.18D Preparation of Reference Salt Slushes. 1995.
Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International. 16th Ed. AOAC
International, Arlington VA.
Campbell, G.S. and W.H. Gardner. 1971. Psychrometric measure-
ment of soil water potential: temperature and bulk density effects.
Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 35:8-12.
Greenspan, L. 1977. Humidity fixed points of binary saturated aque-
ous solutions. J. Res. National Bureau of Stds. A. Physics and
112
 Loading...
Loading...