186
Programming examples: Fixed-wing model
Variable fl ap settings in each fl ight phase using
one of the two INC / DEC buttons,
then you can select a single transmitter control to
vary the basic settings of all eight wing fl aps simulta-
neously, separately for each fl ight phase.
To achieve this you should fi rst move to the menu …
»Control adjust« (page 78)
… where you assign the same INC / DEC button to
the inputs 5, 6 AND 7 – for example CONTROL 5 –
in each fl ight phase, and at the same time reduce the
travel to around 50% or even less, as this provides
very fi ne adjustment of the fl ap trim. It is also possib-
le to fi ne-tune the throws of the individual fl ap pairs in
one menu by entering different travel settings:
«Normal »
ASY
ASY
SYM
0% 0.0
0.0
0%
0%
+25%
+25%
+25%
+25%
+100%
+100%
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
SEL
SEL
0%
SYM
Cnt. 5
+25%
+25%
–time+offset
Cnt. 5
Cnt. 5
Input
Input
Input
Input
free
–travel+
5
6
7
8
Notes:
• Of course, a possible alternative is to use one of
the switches or side-mounted proportional con-
trols, but please note that their positions are not
stored separately for each fl ight phase – in con-
trast to the two INC / DEC buttons CONTROL 5
and 6.
• If you prefer to use a switch, set the “deviation”
from the offset point SYMmetrically or ASYmetri-
cally in the “-travel+” column.
Flap compensation when an elevator command is
given
If you fl ight-test the model and discover that elevator
trim correction is required when the fl aps are raised
or lowered, this can be set up in the menu ...
»Wing mixers« (page 110)
SYM
=>
0%
0%
0%
ASY
«Normal »
2–
>
4
6–
>
3
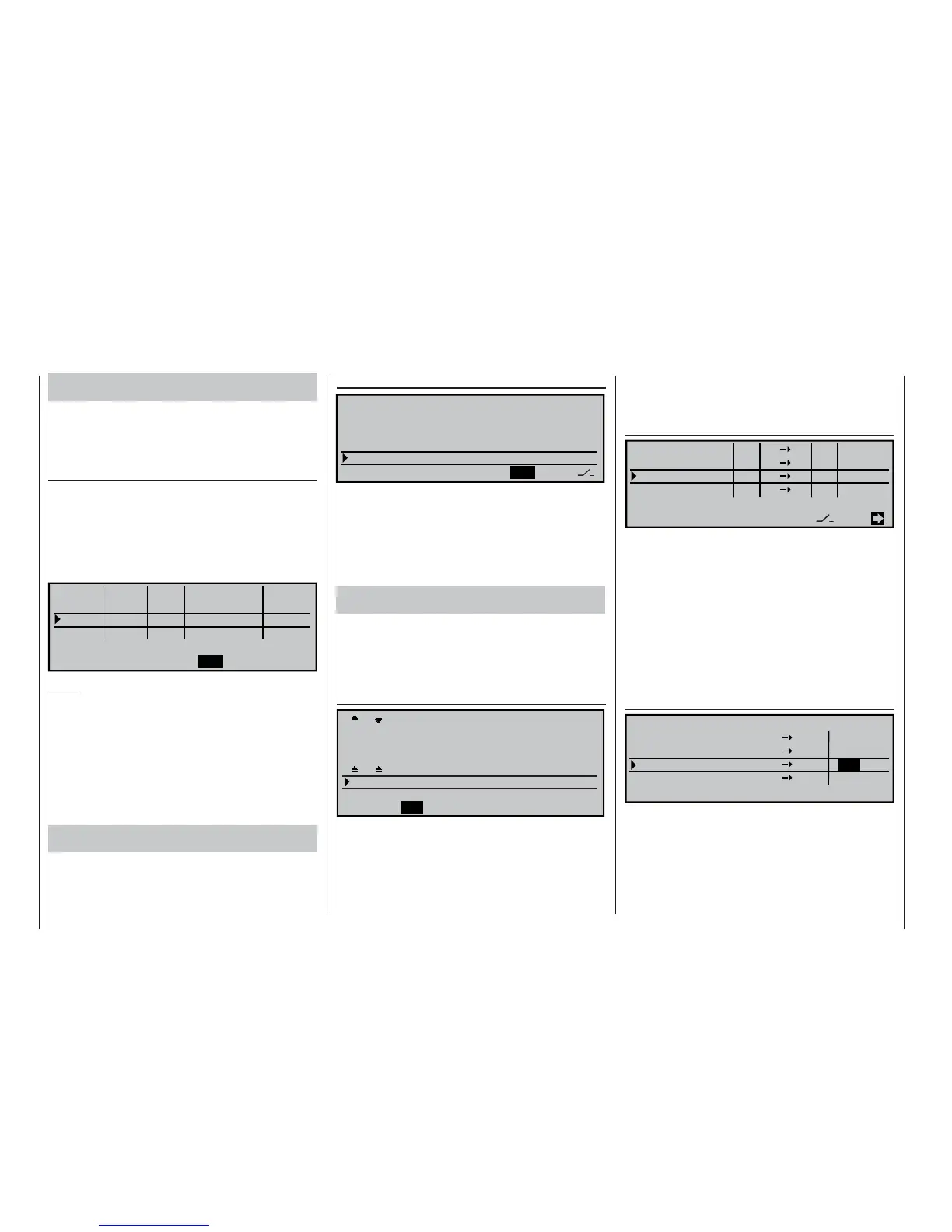
WING MIXERS
Multi-flap menu
Brake settings
Aileron
Flaps
rudder
elevator
… where you select the “Flap 6 3 elevator” line
and enter a suitable value for each fl ight phase. If you
have assigned the same transmitter control to the in-
puts 5, 6 and 7 – as described above – then all eight
wing fl aps will move simultaneously, while the eleva-
tor will follow the movement according to the set mi-
xer ratio.
