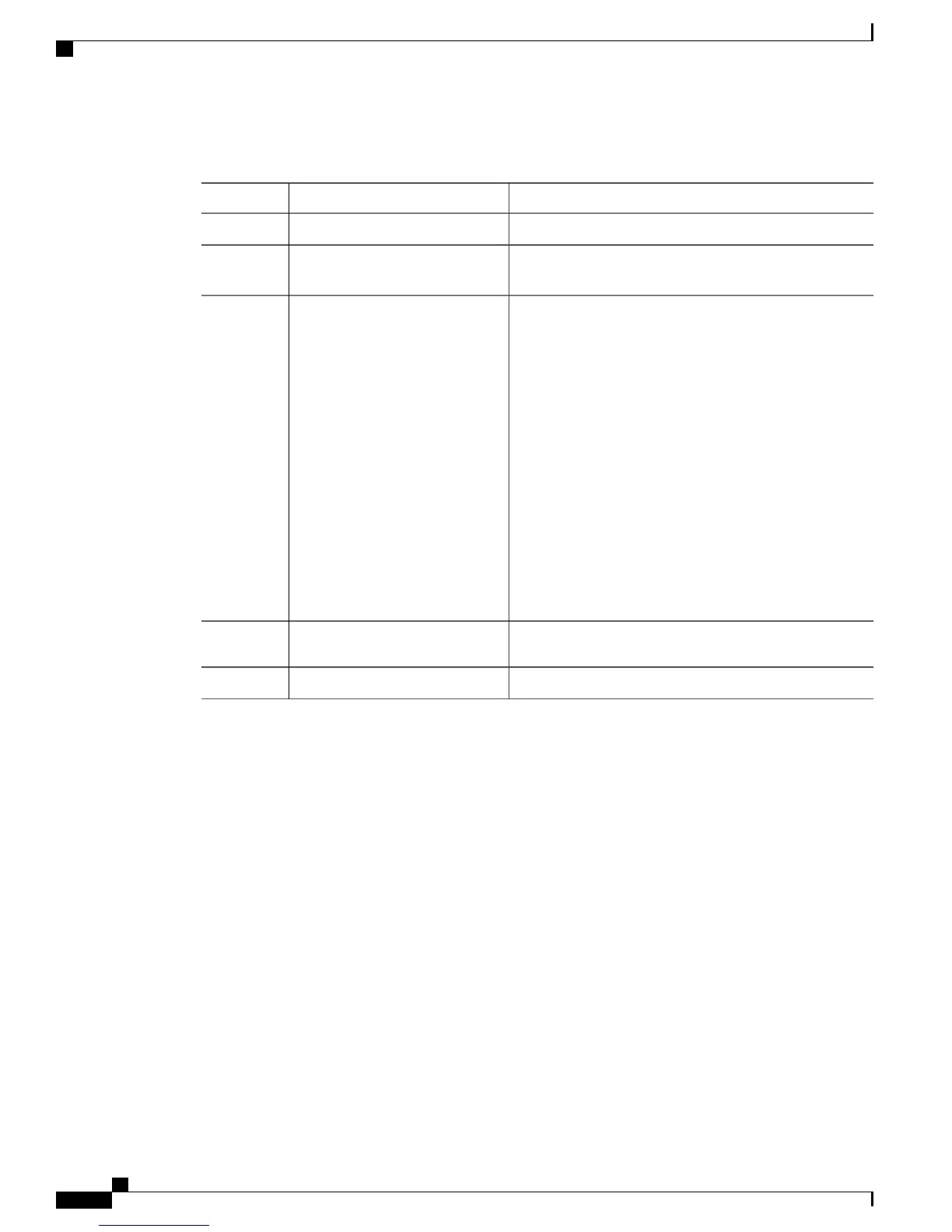
Procedure
PurposeCommand or Action
Enters global configuration mode.switch# configure terminal
Step 1
Creates an interface that connects the server to the NPV
switch.
switch(config)# interface fc
slot/port
Step 2
Sets the speed, which can be 4 G, 8G, or 16 Gswitch(config-if)# switchport
speed speed
Step 3
8 G speed is not supported for server and target
interfaces.
Following is an example of configuring IDLE fill
pattern on a Cisco MDS switch:
Note
Switch(config)# int fc2/3
Switch(config)# switchport fill-pattern IDLE speed
8000
Switch(config)# sh run int fc2/3
interface fc2/3
switchport speed 8000
switchport mode NP
switchport fill-pattern IDLE speed 8000
no shutdown
Configures the interface as an F port.switch(config-if)# switchport
mode F
Step 4
Brings up the interface.switch(config-if)# no shutdown
Step 5
Configuring QoS
Configuring Default QoS
There are four types of FCoE default policies: network QoS, output queuing, input queuing, and QoS. You
can enable the FCoE default policies by enabling the FCoE NPV feature using the feature-set fcoe-npv
command. The default QoS ingress policy, default-fcoe-in-policy, is implicitly attached to all FC and
SAN-port-channel interfaces to enable FC to FCoE traffic; this can be verified by using show interface {fc
slot/port | san-port-channel <no>} all command. The default QoS policy uses CoS3 and Q1 for all FC and
FCoE traffic.
Configuring User-Defined QoS
To use a different queue or CoS value for FCoE traffic, create user-defined policies. The user-defined QoS
ingress policy has to be created and attached explicitly to both FC and FCoE interfaces to enable traffic to
use a different queue or CoS. User-defined QoS policies must be created and activated for system-wide QoS.
Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS FC NPV Configuration Guide
16
Configuring N Port Virtualization
Configuring FC NPV Interfaces

 Loading...
Loading...











