10551803;a1
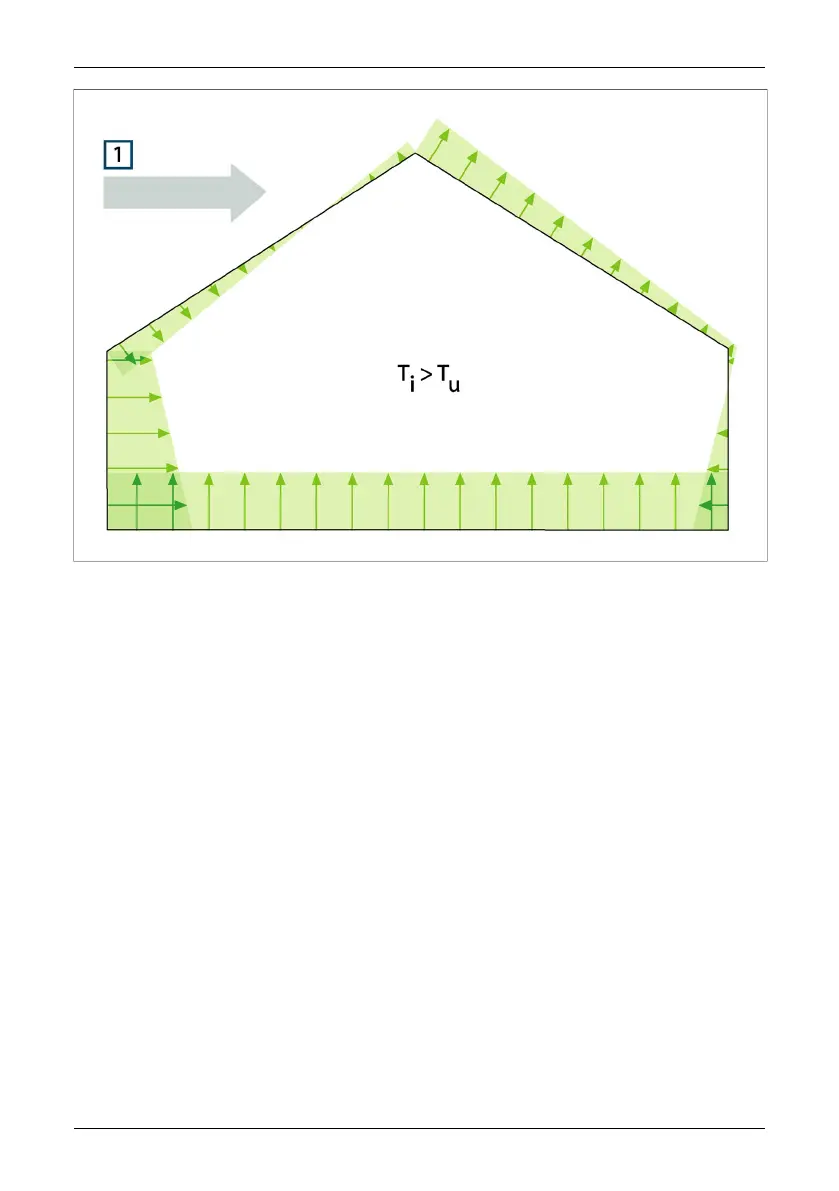
Figure 16.3 Distribution of resultant pressures on a building’s enclosing surfaces depending on wind effects,
ventilation and internal/external temperature difference. 1: Wind direction; T
u
: Thermodynamic air temper-
ature outdoors in K; T
i
: Thermodynamic air temperature indoors in K.
If the whole of the dynamic pressure becomes static pressure, then C = 1. Examples
of stress concentration factor distributions for a building with various wind directions
are shown in the figure on page 78.
The wind therefore causes an internal negative pressure on the windward side and
an internal positive pressure on the leeward side. The air pressure indoors depends
on the wind conditions, leaks in the building and how these are distributed in relation
to the wind direction. If the leaks in the building are evenly distributed, the internal
pressure may vary by ±0.2 p
stat
. If most of the leaks are on the windward side, the
internal pressure increases somewhat. In the opposite case, with most of the leaks
on the leeward side, the internal pressure falls.
Publ. No. T559580 Rev. a486 – ENGLISH (EN) – November 17, 2010 77
16 – Introduction to building thermography
 Loading...
Loading...