44
the space. Pulldown for units is expected to rarely occur, but is
included for the rare situation when it is needed. Most likely
pulldown will occur when mechanical cooling first becomes
available shortly after the control goes into an occupied mode
(after a warm unoccupied mode).
Slow Change Cap Override (SLOW)
With a rooftop unit, the design rise at 100% total unit capacity
is generally around 30F. For a unit with 4 stages, each stage
represents about 7.5F of change to EDT. If stages could reli-
ably be cycled at very fast rates, the setpoint could be main-
tained very precisely. Since it is not desirable to cycle compres-
sors more than 6 cycles per hour, slow change override takes
care of keeping the PID under control when “relatively” close
to setpoint.
SumZ Operation
The SumZ algorithm is an adaptive PID style of control. The
PID is programmed within the control and the relative speed of
staging can only be influenced by the user through the adjust-
ment of the Z.GN configuration. The capacity control algo-
rithm uses a modified PID algorithm, with a self adjusting gain
which compensates for varying conditions, including changing
flow rates across the evaporator coil.
Previous implementations of SumZ made static assumptions
about the actual size of the next capacity jump up or down.
This control uses a “rise per percent capacity” technique in the
calculation of SumZ, instead of the previous “rise per stage”
method. For each jump, up or down in capacity, the control will
know beforehand the exact capacity change brought on. Better
overall staging control can be realized with this technique.
SUM Calculation — The PID calculation of the “SUM” is
evaluated once every 80 seconds.
SUM = Error + “SUM last time through” + (3 * Error Rate)
Where:
SUM = the PID calculation, Error = EDT – Cooling Control
Point, Error Rate = Error – “Error last time through”
NOTE: “Error” is limited to between –50 and +50 and “Error
rate” is limited to between –20 and +20.
This “SUM” will be compared against the “Z” calculations in de-
termining whether cooling stages should be added or subtracted.
Z Calculation — For the “Z” calculation, the control attempts
to determine the entering and the leaving-air temperature of the
evaporator coil and based upon the difference between the two
during mechanical cooling, and then determines whether to add
or subtract a stage of cooling. This is the adaptive element.
The entering-air temperature is referred to as MAT (mixed-air
temperature) and the leaving-air temperature of the evaporator
coil is referred to as EDT (evaporator discharge temperature).
They are found at the local display under the Temperatures
CTRL sub-menu.
The main elements to be calculated and used in the calculation
of SumZ are:
1) the rise per percent capacity (R.PCT)
2) the amount of expected rise for the next cooling stage addition
3) the amount of expected rise for the next cooling stage
subtraction
The calculation of “Z” requires two variables, Z.PLU used
when adding a stage and Z.MIN used when subtracting a stage.
They are calculated with the following formulas:
Z.PLU = Z.GN * (10 + (4*(–ADD.R))) * 0.6
Z.MIN = Z.GN * (–10 + (4*(–SUB.R))) * 0.6
Where:
Z.GN = configuration used to modify the threshold levels used
for staging (Configuration
COOL
Z.GN)
ADD.R = R.PCT * (C.CAP – capacity after adding a cooling
stage)
SUB.R = R.PCT * (C.CAP – capacity after subtracting a cool-
ing stage)
Both of these terms, Z.PLU and Z.MIN, represent a threshold
both positive and negative to which the “SUM” calculation
must build up to cause the compressor to stage up or down.
Comparing SUM and Z — The “SUM” calculation is com-
pared against Z.PLU and Z.MIN.
• If “SUM” rises above Z.PLU, a cooling stage is added.
• If “SUM” falls below Z.MIN, a cooling stage is subtracted.
There is a variable called SMZ which is described in the SumZ
Cooling Algorithm section and which can simplify the task of
watching the demand build up or down over time. It is calculat-
ed as follows:
If SUM is positive: SMZ = 100*(SUM/Z.PLU)
If SUM is negative: SMZ = –100*(SUM/Z.MIN)
Mixed Air Temperature Calculation (MAT)
The mixed-air temperature is calculated and is a function of the
economizer position. Additionally there are some calculations
in the control which can zero in over time on the relationship of
return and outside air as a function of economizer position.
There are two configurations which relate to the calculation of
“MAT.” These configurations can be located at the local dis-
play under Configuration
UNIT.
MAT Calc Config (MAT.S) — This configuration gives the
user two options in the processing of the mixed-air temperature
(MAT) calculation:
• MAT.S = 0
There will be no MAT calculation.
• MAT.S = 1
The control will attempt to learn MAT over time. Any time the
system is in a vent mode and the economizer stays at a particu-
lar position for long enough, MAT = EDT. Using this method,
the control has an internal table whereby it can more closely
determine the true MAT value.
• MAT.S = 2
The control will not attempt to learn MAT over time.
