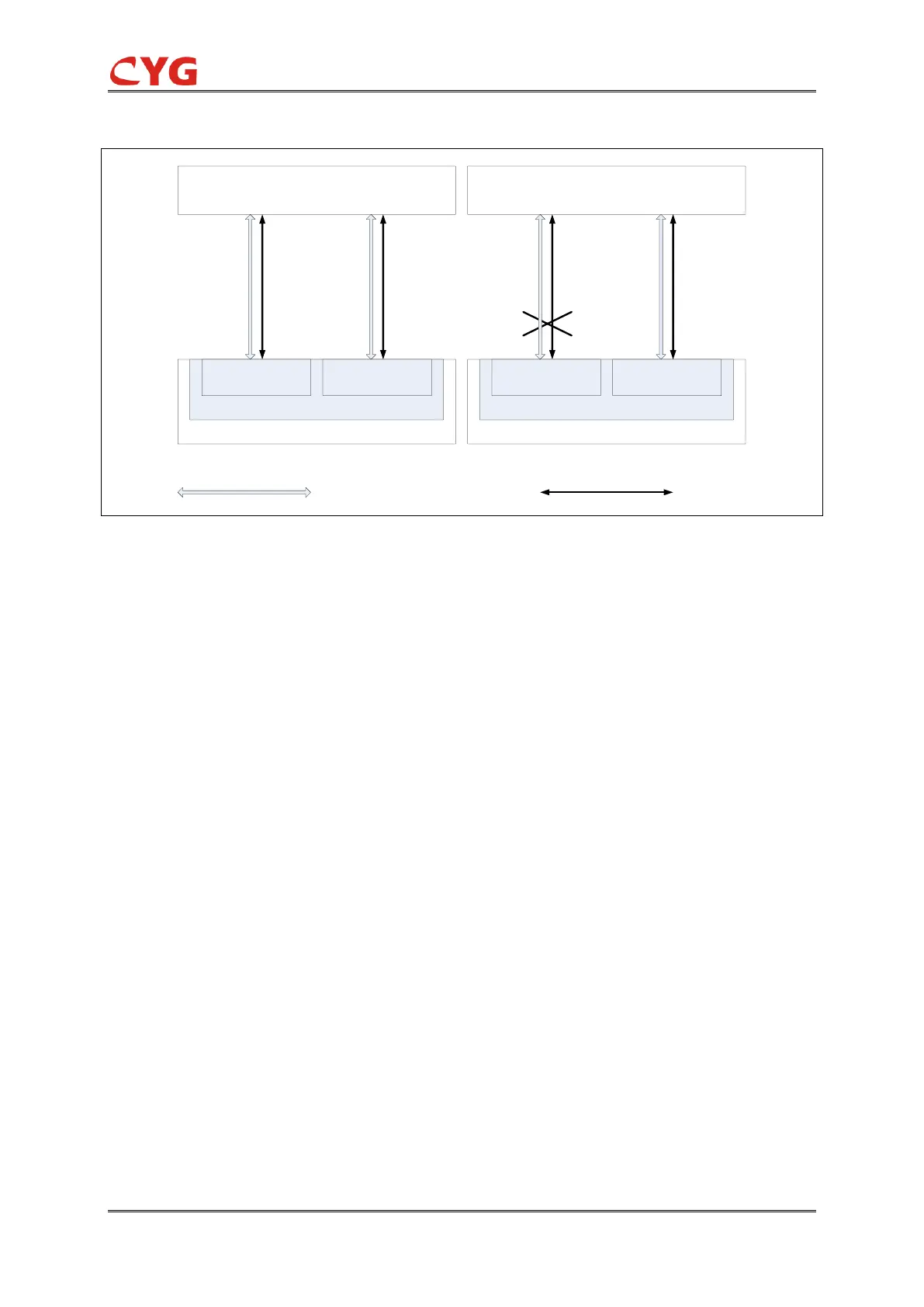
Figure 9.4.3 Dual-net full duplex mode with 2 independent RCB instances
In this mode, IED provides 2 report instances for each RCB, Net A and Net B work independently
from each other, failures of any net will not affect the other net at all. Tow report instances are
required for each client. Therefore, the IED may be unable to provide enough report instances if
there are too many clients.
Net A and Net B send the same report separately when they operates normally, To ensure no
repeated data is saved into database, massive calculation is required for the client.
Moreover, accurate clock synchronization of the IED is required to distinguish whether 2 reports
are the same report according to the timestamps. Clock synchronization error of the IED may lead
to report loss/redundancy.
As a conclusion, for the second mode, it’s difficult to realize seamless switchover between dual
nets, however, for the third mode, the IED may be unable to provide enough report instances if too
many clients are applied on site. Considering client treatment and IED implementation, the first
mode (Dual-net full duplex mode sharing the same report instance) is recommended for MMS
communication network deployment.
9.4.4 Server Data Organization
IEC61850 defines an object-oriented approach to data and services. An IEC61850 physical device
can contain one or more logical device(s) (for proxy). Each logical device can contain many logical
nodes. Each logical node can contain many data objects. Each data object is composed of data
attributes and data attribute components. Services are available at each level for performing
various functions, such as reading, writing, control commands, and reporting.
Each IED represents one IEC61850 physical device. The physical device contains one or more
logical device(s), and the logical device contains many logical nodes. The logical node LPHD
contains information about the IED physical device. The logical node LLN0 contains common
 Loading...
Loading...