4 Temperature Measurement Module DVP 04PT-E2
9. If you need to
add in other control programs, you can edit the program directly in the ladder diagram window in
WPLSoft.
4.9 PID Functions
4.9.1 Introduction to PID
P (Proportional) Control
The proportional control refers to that the output is in proportional to the error. When the temperature is lower
than the proportional band and the output is 100%, the control will enter the proportional band and the output
will be gradually in smaller proportional to the error. When the set temperature value (SV) is consistent with the
present temperature value (PV), i.e. no error, the output will be 0%. (Error = SV – PV)
In a heater: SV = 1,000 (100°C), K
P
= 100 (10°C). See the figure below for the relation between temperature
and output.
100
100%
0%
90
Outpu
Te m p e ra t u re
Propo rt ional
band
H
e
a
t
e
r
In a cooler: SV = 200 (20°C), K
P
= 100 (10°C). See the figure below for the relation between temperature and
output.
20
100%
0%
30
Outpu
Te m p e ra t u re
C
o
o
l
e
r
Proportional
ba n d
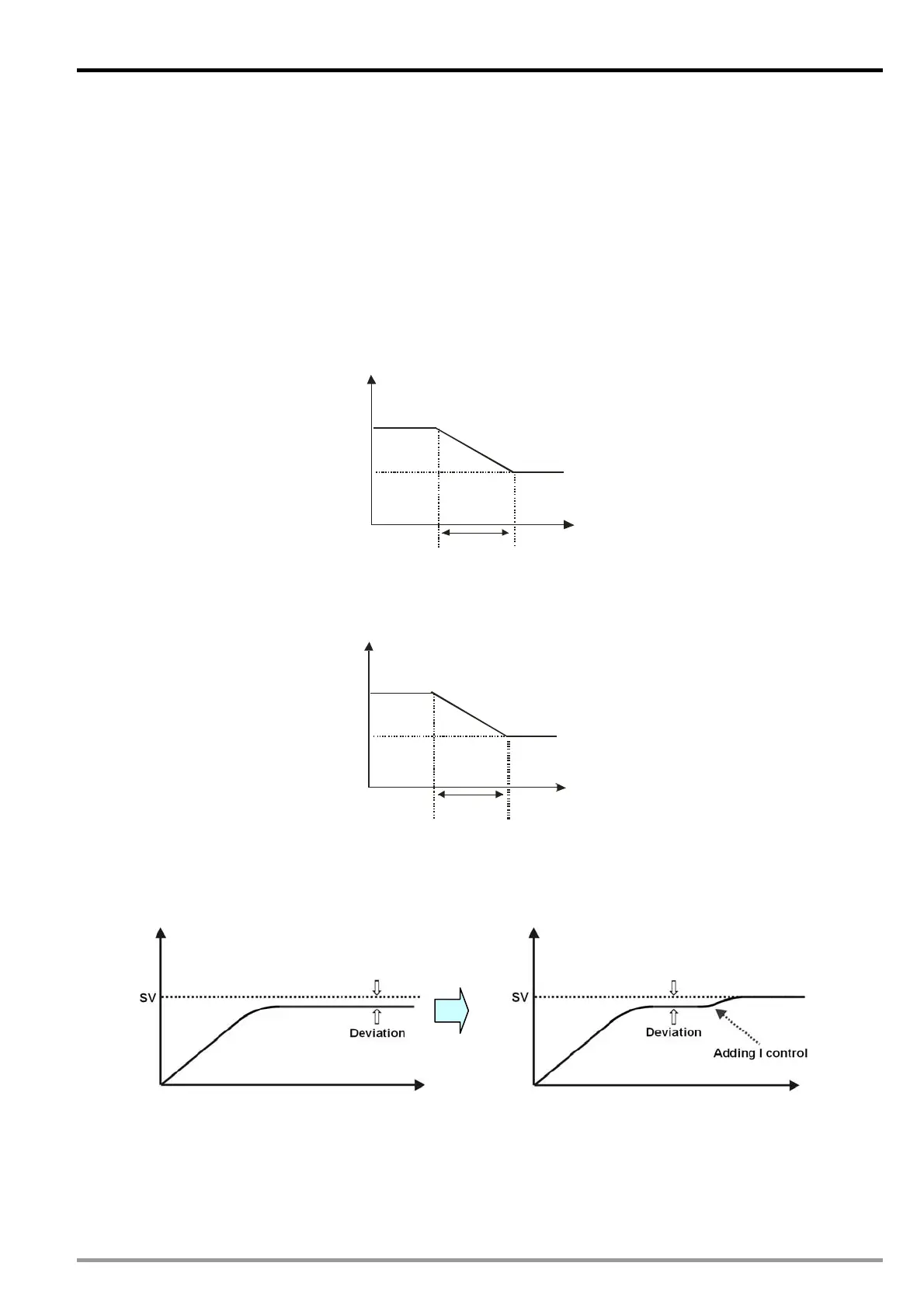
I (Integral) Control
With only P control, the controlled temperature will be deviated in a certain level from the set temperature.
Therefore, we adopt integral control with the proportional control. As time passes by, the deviation of value will
disappear, and the controlled temperature will be consistent with the set temperature.
DVP-ES2 Module Manual
-17

 Loading...
Loading...