To calculate MAT linearly, the user should reset the MAT table
entries by setting MAT.R to YES. Then set MAT.S = 2. The
control will calculate MAT based on the position of the econo-
mizer and outside air and return air temperature.
To freeze the MAT table entries, let the unit run with MAT.S = 1.
Once sufficient data has been collected, change MAT.S = 2. Do
not reset the MAT table.
Reset MAT Table Entries? (MAT.R) — This configuration al-
lows the user to reset the internally stored MAT learned config-
uration data back to the default values. The defaults are set to a
linear relationship between the economizer damper position
and OAT and RAT in the calculation of MAT.
SumZ Overrides
There are a number of overrides to the SumZ algorithm which
may add or subtract stages of cooling.
• High Temp Cap Override (H.TMP)
• Low Temp Cap Override (L.TMP)
• Pull Down Cap Override (PULL)
• Slow Change Cap Override (SLOW)
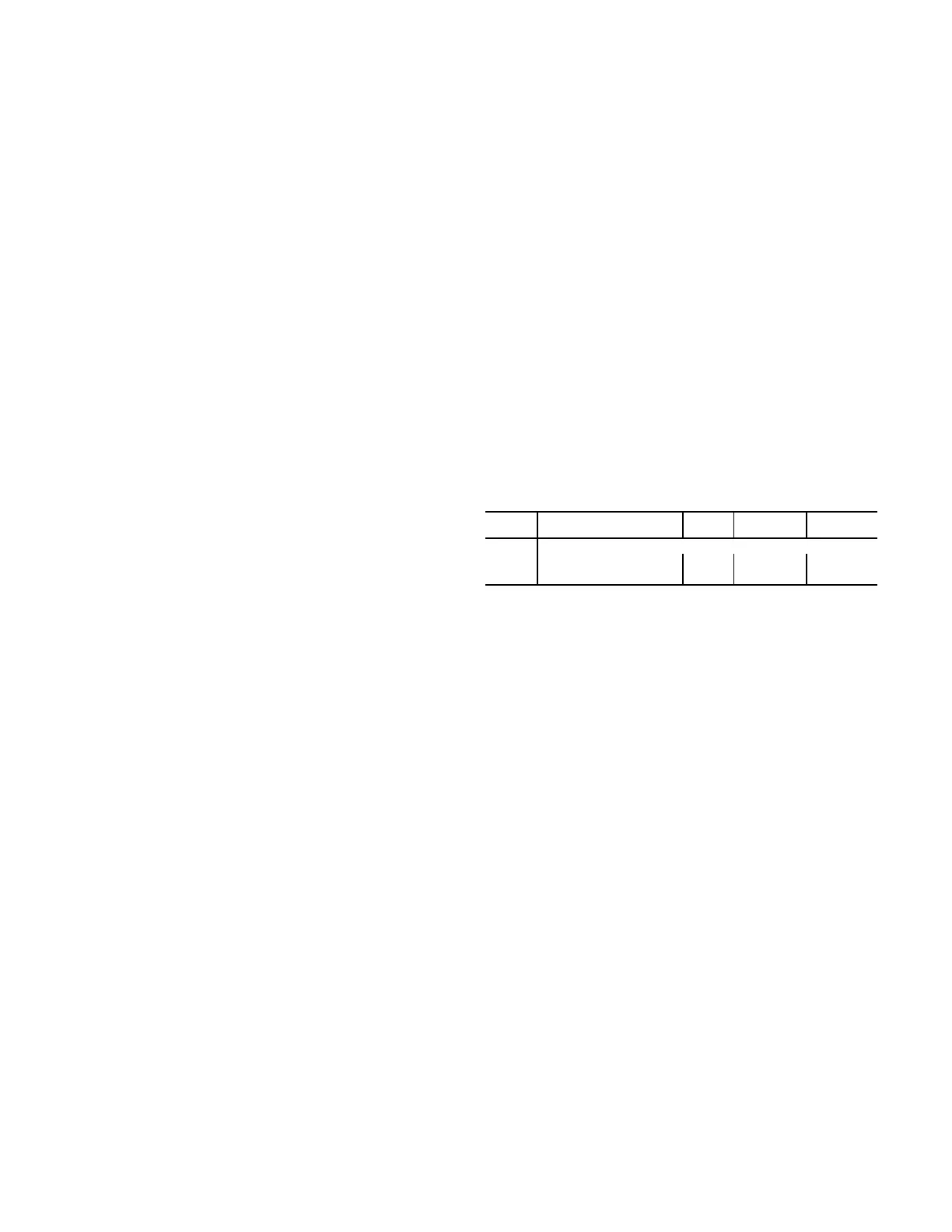
ITEM EXPANSION RANGE
CCN
POINT
DEFAULTS
UNIT UNIT CONFIGURATION
MAT.S MAT Calc Config 0 to 2 MAT_SEL 1
MAT.R Reset MAT Table Entries? Yes/No MATRESET No

 Loading...
Loading...