Design and Selection
30
and the maximum empirical values listed above.
② The top layer whose load is generally larger than the middle or bottom layer should take the
maximum empirical value.
③ The guest room whose load is generally much large should take the value between the
intermediate and the maximum empirical values listed above.
④ For those whose external walls or glass areas are large, it is recommended to take the load
calculation.
⑤ The heating load for the bathroom is generally 500W/room.
3.2 Selection of Tube Spacing of the Underfloor Coils
Tube spacing of the underfloor coils which will directly affect heat dissipation of the floor depends on
the tube material, indoor design temperature, supply water temperature and floor material.
Heat Dissipation of Commonly Used Coils
(Tube material: PE-X, Indoor temperature: 18°C, Average water temperature:45°C)
The dissipated heat of the floor coil is larger than the load for the floor heating system; however the
deviation cannot be larger than 10%.
3.3 Selection of Loop Quantity of Coils for Each Room
3.3.1 Type of Underfloor Coils
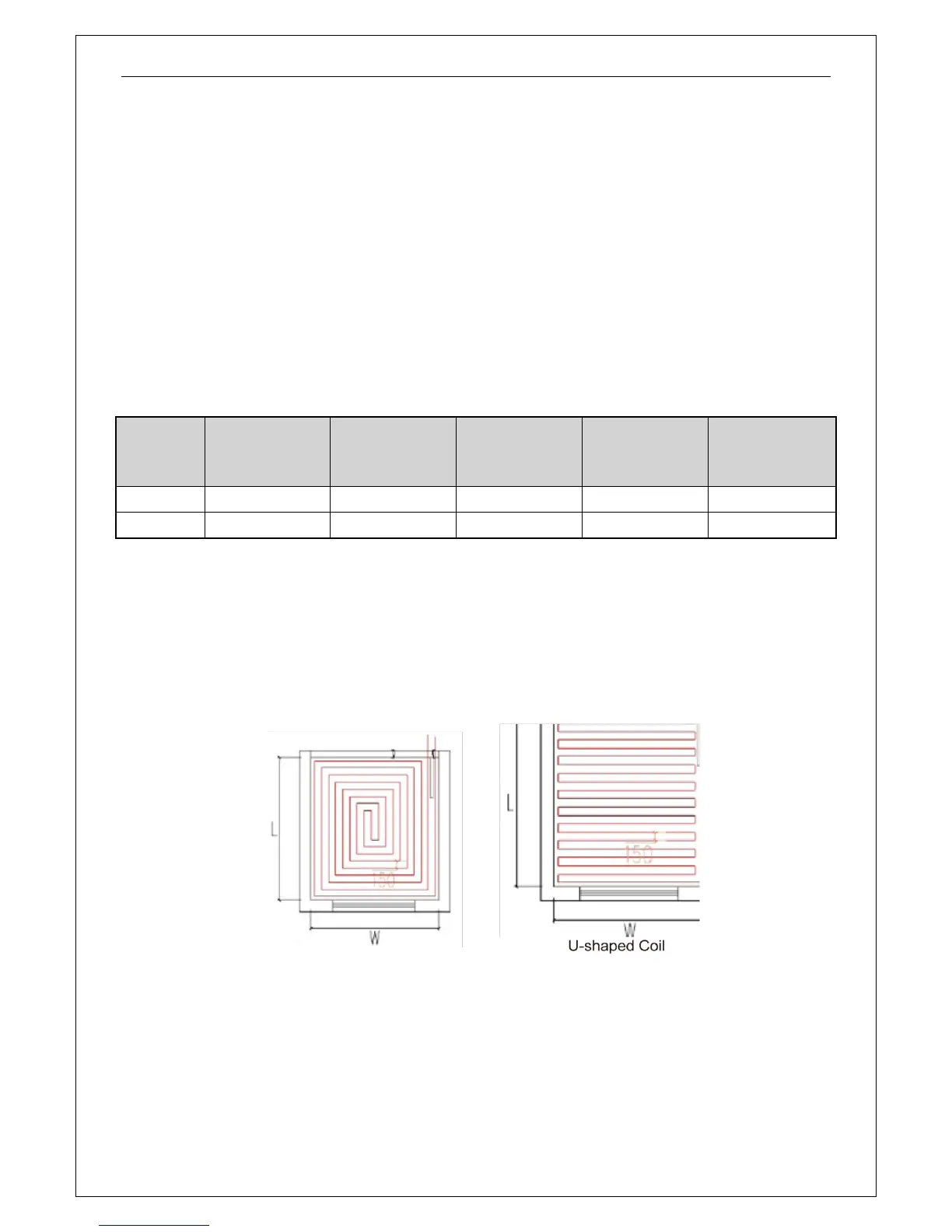
When selecting underfloor coils, we should consider both their comfortability and heating capacity.
The most commonly used coils are as shown below.
Square-shaped Coil (Recommended) U-shaped Coil
Length of coils is calculated as below:
Square-shaped coil: =L*W/tube spacing=area/tube spacing
U-shaped coil: =L-1+L*W/tube spacing=L-1+area/tube spacing
The reason why the square-shaped coils are recommended is because they can keep even
temperature distribution. Special demand can be met by adjusting the tube spacing.
Distance from the room to the water trap/collector should be estimated according to the actual

 Loading...
Loading...











