Page 22
FW-F103-P-XN-M_v2002_03_EN.docx
This setting determines the measurement unit for the flowmeter.
With automatic unit conversion, the units for Total and Flowrate are
derived from this setting. The following can be selected:
AUTO-VOL: L – m3 – US gal – I gal – cf – Oil bbl
AUTO-MAS: kg – ton – US ton – lb
• Changing the type of flowmeter unit (volumetric or mass) causes
the settings of the Total (SETUP 1.1) and Flowrate (SETUP 2.1)
to automatically change to the default unit of that type.
• Change of the flowmeter unit will not change the amount
displayed for Total and accumulated Total.
With the K-factor, the flowmeter pulse signals are converted to a
quantity. The K-factor is based on the number of pulses generated by
the flowmeter per selected measurement unit (SETUP 5.3), for
example per cubic meter. The more accurate the K-factor, the more
accurate the functioning of the system will be.
After pressing PROG, the decimal point will be flashing. The decimal
position can be changed now by pressing the ▲-key.
3.3.7 EXPLANATION OF SETUP-MENU 6 – LINEARIZE
Linearization principle
In normal situations, the calculation of flow is based on flowmeters that follow an ‘ideal line’ and give
a fixed number of pulses over the entire frequency range to represent a certain amount. The
calculation uses an average K-factor (the so-called KF0), which is entered at SETUP-menu 5 (when
automatic unit conversion is disabled, SETUP-menu 1 and 2).
Since many flowmeters do not follow this ‘ideal line’, the linearization function can be used to reflect
the actual flow curve better. This allows for more accurate flowrate and totalization values, as well as
improved analog and pulse output values over the frequency range of the flowmeter.
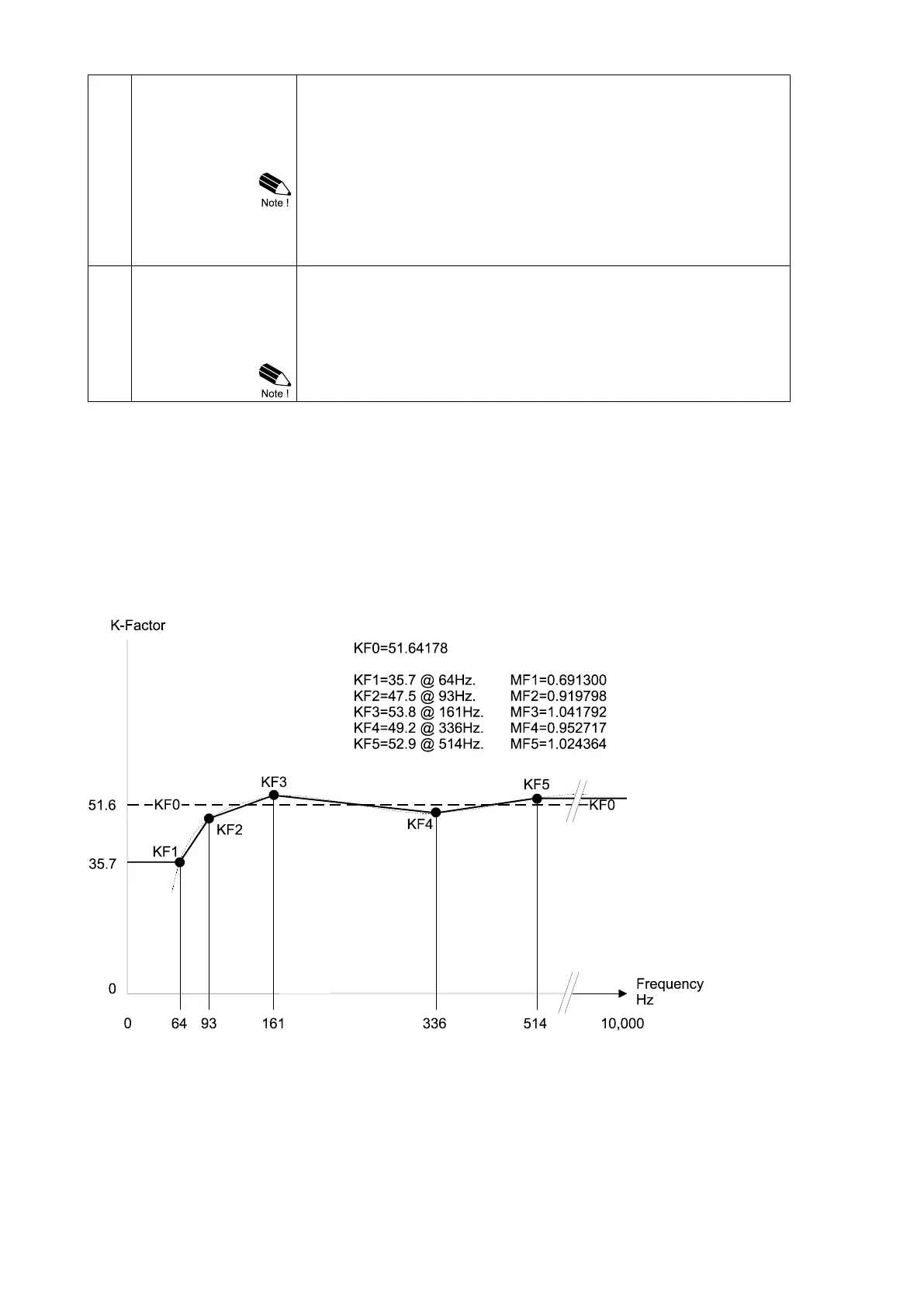
Fig. 11: Example of K-Factors and linearization points
The linearization function uses linearization points to calculate new K-factors based on the
measured flowmeter frequency. As shown in the chart above, each point consists of a frequency and
a Meter Factor (MFx, indicating the deviation of the K-factor KFx from the average K-factor KF0).
When a new frequency is measured, the corresponding Meter Factor is calculated by interpolating
between the linearization points. The new Meter Factor is then used to calculate the actual K-factors
for flowrate and total using this formula:
𝑲-𝒇𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒐𝒓 = 𝑴𝑭 ∗ 𝑲𝑭𝟎
 Loading...
Loading...