Flap movement when elevator commands are gi-
ven
The fl aps can be set up to defl ect when the eleva-
tor stick is moved; this function increases the model’s
agility around the lateral axis, and is normally used
only when the model is fl ying fast. The mixer is set up
in the “Multi-fl ap menu” of the menu …
»Wing mixers« (page 110)
+100%
Diff. 0%
0%
0% +100%+100%
0% 0% 0%
0%
SYM
ASY
ASY
+100%
0%
+100%+100%
0%
0%
«Normal »
ASY
SYM
SYM
AILE
FLAP FL2
+75% +50%
0% 0%
0%
0%
+50%
+75%
AI
Ail–tr
FL.pos
FL
El–
>
Fl
… where you enter the appropriate values in the “El->
Fl” line, separately for each fl ight phase. The fl aps are
usually set to defl ect in the opposite direction to the
elevator. This mixer causes the two fl ap pairs (servos
6 + 7 and 9 + 10) to defl ect in parallel in accordance
with the set mixer ratio, while the ailerons (servos 2 +
5) also follow this movement.
We will now set up the two inboard fl ap servos (ser-
vos 11 + 12) to follow the movement of the other wing
fl aps; this is achieved in the menu …
»Free mixers« (page 135)
Tr
=>
EL
SEL
SEL
AI 12
711
SEL
=>
11
=>
?? ?? ----
1
2
3
4
LinearMIX
type
LinearMIX
LinearMIX
LinearMIX
from to Adjust
… where we invoke an “EL 11” mixer.
Provided that the dual mixer is already set up, as de-
scribed on page 184, the effect of this mixer is to cau-
se the inboard fl aps to follow the travel of the other
wing fl aps when an elevator command is given.
On the second page of the display a mixer input
should be entered to suit the model and the fl ight
phase.
We want this mixer – in our example LinearMIX 3 – to
work in a fl ight phase specifi c manner, and to this end
we must move to the menu …
»MIX active in phase« (page 142)
SEL
«Normal »
AI 12
711
EL 11
??
??
LinearMIX
MIX ACTIV IN PHASE
yes
LinearMIX
LinearMIX
LinearMIX
yes
yes
no
1
2
4
3
… and defi ne the fl ight phases in which the mixer
is to be active (“yes”) and those in which it is to be
disabled (“no”). This requires you to switch between
the fl ight phases and set the mixer to “yes” or “no” ac-
cordingly for each phase.
 Loading...
Loading...











