The SoC is displayed as bar graph and as relative number; 100% means fully
charged.
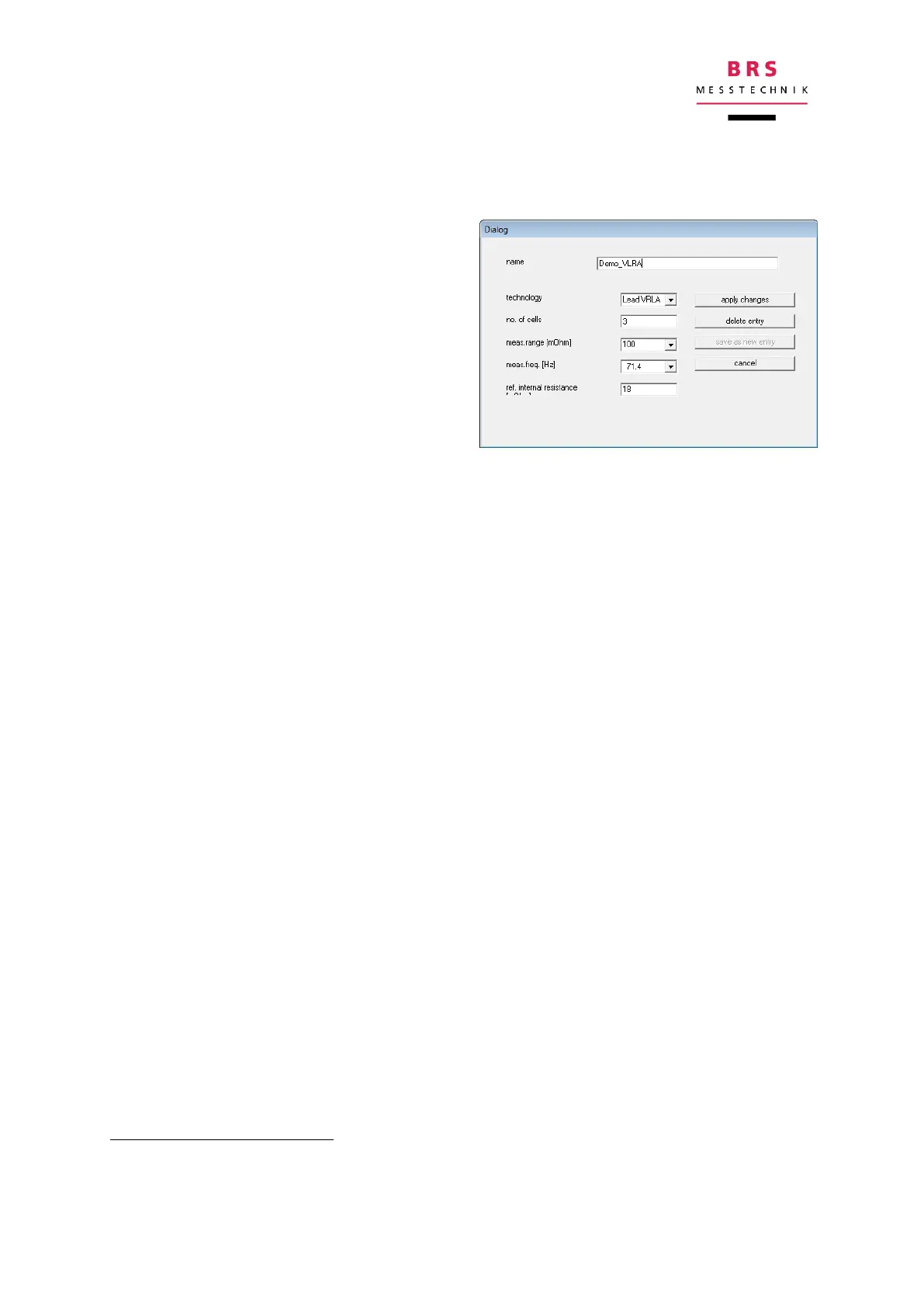
Once at the beginning, the batteries to be
measured have to be specified. This is
done via the dialog box “Configuration”
below the battery selection. The following
values have to be determined:
technology: Lead Acid, Li-Ion,
LiFePo
4
number of cells (example: for a 12V
lead acid battery, enter 6 cells)
the measurement range for the in-
ternal resistance
the measurement frequency for the internal resistance
Finally, the reference value for the internal resistance has to be entered. For doing
so, measure the internal resistance of a new battery and enter the value.
a) Measurement of SoH
The state of health (SoH) is determined by comparing the actually measured internal
resistance with that of a new battery.
In order to minimize side effects it is sensible to conduct these measurements under
similar conditions:
battery stand-alone, i.e. without load
temperatures between 15°C and 35°C
state of charge between 60% und 90%
resting times of more than 1 hour, with lead acid batteries more than 4 hours
(better: 12 hours)
b) Measurement of SoC
The state of charge (SoC) is determined by measuring the open circuit voltage and
compare it with typical, internally stored values. With these technology-typical values
accuracies of around 10% can be obtained
.
Comparable conditions are here recommended too:
battery stand-alone, i.e. without load
temperatures between 15°C and 35°C
resting times of more than 1 hour, with lead acid batteries more than 4 hours
(better: 12 hours)
For higher accuracies battery-specific values are necessary. You might find them in datasheets, or you can ask
us to determine these individually for you.
 Loading...
Loading...