Inteli NT GeCon MINT, SW Version 1.4, ©ComAp – June 2007
IGS-NT-GeCon-MINT-1.4.PDF
9
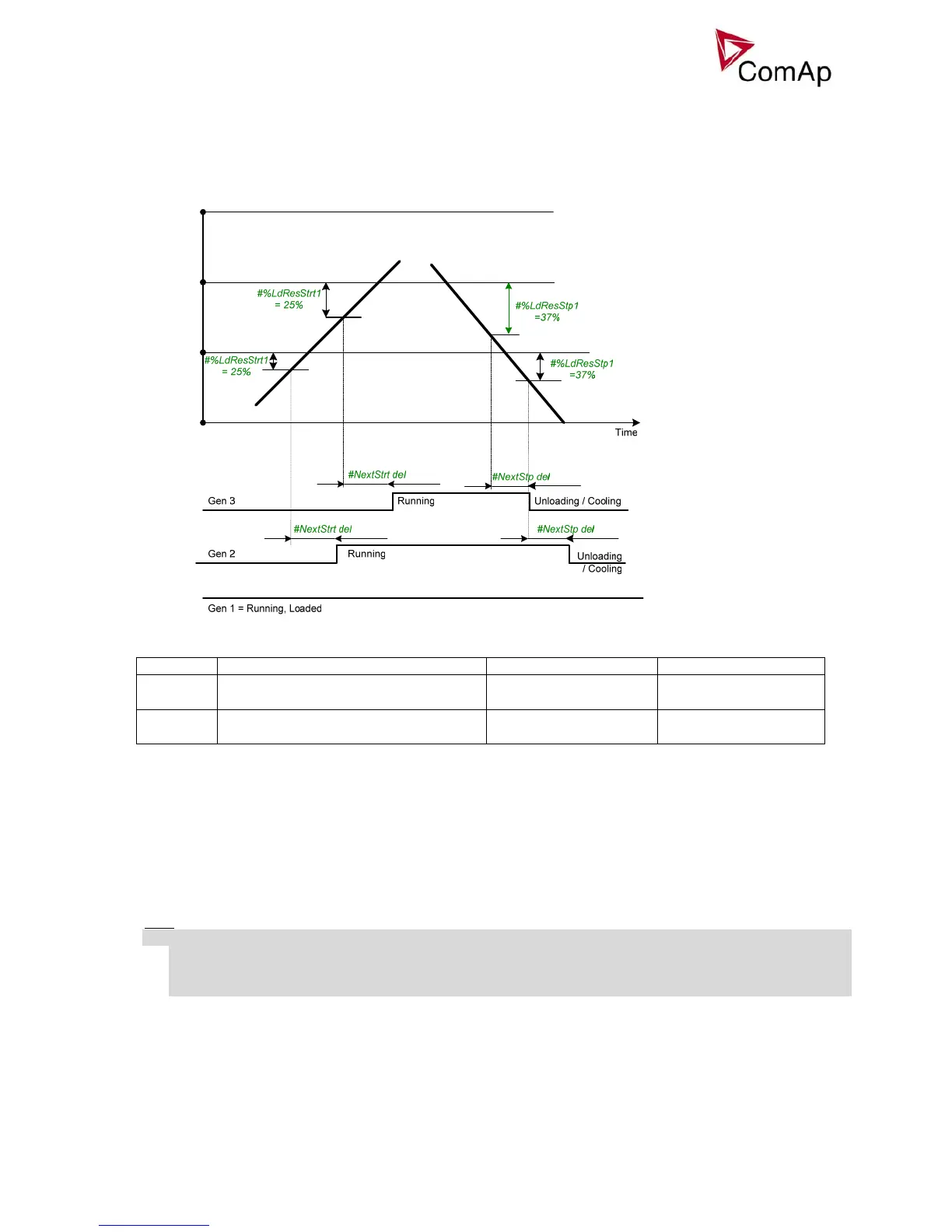
Relative power management in %
Guarantees that the engines be not continuously loaded more than to a certain level, leaving less than
selected relative load reserve. Suitable for engine life-based optimization.
Activation: #Pwr mgmt mode = REL (%)
Gen1
Priority 1
Gen2
Priority 2
Gen3
Priority 3
Actual power [ kW or kVA ]
Start/Stop conditions in Power management
Reserve Actual Reserve Start condition Stop condition
Absolute
kW / kVA
ARstrt = ΣPg
Nom
– ΣPg
Act
ARstp = ΣPg*
Nom
– ΣPg
Act
ARstrt < #LdResStrt ARstp > #LdResStp
Relative
%
RRstrt = (ΣPg
Nom
– ΣPg
Act
) / ΣPg
Nom
RRstp = (ΣPg*
Nom
– ΣPg
Act
) / ΣPg*
Nom
RRstrt < #%LdResStrt RRstp > #%LdResStp
Where
ARstrt Actual Absolute reserve in kW or kVA - for engine start calculation.
ARstp Actual Absolute reserves in kW or kVA - for engine stop calculation.
RRstrt Actual Relative reserve in % - for engine start calculation.
RRstp Actual Relative reserves in % - for engine stop calculation.
ΣPg
Nom
Sum of Nominal power of all gen-sets on the bus.
ΣPg*
Nom
Sum of Nominal power of all gen-sets on the bus apart of the one, which is going to be stopped.
ΣPg
Act
Sum of Actual power of all gen-sets on the bus = system load.
Hint:
Optional functions in absolute or relative Power management are:
- Running hours balancing (equalization),
- Load demand (different size) engines swap and
- Power management of two or more gen-set groups (bus tie support).

 Loading...
Loading...











