11-4 9440300990
Limiters DECS-250
=
×
Equation 11-1. Inverse Pickup Time Characteristic
Where:
t
pickup
= time to pick up in seconds
A = -95.908
B = -17.165
C = 490.864
D = -191.816
TD = time dial setting <0.1, 20>
MOP = multiple of pickup <1.03, 2.5>
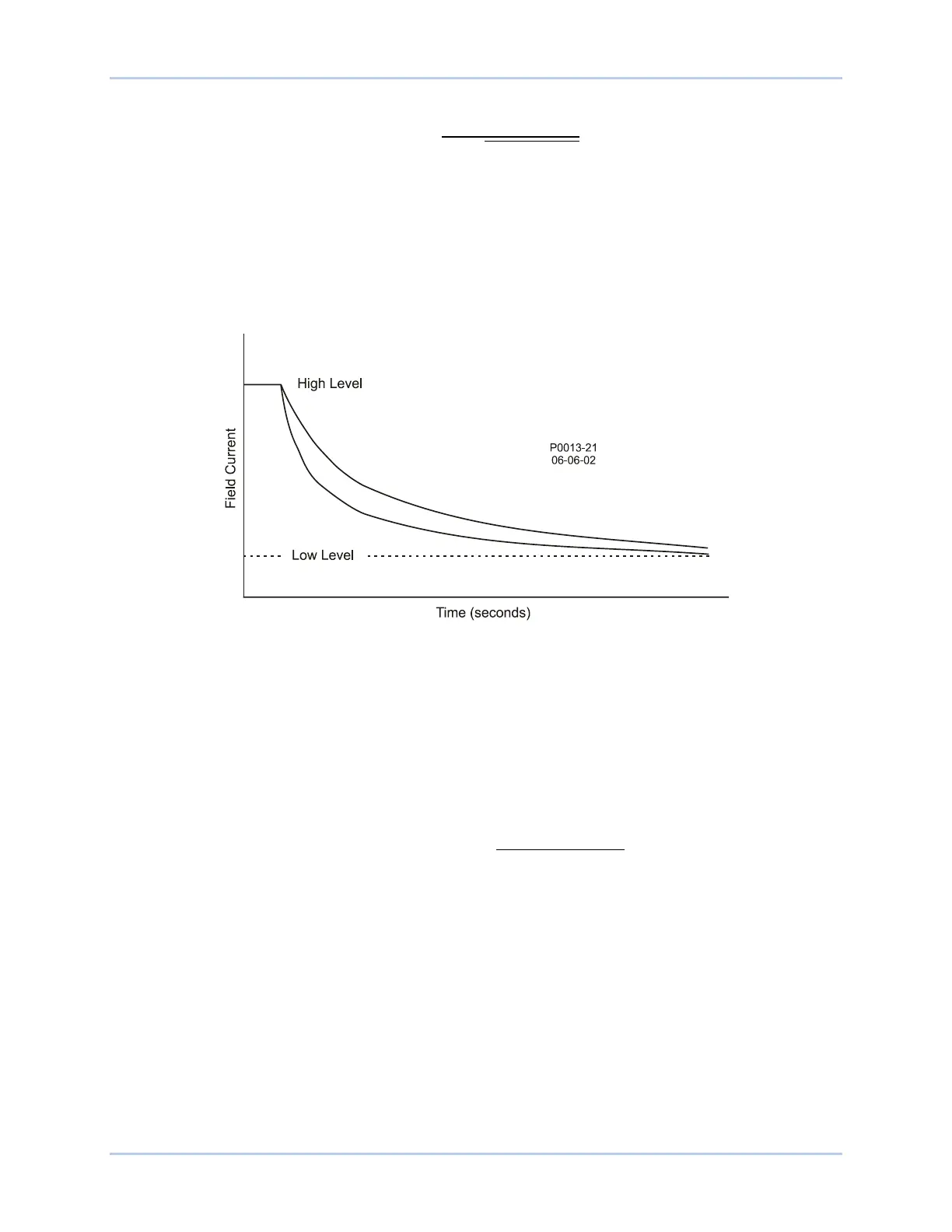
Figure 11-5. Inverse Time Characteristic for Takeover OEL
Primary and secondary setting groups provide additional control for two distinct machine operating
conditions. Each mode of takeover OEL operation (offline and online) has a low-level, high-level, and time
dial setting.
Once the field current decreases below the dropout level (95% of pickup), the function is reset based on
the selected reset method. The available reset methods are inverse, integrating, and instantaneous.
Using the inverse method, the OEL is reset based on time versus multiple of pickup (MOP). The lower the
field current level, the less time is required for reset. Inverse reset uses the following curve (Equation
11-2) to calculate maximum reset time.
=
× × 0.05
1 −
(
× 1.03
)
2
Equation 11-2. Inverse Reset Time Characteristic
Where:
Reset Time Constant = maximum time to reset in seconds
RC = reset coefficient setting <0.01, 100>
TD = time dial setting <0.1, 20>
MOP = multiple of pickup
For the integrating reset method, the reset time is equal to the pickup time. In other words, the amount of
time spent above the low level threshold is the amount of time required to reset.
Instantaneous reset has no intentional time delay.
In BESTCOMSPlus
®
, a plot of the takeover OEL setting curves is displayed. Settings enable selection of
the displayed curves. The plot can display the primary or secondary setting curves, the offline or online
settings curves, and the pick up or reset settings curves.
 Loading...
Loading...